前言:
之前分析tmin工具的时候,提到tmin的命令目前只能对文件进行操作,很多博客也提供了写脚本的方式对文件夹进行操作。本文是想通过修改tmin源代码的方式,实现添加新命令参数就可以对文件夹进行操作。
本文分为三部分:主要思路、部分实现细节、演示。
在文章最后给出了git地址,可以pull下来直接替换afl-tmin.c用。
主要思路:
【一】分析源码
在main函数入口之前,有几个自变量、函数需要仔细查看:
1. 自变量
static u8 *in_file, /* Minimizer input test case */ *out_file, /* Minimizer output file */
in_file 和 out_file 分别是 -i 和 -o 之后的参数存放的自变量。in_file 就相当于字符串,如果输出,可以直接用来输出文件名。
2. 文件读取函数 static void read_initial_file(void)
用 in_file 作为路径,除了读取文件,还会在读取文件之前进行分析路径是否合适等等。

static void read_initial_file(void) { struct stat st; s32 fd = open(in_file, O_RDONLY); if (fd < 0) PFATAL("Unable to open '%s'", in_file); if (fstat(fd, &st) || !st.st_size) FATAL("Zero-sized input file."); if (st.st_size >= TMIN_MAX_FILE) FATAL("Input file is too large (%u MB max)", TMIN_MAX_FILE / 1024 / 1024); in_len = st.st_size; in_data = ck_alloc_nozero(in_len); ck_read(fd, in_data, in_len, in_file); close(fd); OKF("Read %u byte%s from '%s'.", in_len, in_len == 1 ? "" : "s", in_file); }
3.文件输出函数 static s32 write_to_file(u8* path, u8* mem, u32 len)
用 path 作为路径,将处理好的数据,写到文件中。

static s32 write_to_file(u8* path, u8* mem, u32 len) { s32 ret; unlink(path); /* Ignore errors */ ret = open(path, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, 0600); if (ret < 0) PFATAL("Unable to create '%s'", path); ck_write(ret, mem, len, path); lseek(ret, 0, SEEK_SET); return ret; }
4.真正的最小化处理函数 static void minimize(char** argv)
tmin最核心的部分,用来处理读取到的数据。

static void minimize(char** argv) { static u32 alpha_map[256]; u8* tmp_buf = ck_alloc_nozero(in_len); u32 orig_len = in_len, stage_o_len; u32 del_len, set_len, del_pos, set_pos, i, alpha_size, cur_pass = 0; u32 syms_removed, alpha_del0 = 0, alpha_del1, alpha_del2, alpha_d_total = 0; u8 changed_any, prev_del; /*********************** * BLOCK NORMALIZATION * ***********************/ set_len = next_p2(in_len / TMIN_SET_STEPS); set_pos = 0; if (set_len < TMIN_SET_MIN_SIZE) set_len = TMIN_SET_MIN_SIZE; ACTF(cBRI "Stage #0: " cRST "One-time block normalization..."); while (set_pos < in_len) { u8 res; u32 use_len = MIN(set_len, in_len - set_pos); for (i = 0; i < use_len; i++) if (in_data[set_pos + i] != '0') break; if (i != use_len) { memcpy(tmp_buf, in_data, in_len); memset(tmp_buf + set_pos, '0', use_len); res = run_target(argv, tmp_buf, in_len, 0); if (res) { memset(in_data + set_pos, '0', use_len); changed_any = 1; alpha_del0 += use_len; } } set_pos += set_len; } alpha_d_total += alpha_del0; OKF("Block normalization complete, %u byte%s replaced.", alpha_del0, alpha_del0 == 1 ? "" : "s"); next_pass: ACTF(cYEL "--- " cBRI "Pass #%u " cYEL "---", ++cur_pass); changed_any = 0; /****************** * BLOCK DELETION * ******************/ del_len = next_p2(in_len / TRIM_START_STEPS); stage_o_len = in_len; ACTF(cBRI "Stage #1: " cRST "Removing blocks of data..."); next_del_blksize: if (!del_len) del_len = 1; del_pos = 0; prev_del = 1; SAYF(cGRA " Block length = %u, remaining size = %u " cRST, del_len, in_len); while (del_pos < in_len) { u8 res; s32 tail_len; tail_len = in_len - del_pos - del_len; if (tail_len < 0) tail_len = 0; /* If we have processed at least one full block (initially, prev_del == 1), and we did so without deleting the previous one, and we aren't at the very end of the buffer (tail_len > 0), and the current block is the same as the previous one... skip this step as a no-op. */ if (!prev_del && tail_len && !memcmp(in_data + del_pos - del_len, in_data + del_pos, del_len)) { del_pos += del_len; continue; } prev_del = 0; /* Head */ memcpy(tmp_buf, in_data, del_pos); /* Tail */ memcpy(tmp_buf + del_pos, in_data + del_pos + del_len, tail_len); res = run_target(argv, tmp_buf, del_pos + tail_len, 0); if (res) { memcpy(in_data, tmp_buf, del_pos + tail_len); prev_del = 1; in_len = del_pos + tail_len; changed_any = 1; } else del_pos += del_len; } if (del_len > 1 && in_len >= 1) { del_len /= 2; goto next_del_blksize; } OKF("Block removal complete, %u bytes deleted.", stage_o_len - in_len); if (!in_len && changed_any) WARNF(cLRD "Down to zero bytes - check the command line and mem limit!" cRST); if (cur_pass > 1 && !changed_any) goto finalize_all; /************************* * ALPHABET MINIMIZATION * *************************/ alpha_size = 0; alpha_del1 = 0; syms_removed = 0; memset(alpha_map, 0, 256 * sizeof(u32)); for (i = 0; i < in_len; i++) { if (!alpha_map[in_data[i]]) alpha_size++; alpha_map[in_data[i]]++; } ACTF(cBRI "Stage #2: " cRST "Minimizing symbols (%u code point%s)...", alpha_size, alpha_size == 1 ? "" : "s"); for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) { u32 r; u8 res; if (i == '0' || !alpha_map[i]) continue; memcpy(tmp_buf, in_data, in_len); for (r = 0; r < in_len; r++) if (tmp_buf[r] == i) tmp_buf[r] = '0'; res = run_target(argv, tmp_buf, in_len, 0); if (res) { memcpy(in_data, tmp_buf, in_len); syms_removed++; alpha_del1 += alpha_map[i]; changed_any = 1; } } alpha_d_total += alpha_del1; OKF("Symbol minimization finished, %u symbol%s (%u byte%s) replaced.", syms_removed, syms_removed == 1 ? "" : "s", alpha_del1, alpha_del1 == 1 ? "" : "s"); /************************** * CHARACTER MINIMIZATION * **************************/ alpha_del2 = 0; ACTF(cBRI "Stage #3: " cRST "Character minimization..."); memcpy(tmp_buf, in_data, in_len); for (i = 0; i < in_len; i++) { u8 res, orig = tmp_buf[i]; if (orig == '0') continue; tmp_buf[i] = '0'; res = run_target(argv, tmp_buf, in_len, 0); if (res) { in_data[i] = '0'; alpha_del2++; changed_any = 1; } else tmp_buf[i] = orig; } alpha_d_total += alpha_del2; OKF("Character minimization done, %u byte%s replaced.", alpha_del2, alpha_del2 == 1 ? "" : "s"); if (changed_any) goto next_pass; finalize_all: SAYF(" " cGRA " File size reduced by : " cRST "%0.02f%% (to %u byte%s) " cGRA " Characters simplified : " cRST "%0.02f%% " cGRA " Number of execs done : " cRST "%u " cGRA " Fruitless execs : " cRST "path=%u crash=%u hang=%s%u ", 100 - ((double)in_len) * 100 / orig_len, in_len, in_len == 1 ? "" : "s", ((double)(alpha_d_total)) * 100 / (in_len ? in_len : 1), total_execs, missed_paths, missed_crashes, missed_hangs ? cLRD : "", missed_hangs); if (total_execs > 50 && missed_hangs * 10 > total_execs) WARNF(cLRD "Frequent timeouts - results may be skewed." cRST); }
5.显示提示 static void usage(u8* argv0)
用来显示提示部分,添加新参数之后,在此修改提示。

static void usage(u8* argv0) { SAYF(" %s [ options ] -- /path/to/target_app [ ... ] " "Required parameters: " " -d 0/1 - 0:not dir mode, 1:is dir mode " " -i file - input test case to be shrunk by the tool " " -o file - final output location for the minimized data " "Execution control settings: " " -f file - input file read by the tested program (stdin) " " -t msec - timeout for each run (%u ms) " " -m megs - memory limit for child process (%u MB) " " -Q - use binary-only instrumentation (QEMU mode) " "Minimization settings: " " -e - solve for edge coverage only, ignore hit counts " " -x - treat non-zero exit codes as crashes " "For additional tips, please consult %s/README. ", argv0, EXEC_TIMEOUT, MEM_LIMIT, doc_path); exit(1); }
main函数流程简析
1.第一个主要部分:while循环
while内的参数 (opt = getopt(argc,argv,"+d:i:o:f:m:t:B:xeQ")) > 0 可见其实我已经加入了 d 参数,while实现对命令行所有参数都能读取,并通过一个switch实现对读取到的命令行参数进行判断。
2.初步检查参数合法性
在开始对文件进行处理之前,要对while过程读取到的一些参数进行初步检查,保证之后不能报错。
3.文件操作
一直到 close(write_to_file(out_file, in_data, in_len)); 之前,都是对文件的操作部分,这一部分可以当作一个代码块(或者是没有抽象出来的函数)对待,利用读文件函数,最小化函数,输出到文件函数,实现 tmin 核心操作。
【二】设计代码思路
经过刚刚的分析,有两点可以确定:第一、最核心的最小化函数是数据为参数进行操作,所有写代码的时候没有设计文件夹操作(要不然一定会把以文件文件的操作单独抽象出来);第二、要想实现功能需要单独自己添加文件夹的操作;
所以思路就是:先添加命令行新参数 -d -> 然后根据 -d 判断是文件夹操作 -> 文件夹进行循环 -> 循环内对单个文件进行操作 -> 跳出循环结束。
部分实现细节:
【一】新参数和对参数的判断
添加新参数,输入文件夹,输出文件夹,输入模式保存 -d(1代表文件夹模式,0代表文件模式)
static u8 *in_dir, /* Minimizer input direction */ *out_dir; /* Minimizer output direction */ static u8 *dir_mode; /* dir mode : 1(yes) / 0(no) */
并在 main 函数的 while 的 switch 里进行判断
case 'd': if (dir_mode) FATAL("Multiple -d options not supported"); dir_mode = optarg; break; case 'i': if (in_file) FATAL("Multiple -i options not supported"); if (*dir_mode == '1') in_dir = optarg; else in_file = optarg; break; case 'o': if (out_file) FATAL("Multiple -o options not supported"); if (*dir_mode == '1') out_dir = optarg; else out_file = optarg; break;
【二】文件夹循环和对单个文件的操作
利用 goto 实现循环(一开始我是想用while实现,但是发现afl源码里出现很多的 goto,虽然 c 语言老师一再强调不要用 goto,影响可读性,但是现在看来,管他可不可读,在源码基础上改,还是用 goto 舒服)。
如果是文件操作模式:
还是按照原计划进行,但是在刚刚提到的文件操作代码块的前面加上 deal_file: 用来跳转,在代码块之后,用判断是否是文件夹操作模式的 goto deal_dir; 实现文件夹模式,跳转回循环。
如果是文件夹操作模式:
if (*dir_mode == '1'){ if ( !in_dir || !out_dir){ usage(argv[0]); } /* 读取文件夹下的所有文件,每个文件进行操作,在输出文件夹生成相应的文件【暂时不递归文件夹下面的文件】 */ /* 利用loop实现全部文件循环读取 */ DIR *d = NULL; struct dirent *dp = NULL; struct stat st; char p_in[256] = {0}; char p_out[256] = {0}; //检查路径合理性 if((!(d=opendir(in_dir))) || stat(in_dir, &st) < 0 || !S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)){ ACTF("invalid path:%s ", in_dir); goto finish_tmin; } deal_dir: if((dp = readdir(d)) == NULL){ closedir(d); goto finish_tmin; } //当前路径和上一级路径以及隐藏文件去掉,避免死循环 if ((!strncmp(dp->d_name, ".", 1)) || (!strncmp(dp->d_name, "..", 2))) goto deal_dir; snprintf(p_in, sizeof(p_in) - 1, "%s/%s", in_dir, dp->d_name); stat(p_in, &st); snprintf(p_out, sizeof(p_out) - 1, "%s/%s", out_dir, dp->d_name); if(!S_ISDIR(st.st_mode)) { in_file = p_in; out_file = p_out; goto deal_file; } else{ //文件夹下面的文件也是文件夹的话,在此操作留作递归操作 }
演示:
重新安装魔改后的afl
修改afl-tmin之后,利用指令实现重新安装:
make
sudo make install
注意,要在afl源文件路径下进行此操作。
添加新参数后的测试
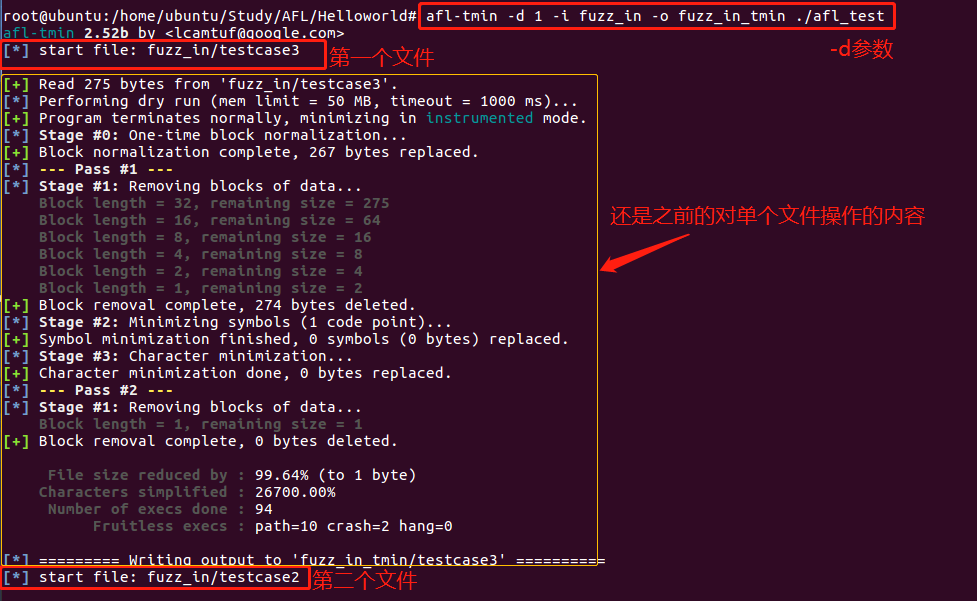
可以看到效果还是很好的,对文件夹每个文件的操作,操作的细则会按文件一块一块展示。
源码
GitHub地址:https://github.com/WayneDevMaze/Chinese_noted_AFL
Reference
【1】Linux C 编程的文件夹遍历:Linux c 遍历目录及目录下文件 - guotianqing的博客 - CSDN博客
【2】C语言拼接字符:C语言拼接字符串 -- 使用strcat()函数 - 白菜菜白 - 博客园
【3】Linux C 编程:linux下c编程 基础 - konglingbin - 博客园
