1. Graylog2 简介
Graylog 是一个简单易用、功能较全面的日志管理工具,相比 ELK 组合, 优点:
-
- 部署维护简单,一体化解决方案,不像ELK三个独立系统集成。
- 查相比ES json语法,搜索语法更加简单,如 source:mongo AND reponse_time_ms:>5000。
- 内置简单的告警。
- 可以将搜索条件导出为 json格式文本,方便开发调用ES rest api搜索脚本。
- 自己开发采集日志的脚本,并用curl/nc发送到Graylog Server,发送格式是自定义的GELF,Flunted和Logstash都有相应的输出GELF消息的插件。自己开发带来很大的自由度。实际上只需要用inotifywait监控日志的modify事件,并把日志的新增行用curl/netcat发送到Graylog Server就可。
- UI 比较友好,搜索结果高亮显示。
当然,在拓展性上,graylog还是不如ELK。
Graylog整体组成:
-
- Graylog提供 graylog 对外接口, CPU 密集
- Elasticsearch 日志文件的持久化存储和检索, IO 密集
- MongoDB 存储一些 Graylog 的配置
2. Graylog架构
单server架构 :
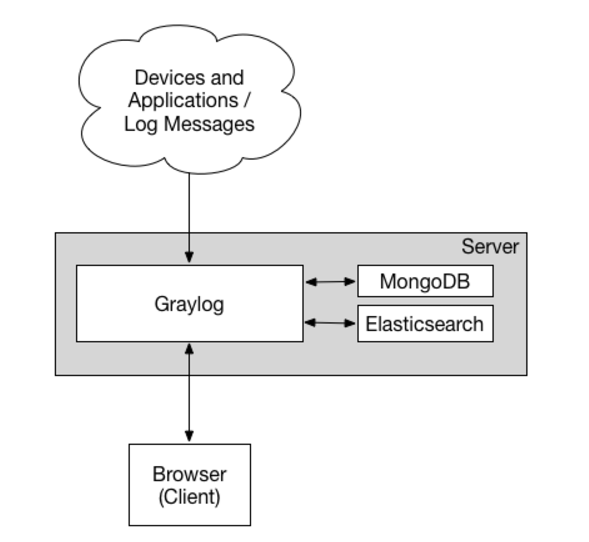
Graylog集群架构 :
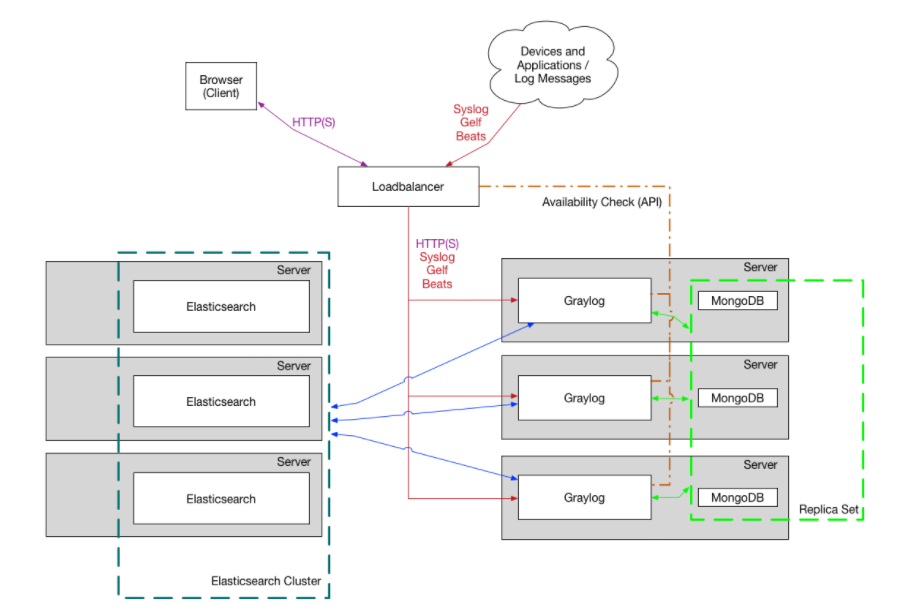
3. Graylog安装
这里我搭建的是集群方案,但是将ES与Graylog和MongoDB部署在同一台server上。
① 前提条件:
$ sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-headless.x86_64
$ sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
$ setenforce 0
#安装pwgen
$ sudo yum install epel-release
$ sudo yum install pwgen
② MongoDB安装:
创建/etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-3.2.repo文件,添加如下内容:
[mongodb-org-3.2] name=MongoDB Repository baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/3.2/x86_64/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-3.2.asc
安装MongoDB:
sudo yum install mongodb-org
启动服务:
$ sudo chkconfig --add mongod $ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo systemctl enable mongod.service $ sudo systemctl start mongod.service
③Elasticsearch安装:
Graylog 2.3.x 支持 Elasticsearch 5.x版本。
首先安装Elastic GPG key以及repository文件,然后yum安装:
$ rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
$ cat /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo [elasticsearch-5.x] name=Elasticsearch repository for 5.x packages baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/5.x/yum gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch enabled=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md
$ sudo yum install elasticsearch
编辑Elasticsearch配置文件/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml,添加cluster信息:

# cat /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml # ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: graylog # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: shop-log-02 # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # path.data: /data/elasticsearch/db # # Path to log files: # path.logs: /data/elasticsearch/logs # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): # network.host: 10.2.2.42 # # Set a custom port for HTTP: # http.port: 9200 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # # 这里给其他两个节点的地址 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["10.2.2.41", "10.2.2.43"] # # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): # discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 # # For more information, consult the zen discovery module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Gateway ----------------------------------- # # Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started: # #gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3 # # For more information, consult the gateway module documentation. # # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # #action.destructive_requires_name: true http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
启动Elasticsearch服务:
$ sudo chkconfig --add elasticsearch $ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch.service $ sudo systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
④Graylog安装
$ sudo rpm -Uvh https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-2.3-repository_latest.rpm $ sudo yum install graylog-server
编辑graylog配置文件 /etc/graylog/server/server.conf,添加 password_secret和 password_secret_sha2(必须)
可以使用 echo -n yourpassword | sha256sum 命令来生成 password_secret_sha2。
设置rest_listen_uri以及web_listen_uri为公共ip或公共hostname,以便连接graylog。

1 # cat /etc/graylog/server/server.conf 2 ############################ 3 # GRAYLOG CONFIGURATION FILE 4 ############################ 5 # 6 # This is the Graylog configuration file. The file has to use ISO 8859-1/Latin-1 character encoding. 7 # Characters that cannot be directly represented in this encoding can be written using Unicode escapes 8 # as defined in https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jls/se8/html/jls-3.html#jls-3.3, using the u prefix. 9 # For example, u002c. 10 # 11 # * Entries are generally expected to be a single line of the form, one of the following: 12 # 13 # propertyName=propertyValue 14 # propertyName:propertyValue 15 # 16 # * White space that appears between the property name and property value is ignored, 17 # so the following are equivalent: 18 # 19 # name=Stephen 20 # name = Stephen 21 # 22 # * White space at the beginning of the line is also ignored. 23 # 24 # * Lines that start with the comment characters ! or # are ignored. Blank lines are also ignored. 25 # 26 # * The property value is generally terminated by the end of the line. White space following the 27 # property value is not ignored, and is treated as part of the property value. 28 # 29 # * A property value can span several lines if each line is terminated by a backslash (鈥榎鈥 character. 30 # For example: 31 # 32 # targetCities= 33 # Detroit, 34 # Chicago, 35 # Los Angeles 36 # 37 # This is equivalent to targetCities=Detroit,Chicago,Los Angeles (white space at the beginning of lines is ignored). 38 # 39 # * The characters newline, carriage return, and tab can be inserted with characters , , and , respectively. 40 # 41 # * The backslash character must be escaped as a double backslash. For example: 42 # 43 # path=c:\docs\doc1 44 # 45 46 # If you are running more than one instances of Graylog server you have to select one of these 47 # instances as master. The master will perform some periodical tasks that non-masters won't perform. 48 is_master = false 49 50 # The auto-generated node ID will be stored in this file and read after restarts. It is a good idea 51 # to use an absolute file path here if you are starting Graylog server from init scripts or similar. 52 node_id_file = /etc/graylog/server/node-id 53 54 # You MUST set a secret to secure/pepper the stored user passwords here. Use at least 64 characters. 55 # Generate one by using for example: pwgen -N 1 -s 96 56 password_secret = BjwAAuTEWDQNtAKhUL5lQ3TvW41saWseKpRdTSrecBFifsCJDXak4fudnACBcaMyl0I4yzJDF801Kyasdfsdfasdfasdfasd 57 58 # The default root user is named 'admin' 59 root_username = admin 60 61 # You MUST specify a hash password for the root user (which you only need to initially set up the 62 # system and in case you lose connectivity to your authentication backend) 63 # This password cannot be changed using the API or via the web interface. If you need to change it, 64 # modify it in this file. 65 # Create one by using for example: echo -n yourpassword | shasum -a 256 66 # and put the resulting hash value into the following line 67 root_password_sha2 = 926c00b3f65df24b65a9a7b58a989add920c81441dccd2 68 dsfasdfasdf 69 # The email address of the root user. 70 # Default is empty 71 #root_email = "" 72 73 # The time zone setting of the root user. See http://www.joda.org/joda-time/timezones.html for a list of valid time zones. 74 # Default is UTC 75 root_timezone = Asia/Shanghai 76 77 # Set plugin directory here (relative or absolute) 78 plugin_dir = /usr/share/graylog-server/plugin 79 80 # REST API listen URI. Must be reachable by other Graylog server nodes if you run a cluster. 81 # When using Graylog Collectors, this URI will be used to receive heartbeat messages and must be accessible for all collectors. 82 rest_listen_uri = http://10.2.2.42:9000/api/ 83 84 # REST API transport address. Defaults to the value of rest_listen_uri. Exception: If rest_listen_uri 85 # is set to a wildcard IP address (0.0.0.0) the first non-loopback IPv4 system address is used. 86 # If set, this will be promoted in the cluster discovery APIs, so other nodes may try to connect on 87 # this address and it is used to generate URLs addressing entities in the REST API. (see rest_listen_uri) 88 # You will need to define this, if your Graylog server is running behind a HTTP proxy that is rewriting 89 # the scheme, host name or URI. 90 # This must not contain a wildcard address (0.0.0.0). 91 rest_transport_uri = http://10.2.2.42:9000/api/ 92 93 # Enable CORS headers for REST API. This is necessary for JS-clients accessing the server directly. 94 # If these are disabled, modern browsers will not be able to retrieve resources from the server. 95 # This is enabled by default. Uncomment the next line to disable it. 96 #rest_enable_cors = false 97 98 # Enable GZIP support for REST API. This compresses API responses and therefore helps to reduce 99 # overall round trip times. This is enabled by default. Uncomment the next line to disable it. 100 #rest_enable_gzip = false 101 102 # Enable HTTPS support for the REST API. This secures the communication with the REST API with 103 # TLS to prevent request forgery and eavesdropping. This is disabled by default. Uncomment the 104 # next line to enable it. 105 #rest_enable_tls = true 106 107 # The X.509 certificate chain file in PEM format to use for securing the REST API. 108 #rest_tls_cert_file = /path/to/graylog.crt 109 110 # The PKCS#8 private key file in PEM format to use for securing the REST API. 111 #rest_tls_key_file = /path/to/graylog.key 112 113 # The password to unlock the private key used for securing the REST API. 114 #rest_tls_key_password = secret 115 116 # The maximum size of the HTTP request headers in bytes. 117 #rest_max_header_size = 8192 118 119 # The maximal length of the initial HTTP/1.1 line in bytes. 120 #rest_max_initial_line_length = 4096 121 122 # The size of the thread pool used exclusively for serving the REST API. 123 #rest_thread_pool_size = 16 124 125 # Comma separated list of trusted proxies that are allowed to set the client address with X-Forwarded-For 126 # header. May be subnets, or hosts. 127 #trusted_proxies = 127.0.0.1/32, 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1/128 128 129 # Enable the embedded Graylog web interface. 130 # Default: true 131 web_enable = true 132 133 # Web interface listen URI. 134 # Configuring a path for the URI here effectively prefixes all URIs in the web interface. This is a replacement 135 # for the application.context configuration parameter in pre-2.0 versions of the Graylog web interface. 136 web_listen_uri = http://10.2.2.42:9000/ 137 138 # Web interface endpoint URI. This setting can be overriden on a per-request basis with the X-Graylog-Server-URL header. 139 # Default: $rest_transport_uri 140 web_endpoint_uri = http://42.111.111.111:9000/api 141 142 # Enable CORS headers for the web interface. This is necessary for JS-clients accessing the server directly. 143 # If these are disabled, modern browsers will not be able to retrieve resources from the server. 144 web_enable_cors = true 145 146 # Enable/disable GZIP support for the web interface. This compresses HTTP responses and therefore helps to reduce 147 # overall round trip times. This is enabled by default. Uncomment the next line to disable it. 148 #web_enable_gzip = false 149 150 # Enable HTTPS support for the web interface. This secures the communication of the web browser with the web interface 151 # using TLS to prevent request forgery and eavesdropping. 152 # This is disabled by default. Uncomment the next line to enable it and see the other related configuration settings. 153 #web_enable_tls = true 154 155 # The X.509 certificate chain file in PEM format to use for securing the web interface. 156 #web_tls_cert_file = /path/to/graylog-web.crt 157 158 # The PKCS#8 private key file in PEM format to use for securing the web interface. 159 #web_tls_key_file = /path/to/graylog-web.key 160 161 # The password to unlock the private key used for securing the web interface. 162 #web_tls_key_password = secret 163 164 # The maximum size of the HTTP request headers in bytes. 165 #web_max_header_size = 8192 166 167 # The maximal length of the initial HTTP/1.1 line in bytes. 168 #web_max_initial_line_length = 4096 169 170 # The size of the thread pool used exclusively for serving the web interface. 171 #web_thread_pool_size = 16 172 173 # List of Elasticsearch hosts Graylog should connect to. 174 # Need to be specified as a comma-separated list of valid URIs for the http ports of your elasticsearch nodes. 175 # If one or more of your elasticsearch hosts require authentication, include the credentials in each node URI that 176 # requires authentication. 177 # 178 # Default: http://127.0.0.1:9200 179 elasticsearch_hosts = http://grayloguser:3KKLg8294CE0@10.2.2.41:9200,http://grayloguser:3KKLg8294CE0@10.2.2.42:9200,http://grayloguser:3KKLg8294CE0@10.2.2.43:9200 180 181 # Maximum amount of time to wait for successfull connection to Elasticsearch HTTP port. 182 # 183 # Default: 10 Seconds 184 #elasticsearch_connect_timeout = 10s 185 186 # Maximum amount of time to wait for reading back a response from an Elasticsearch server. 187 # 188 # Default: 60 seconds 189 #elasticsearch_socket_timeout = 60s 190 191 # Maximum idle time for an Elasticsearch connection. If this is exceeded, this connection will 192 # be tore down. 193 # 194 # Default: inf 195 #elasticsearch_idle_timeout = -1s 196 197 # Maximum number of total connections to Elasticsearch. 198 # 199 # Default: 20 200 #elasticsearch_max_total_connections = 20 201 202 # Maximum number of total connections per Elasticsearch route (normally this means per 203 # elasticsearch server). 204 # 205 # Default: 2 206 #elasticsearch_max_total_connections_per_route = 2 207 208 # Maximum number of times Graylog will retry failed requests to Elasticsearch. 209 # 210 # Default: 2 211 #elasticsearch_max_retries = 2 212 213 # Enable automatic Elasticsearch node discovery through Nodes Info, 214 # see https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.4/cluster-nodes-info.html 215 # 216 # WARNING: Automatic node discovery does not work if Elasticsearch requires authentication, e. g. with Shield. 217 # 218 # Default: false 219 #elasticsearch_discovery_enabled = true 220 221 # Filter for including/excluding Elasticsearch nodes in discovery according to their custom attributes, 222 # see https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/5.4/cluster.html#cluster-nodes 223 # 224 # Default: empty 225 #elasticsearch_discovery_filter = rack:42 226 227 # Frequency of the Elasticsearch node discovery. 228 # 229 # Default: 30s 230 # elasticsearch_discovery_frequency = 30s 231 232 # Enable payload compression for Elasticsearch requests. 233 # 234 # Default: false 235 #elasticsearch_compression_enabled = true 236 237 # Graylog will use multiple indices to store documents in. You can configured the strategy it uses to determine 238 # when to rotate the currently active write index. 239 # It supports multiple rotation strategies: 240 # - "count" of messages per index, use elasticsearch_max_docs_per_index below to configure 241 # - "size" per index, use elasticsearch_max_size_per_index below to configure 242 # valid values are "count", "size" and "time", default is "count" 243 # 244 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 245 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 246 rotation_strategy = count 247 248 # (Approximate) maximum number of documents in an Elasticsearch index before a new index 249 # is being created, also see no_retention and elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices. 250 # Configure this if you used 'rotation_strategy = count' above. 251 # 252 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 253 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 254 elasticsearch_max_docs_per_index = 20000000 255 256 # (Approximate) maximum size in bytes per Elasticsearch index on disk before a new index is being created, also see 257 # no_retention and elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices. Default is 1GB. 258 # Configure this if you used 'rotation_strategy = size' above. 259 # 260 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 261 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 262 #elasticsearch_max_size_per_index = 1073741824 263 264 # (Approximate) maximum time before a new Elasticsearch index is being created, also see 265 # no_retention and elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices. Default is 1 day. 266 # Configure this if you used 'rotation_strategy = time' above. 267 # Please note that this rotation period does not look at the time specified in the received messages, but is 268 # using the real clock value to decide when to rotate the index! 269 # Specify the time using a duration and a suffix indicating which unit you want: 270 # 1w = 1 week 271 # 1d = 1 day 272 # 12h = 12 hours 273 # Permitted suffixes are: d for day, h for hour, m for minute, s for second. 274 # 275 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 276 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 277 #elasticsearch_max_time_per_index = 1d 278 279 # Disable checking the version of Elasticsearch for being compatible with this Graylog release. 280 # WARNING: Using Graylog with unsupported and untested versions of Elasticsearch may lead to data loss! 281 #elasticsearch_disable_version_check = true 282 283 # Disable message retention on this node, i. e. disable Elasticsearch index rotation. 284 #no_retention = false 285 286 # How many indices do you want to keep? 287 # 288 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 289 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 290 elasticsearch_max_number_of_indices = 20 291 292 # Decide what happens with the oldest indices when the maximum number of indices is reached. 293 # The following strategies are availble: 294 # - delete # Deletes the index completely (Default) 295 # - close # Closes the index and hides it from the system. Can be re-opened later. 296 # 297 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in 2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 298 # to your previous 1.x settings so they will be migrated to the database! 299 retention_strategy = delete 300 301 # How many Elasticsearch shards and replicas should be used per index? Note that this only applies to newly created indices. 302 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 303 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 304 elasticsearch_shards = 3 305 elasticsearch_replicas = 1 306 307 # Prefix for all Elasticsearch indices and index aliases managed by Graylog. 308 # 309 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 310 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 311 elasticsearch_index_prefix = graylog 312 313 # Name of the Elasticsearch index template used by Graylog to apply the mandatory index mapping. 314 # Default: graylog-internal 315 # 316 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 317 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 318 #elasticsearch_template_name = graylog-internal 319 320 # Do you want to allow searches with leading wildcards? This can be extremely resource hungry and should only 321 # be enabled with care. See also: http://docs.graylog.org/en/2.1/pages/queries.html 322 allow_leading_wildcard_searches = false 323 324 # Do you want to allow searches to be highlighted? Depending on the size of your messages this can be memory hungry and 325 # should only be enabled after making sure your Elasticsearch cluster has enough memory. 326 allow_highlighting = true 327 328 # Analyzer (tokenizer) to use for message and full_message field. The "standard" filter usually is a good idea. 329 # All supported analyzers are: standard, simple, whitespace, stop, keyword, pattern, language, snowball, custom 330 # Elasticsearch documentation: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/2.3/analysis.html 331 # Note that this setting only takes effect on newly created indices. 332 # 333 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 334 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 335 elasticsearch_analyzer = standard 336 337 # Global request timeout for Elasticsearch requests (e. g. during search, index creation, or index time-range 338 # calculations) based on a best-effort to restrict the runtime of Elasticsearch operations. 339 # Default: 1m 340 #elasticsearch_request_timeout = 1m 341 342 # Global timeout for index optimization (force merge) requests. 343 # Default: 1h 344 #elasticsearch_index_optimization_timeout = 1h 345 346 # Maximum number of concurrently running index optimization (force merge) jobs. 347 # If you are using lots of different index sets, you might want to increase that number. 348 # Default: 20 349 #elasticsearch_index_optimization_jobs = 20 350 351 # Time interval for index range information cleanups. This setting defines how often stale index range information 352 # is being purged from the database. 353 # Default: 1h 354 #index_ranges_cleanup_interval = 1h 355 356 # Batch size for the Elasticsearch output. This is the maximum (!) number of messages the Elasticsearch output 357 # module will get at once and write to Elasticsearch in a batch call. If the configured batch size has not been 358 # reached within output_flush_interval seconds, everything that is available will be flushed at once. Remember 359 # that every outputbuffer processor manages its own batch and performs its own batch write calls. 360 # ("outputbuffer_processors" variable) 361 output_batch_size = 500 362 363 # Flush interval (in seconds) for the Elasticsearch output. This is the maximum amount of time between two 364 # batches of messages written to Elasticsearch. It is only effective at all if your minimum number of messages 365 # for this time period is less than output_batch_size * outputbuffer_processors. 366 output_flush_interval = 1 367 368 # As stream outputs are loaded only on demand, an output which is failing to initialize will be tried over and 369 # over again. To prevent this, the following configuration options define after how many faults an output will 370 # not be tried again for an also configurable amount of seconds. 371 output_fault_count_threshold = 5 372 output_fault_penalty_seconds = 30 373 374 # The number of parallel running processors. 375 # Raise this number if your buffers are filling up. 376 processbuffer_processors = 5 377 outputbuffer_processors = 3 378 379 #outputbuffer_processor_keep_alive_time = 5000 380 #outputbuffer_processor_threads_core_pool_size = 3 381 #outputbuffer_processor_threads_max_pool_size = 30 382 383 # UDP receive buffer size for all message inputs (e. g. SyslogUDPInput). 384 #udp_recvbuffer_sizes = 1048576 385 386 # Wait strategy describing how buffer processors wait on a cursor sequence. (default: sleeping) 387 # Possible types: 388 # - yielding 389 # Compromise between performance and CPU usage. 390 # - sleeping 391 # Compromise between performance and CPU usage. Latency spikes can occur after quiet periods. 392 # - blocking 393 # High throughput, low latency, higher CPU usage. 394 # - busy_spinning 395 # Avoids syscalls which could introduce latency jitter. Best when threads can be bound to specific CPU cores. 396 processor_wait_strategy = blocking 397 398 # Size of internal ring buffers. Raise this if raising outputbuffer_processors does not help anymore. 399 # For optimum performance your LogMessage objects in the ring buffer should fit in your CPU L3 cache. 400 # Must be a power of 2. (512, 1024, 2048, ...) 401 ring_size = 65536 402 403 inputbuffer_ring_size = 65536 404 inputbuffer_processors = 2 405 inputbuffer_wait_strategy = blocking 406 407 # Enable the disk based message journal. 408 message_journal_enabled = true 409 410 # The directory which will be used to store the message journal. The directory must me exclusively used by Graylog and 411 # must not contain any other files than the ones created by Graylog itself. 412 # 413 # ATTENTION: 414 # If you create a seperate partition for the journal files and use a file system creating directories like 'lost+found' 415 # in the root directory, you need to create a sub directory for your journal. 416 # Otherwise Graylog will log an error message that the journal is corrupt and Graylog will not start. 417 message_journal_dir = /var/lib/graylog-server/journal 418 419 # Journal hold messages before they could be written to Elasticsearch. 420 # For a maximum of 12 hours or 5 GB whichever happens first. 421 # During normal operation the journal will be smaller. 422 #message_journal_max_age = 12h 423 #message_journal_max_size = 5gb 424 425 #message_journal_flush_age = 1m 426 #message_journal_flush_interval = 1000000 427 #message_journal_segment_age = 1h 428 #message_journal_segment_size = 100mb 429 430 # Number of threads used exclusively for dispatching internal events. Default is 2. 431 #async_eventbus_processors = 2 432 433 # How many seconds to wait between marking node as DEAD for possible load balancers and starting the actual 434 # shutdown process. Set to 0 if you have no status checking load balancers in front. 435 lb_recognition_period_seconds = 3 436 437 # Journal usage percentage that triggers requesting throttling for this server node from load balancers. The feature is 438 # disabled if not set. 439 #lb_throttle_threshold_percentage = 95 440 441 # Every message is matched against the configured streams and it can happen that a stream contains rules which 442 # take an unusual amount of time to run, for example if its using regular expressions that perform excessive backtracking. 443 # This will impact the processing of the entire server. To keep such misbehaving stream rules from impacting other 444 # streams, Graylog limits the execution time for each stream. 445 # The default values are noted below, the timeout is in milliseconds. 446 # If the stream matching for one stream took longer than the timeout value, and this happened more than "max_faults" times 447 # that stream is disabled and a notification is shown in the web interface. 448 #stream_processing_timeout = 2000 449 #stream_processing_max_faults = 3 450 451 # Length of the interval in seconds in which the alert conditions for all streams should be checked 452 # and alarms are being sent. 453 #alert_check_interval = 60 454 455 # Since 0.21 the Graylog server supports pluggable output modules. This means a single message can be written to multiple 456 # outputs. The next setting defines the timeout for a single output module, including the default output module where all 457 # messages end up. 458 # 459 # Time in milliseconds to wait for all message outputs to finish writing a single message. 460 #output_module_timeout = 10000 461 462 # Time in milliseconds after which a detected stale master node is being rechecked on startup. 463 #stale_master_timeout = 2000 464 465 # Time in milliseconds which Graylog is waiting for all threads to stop on shutdown. 466 #shutdown_timeout = 30000 467 468 # MongoDB connection string 469 # See https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/reference/connection-string/ for details 470 mongodb_uri = mongodb://graylog:75PN76Db66En@10.2.2.41:27017,10.2.2.42:27017,10.2.2.43:27017/graylog?replicaSet=rs0 471 472 # Authenticate against the MongoDB server 473 #mongodb_uri = mongodb://grayloguser:secret@localhost:27017/graylog 474 475 # Use a replica set instead of a single host 476 #mongodb_uri = mongodb://grayloguser:secret@localhost:27017,localhost:27018,localhost:27019/graylog 477 478 # Increase this value according to the maximum connections your MongoDB server can handle from a single client 479 # if you encounter MongoDB connection problems. 480 mongodb_max_connections = 1000 481 482 # Number of threads allowed to be blocked by MongoDB connections multiplier. Default: 5 483 # If mongodb_max_connections is 100, and mongodb_threads_allowed_to_block_multiplier is 5, 484 # then 500 threads can block. More than that and an exception will be thrown. 485 # http://api.mongodb.com/java/current/com/mongodb/MongoOptions.html#threadsAllowedToBlockForConnectionMultiplier 486 mongodb_threads_allowed_to_block_multiplier = 5 487 488 # Drools Rule File (Use to rewrite incoming log messages) 489 # See: http://docs.graylog.org/en/2.1/pages/drools.html 490 #rules_file = /etc/graylog/server/rules.drl 491 492 # Email transport 493 #transport_email_enabled = false 494 #transport_email_hostname = mail.example.com 495 #transport_email_port = 587 496 #transport_email_use_auth = true 497 #transport_email_use_tls = true 498 #transport_email_use_ssl = true 499 #transport_email_auth_username = you@example.com 500 #transport_email_auth_password = secret 501 #transport_email_subject_prefix = [graylog] 502 #transport_email_from_email = graylog@example.com 503 504 # Specify and uncomment this if you want to include links to the stream in your stream alert mails. 505 # This should define the fully qualified base url to your web interface exactly the same way as it is accessed by your users. 506 #transport_email_web_interface_url = https://graylog.example.com 507 508 # The default connect timeout for outgoing HTTP connections. 509 # Values must be a positive duration (and between 1 and 2147483647 when converted to milliseconds). 510 # Default: 5s 511 #http_connect_timeout = 5s 512 513 # The default read timeout for outgoing HTTP connections. 514 # Values must be a positive duration (and between 1 and 2147483647 when converted to milliseconds). 515 # Default: 10s 516 #http_read_timeout = 10s 517 518 # The default write timeout for outgoing HTTP connections. 519 # Values must be a positive duration (and between 1 and 2147483647 when converted to milliseconds). 520 # Default: 10s 521 #http_write_timeout = 10s 522 523 # HTTP proxy for outgoing HTTP connections 524 #http_proxy_uri = 525 526 # Disable the optimization of Elasticsearch indices after index cycling. This may take some load from Elasticsearch 527 # on heavily used systems with large indices, but it will decrease search performance. The default is to optimize 528 # cycled indices. 529 # 530 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 531 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 532 #disable_index_optimization = true 533 534 # Optimize the index down to <= index_optimization_max_num_segments. A higher number may take some load from Elasticsearch 535 # on heavily used systems with large indices, but it will decrease search performance. The default is 1. 536 # 537 # ATTENTION: These settings have been moved to the database in Graylog 2.2.0. When you upgrade, make sure to set these 538 # to your previous settings so they will be migrated to the database! 539 #index_optimization_max_num_segments = 1 540 541 # The threshold of the garbage collection runs. If GC runs take longer than this threshold, a system notification 542 # will be generated to warn the administrator about possible problems with the system. Default is 1 second. 543 #gc_warning_threshold = 1s 544 545 # Connection timeout for a configured LDAP server (e. g. ActiveDirectory) in milliseconds. 546 #ldap_connection_timeout = 2000 547 548 # Disable the use of SIGAR for collecting system stats 549 #disable_sigar = false 550 551 # The default cache time for dashboard widgets. (Default: 10 seconds, minimum: 1 second) 552 #dashboard_widget_default_cache_time = 10s 553 554 # Automatically load content packs in "content_packs_dir" on the first start of Graylog. 555 #content_packs_loader_enabled = true 556 557 # The directory which contains content packs which should be loaded on the first start of Graylog. 558 content_packs_dir = /usr/share/graylog-server/contentpacks 559 560 # A comma-separated list of content packs (files in "content_packs_dir") which should be applied on 561 # the first start of Graylog. 562 # Default: empty 563 content_packs_auto_load = grok-patterns.json 564 565 # For some cluster-related REST requests, the node must query all other nodes in the cluster. This is the maximum number 566 # of threads available for this. Increase it, if '/cluster/*' requests take long to complete. 567 # Should be rest_thread_pool_size * average_cluster_size if you have a high number of concurrent users. 568 proxied_requests_thread_pool_size = 32
启动graylog服务:
$ sudo chkconfig --add graylog-server $ sudo systemctl daemon-reload $ sudo systemctl enable graylog-server.service $ sudo systemctl start graylog-server.service
4. 多节点集群配置安装
① MongoDB集群配置:
修改所有mongdb节点的配置文件/etc/mongod.conf,添加集群replication信息replSetName: rs0,并重启服务。

# cat /etc/mongod.conf # mongod.conf # for documentation of all options, see: # http://docs.mongodb.org/manual/reference/configuration-options/ # where to write logging data. systemLog: destination: file logAppend: true path: /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log # Where and how to store data. storage: dbPath: /var/lib/mongo journal: enabled: true # engine: # mmapv1: # wiredTiger: # how the process runs processManagement: fork: true # fork and run in background pidFilePath: /var/run/mongodb/mongod.pid # location of pidfile # network interfaces net: port: 27017 # bindIp: 127.0.0.1 # Listen to local interface only, comment to listen on all interfaces. #security: #operationProfiling: replication: replSetName: rs0 #sharding: ## Enterprise-Only Options #auditLog: #snmp:
$ sudo systemctl restart mongod.service
在集群其中一个节点,启动mongo命令行:
$ mongo
初始化mongodb集群,使用本机hostname或IP加端口:
$ rs.initiate( { _id : "rs0", members: [ { _id : 0, host : "mongodb0.example.net:27017" } ] })
验证集群配置:

$ rs.conf() { "_id" : "rs0", "version" : 1, "protocolVersion" : NumberLong(1), "members" : [ { "_id" : 0, "host" : "mongodb0.example.net:27017", "arbiterOnly" : false, "buildIndexes" : true, "hidden" : false, "priority" : 1, "tags" : { }, "slaveDelay" : NumberLong(0), "votes" : 1 } ], "settings" : { "chainingAllowed" : true, "heartbeatIntervalMillis" : 2000, "heartbeatTimeoutSecs" : 10, "electionTimeoutMillis" : 10000, "catchUpTimeoutMillis" : 2000, "getLastErrorModes" : { }, "getLastErrorDefaults" : { "w" : 1, "wtimeout" : 0 }, "replicaSetId" : ObjectId("585ab9df685f726db2c6a840") } }
将其他节点加入集群,并查看集群配置:
rs0:PRIMARY> rs.add("mongodb1.example.net") rs0:PRIMARY> rs.add("mongodb2.example.net")
rs0:PRIMARY> rs.status()
创建graylog数据库,并添加graylog用户,赋予readWrite和dbAdmin权限:
rs0:PRIMARY> use graylog switched to db graylog rs0:PRIMARY> db.createUser( { user: "graylog", pwd: "75PN76Db66En", roles: [ { role: "readWrite", db: "graylog" } ] }); rs0:PRIMARY> db.grantRolesToUser( "graylog" , [ { role: "dbAdmin", db: "graylog" } ]) rs0:PRIMARY> show users rs0:PRIMARY> db.auth("graylog","75sdfsdsdfn")
② Elasticsearch 集群配置:
修改elasticsearch配置文件并重启服务:
# cat /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml | grep cluster.name cluster.name: graylog # cat /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml | grep discovery.zen.ping discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["10.2.2.41", "10.2.2.43"] # cat /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml | grep network.host network.host: 10.2.2.42
③ graylog集群配置
graylog master节点修改配置server.conf 中 is_master = true,其他节点为false,同时rest_listen_uri以及rest_transport_uri必须可以被集群中的其他节点连通。
修改mongodb连接配置:
# cat /etc/graylog/server/server.conf|grep mongodb_uri mongodb_uri = mongodb://graylog:75PsdfsDb66En@10.2.2.41:27017,10.2.2.42:27017,10.2.2.43:27017/graylog?replicaSet=rs0
修改elasticsearch连接配置:
# cat /etc/graylog/server/server.conf|grep elasticsearch_hosts elasticsearch_hosts = http://grayloguser:3KKLg8sdf340@10.2.2.41:9200,http://grayloguser:3KKLg8294CE0@10.2.2.42:9200,http://grayloguser:
3KKLg8sdf340
@10.2.2.43:9200
开启web界面:
# cat /etc/graylog/server/server.conf|grep web_enable
web_enable = true
④ 创建负载均衡器,对graylog配置负载均衡,我使用的是微软云负载均衡,这里不再说明。
此时可以通过 负载均衡器IP:9000 对graylog进行访问。
5. 日志接入
接入 syslog
首先在 webui 创建 input:
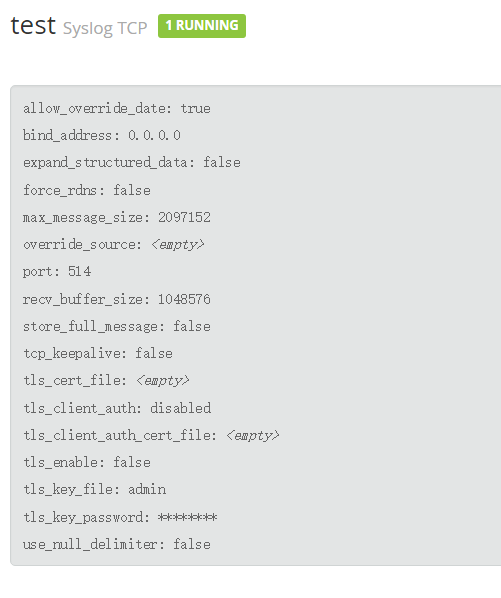
以 rsyslog 为例:
/etc/rsyslog.d/graylog.conf: *.* @@x.x.x.x:514;RSYSLOG_SyslogProtocol23Format
service rsyslog restart
即可查看该 input 的 message:
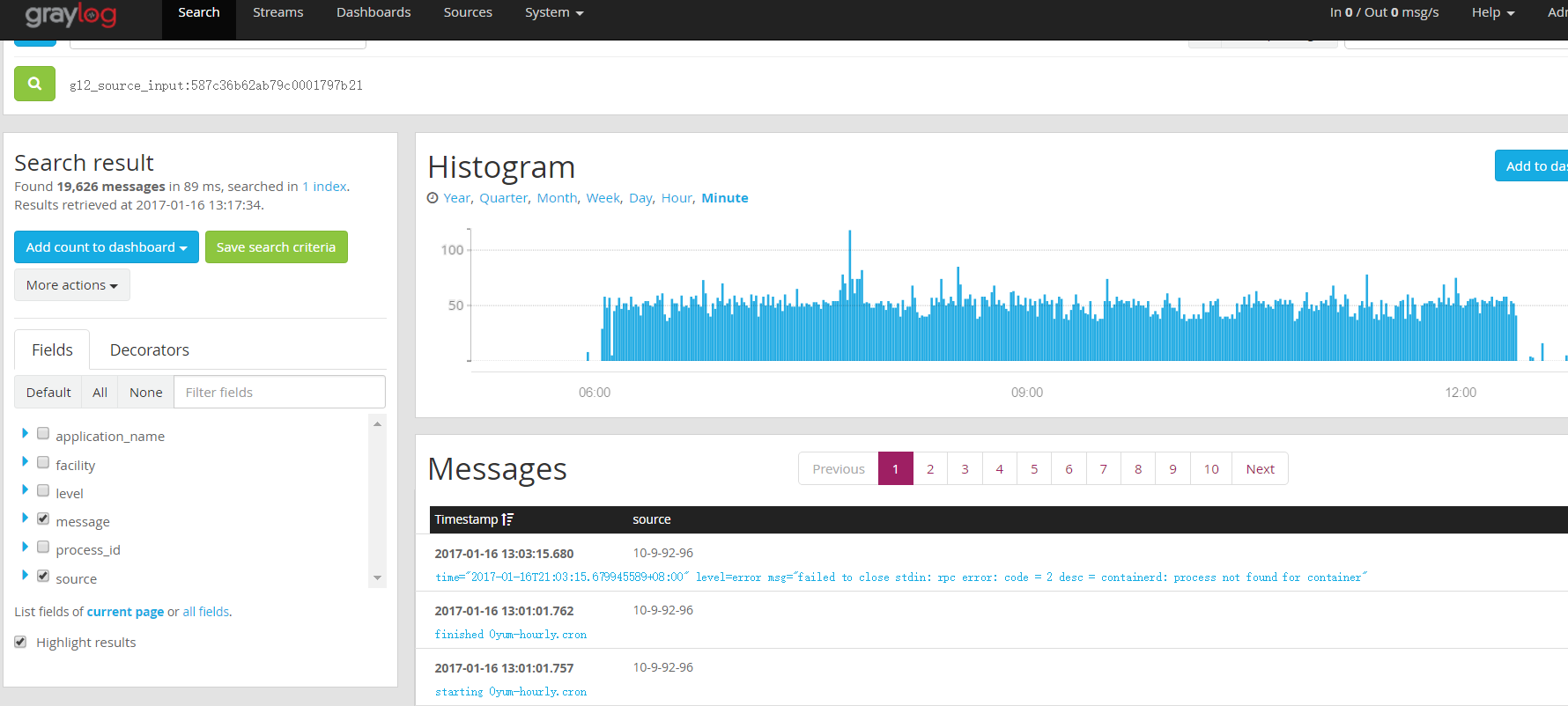
GELF (http 为例)
GELF (Graylog Extended Log Format) 可以接收结构化的事件, 支持压缩(GZIP’d or ZLIB’d)和分块。
GELF message:
-
- version
string - host
string - short_message
string - full_message
string - timestamp
number - level
number - facility
string - line
number - file
string - _[additional field]
stringornumber, 通过_前缀添加自定义的字段
- version
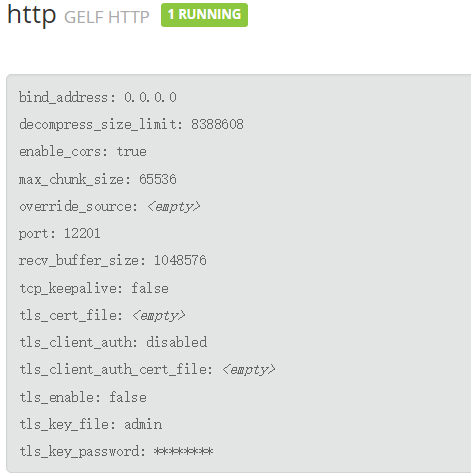
新建一个 GELF HTTP input:
推送日志:
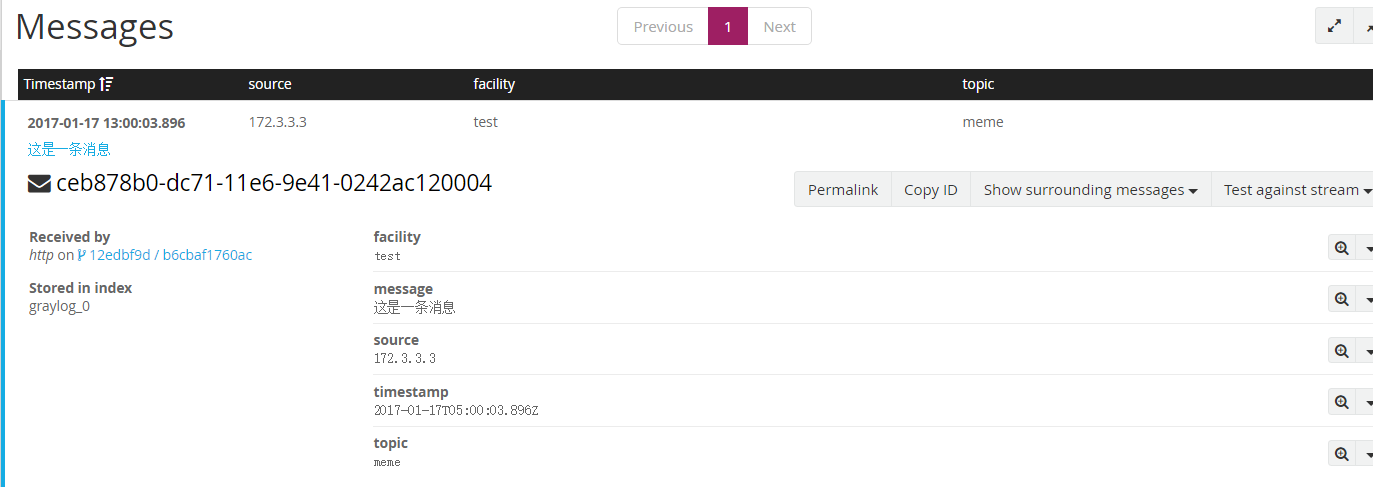
curl -XPOST http://106.75.62.142:12201/gelf -p0 -d '{"message":"这是一条消息", "host":"172.3.3.3", "facility":"test", "topic": "meme"}'
查看推送的日志:
收集服务日志( nodejs 为例)
log4js, bunyan, winston 等等 nodejs 日志框架都可以, 这里我们以 bunyan 为例, 因为 bunyan 可以将日志以 json 的形式打印。
const express = require('express'); const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); const bunyan = require('bunyan'); const log = bunyan.createLogger({ name: 'server-bunyan', level: 'debug', streams: [{ type: 'rotating-file', path: '/data/logs/server-bunyan.log', period: '1d', count: 3 }] }); const app = express(); app.use(bodyParser.json()); app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true })); app.get('/hello', (req, res) => { log.info({ query: req.query }, 'hello'); res.send('hello world'); }); app.listen(5004, '0.0.0.0', () => { log.info('app listening on 5004'); });
rsyslog:
module(load="imfile" PollingInterval="10") # input
input(type="imfile" File="/data/logs/server.log" Tag="server" ruleset="push_remote") input(type="imfile" File="/data/logs/detail.log" Tag="detail" ruleset="push_remote") input(type="imfile" File="/data/logs/server-bunyan.log" Tag="bunyan_server" ruleset="push_remote") # template template(name="mytpl" type="string" string="node1 %programname% %msg% " ) # output ruleset(name="push_remote") { action( type="omfwd" protocol="tcp" target="x.x.x.x" port="515" template="mytpl" action.resumeRetryCount="-1" action.resumeInterval="1" queue.filename="push-remote" queue.size="100000" queue.highwatermark="60000" queue.lowwatermark="2000" queue.maxdiskspace="100g" queue.saveonshutdown="on" queue.type="LinkedList" queue.maxfilesize="128m" ) }
新建 input, 监听 515 端口,这里我们体验一下 graylog 的 Extractor,给改 input 添加一个 Extractor:
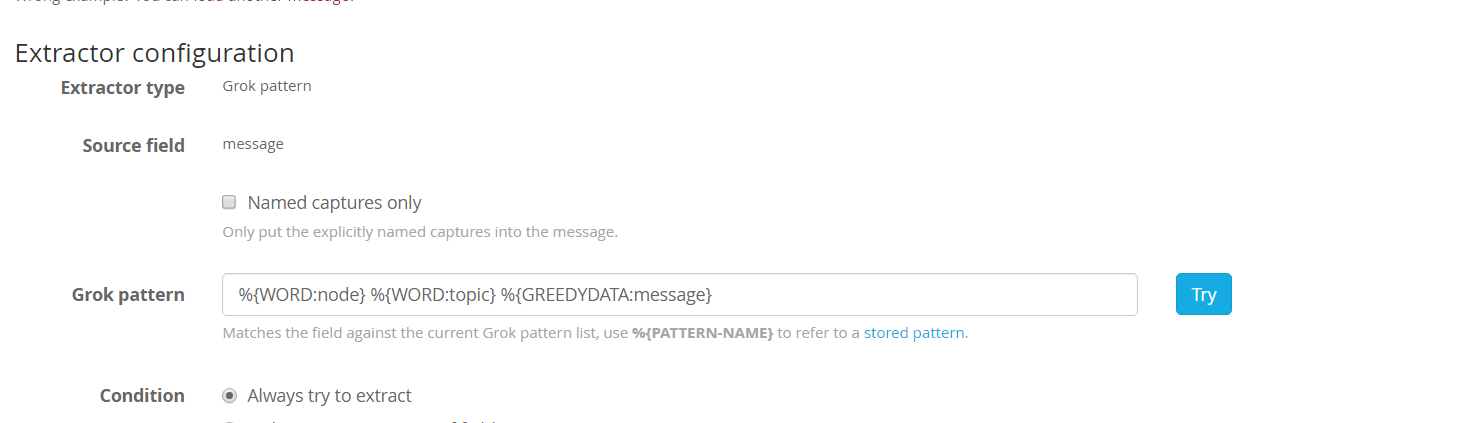
我们加了一个抓取器,来提取 node, topic 两个字段。
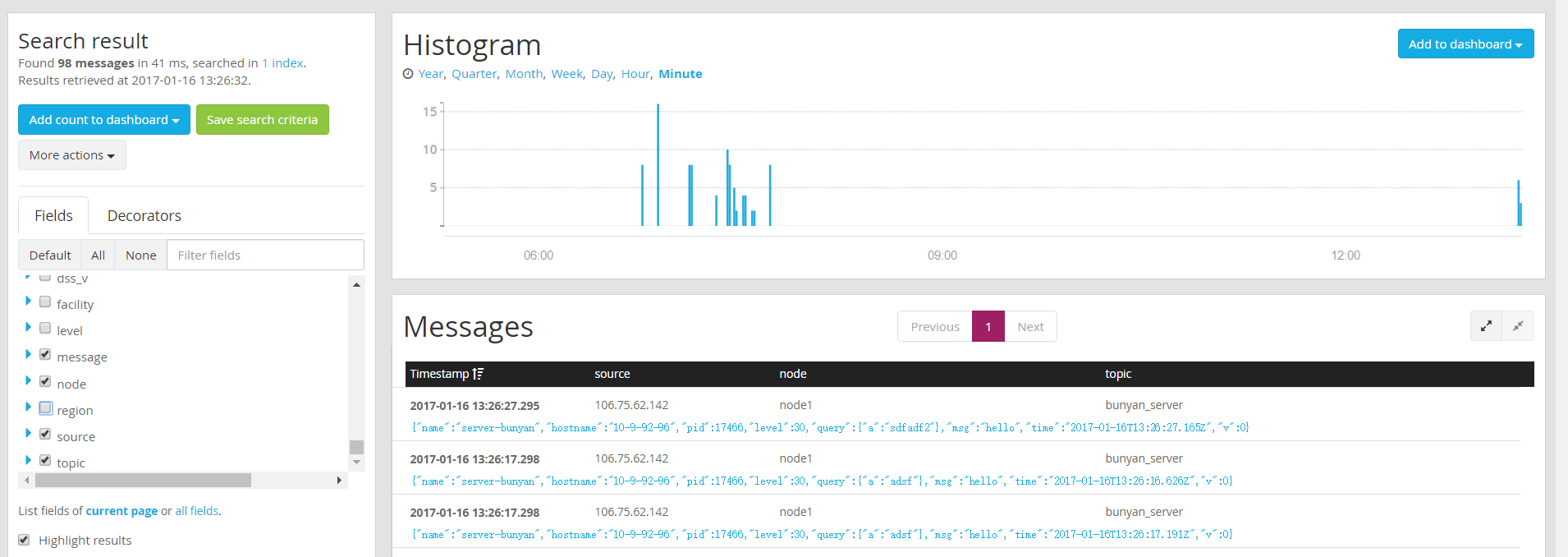
在 webui 查看该 input 的 message:
Alerts
Graylog 内置的告警条件:
-
- 消息数量
- 字段值(number)
- 字段内容
内置告警方式:
-
- HTTP 回调
体验一下 HTTP 回调。
新建一个 Stream, 进入 manager alerts, 新建一个告警条件:
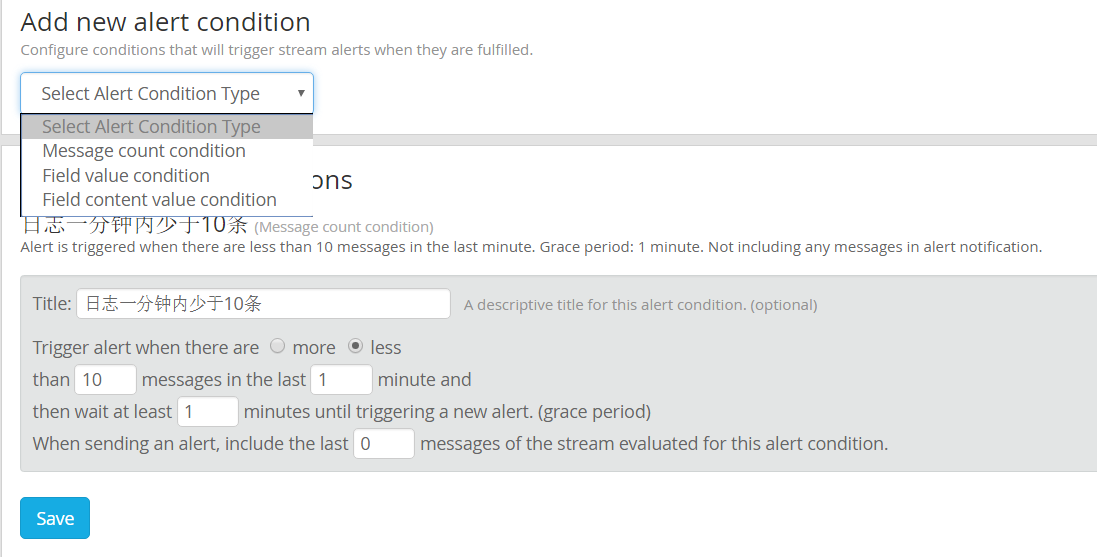
创建一个 HTTP 回调:
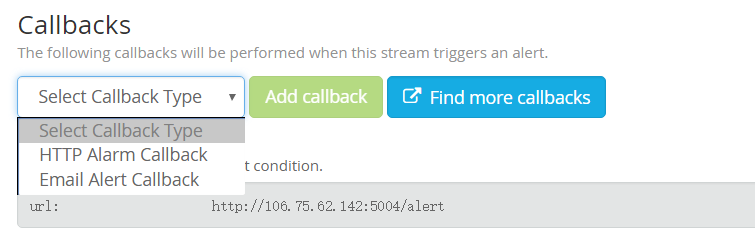
告警以 post 方式请求回调, 请求的 body 内容:
{ "check_result": { "result_description": "Stream had 0 messages in the last 1 minutes with trigger condition less than 10 messages. (Current grace time: 1 minutes)", "triggered_condition": { "id": "6bacc1c1-1eac-49f9-9ac8-998ea851f101", "type": "message_count", "created_at": "2017-01-17T05:25:13.592Z", "creator_user_id": "admin", "title": "日志一分钟内少于10条", "parameters": { "grace": 1, "threshold_type": "less", "threshold": 10, "time": 1, "backlog": 0 } }, "triggered_at": "2017-01-17T05:44:11.921Z", "triggered": true, "matching_messages": [] }, "stream": { "creator_user_id": "admin", "outputs": [], "alert_receivers": { "emails": [ "dongsoso@hotmail.com" ], "users": [ "dongsoso@hotmail.com" ] }, "matching_type": "AND", "description": "alert", "created_at": "2017-01-17T05:21:58.852Z", "disabled": false, "rules": [], "alert_conditions": [ { "creator_user_id": "admin", "created_at": "2017-01-17T05:25:13.592Z", "id": "6bacc1c1-1eac-49f9-9ac8-998ea851f101", "type": "message_count", "title": "日志一分钟内少于10条", "parameters": { "grace": 1, "threshold_type": "less", "threshold": 10, "time": 1, "backlog": 0 } } ], "id": "587da9f62ab79c0001352b7a", "title": "test", "content_pack": null } }
查看告警历史:
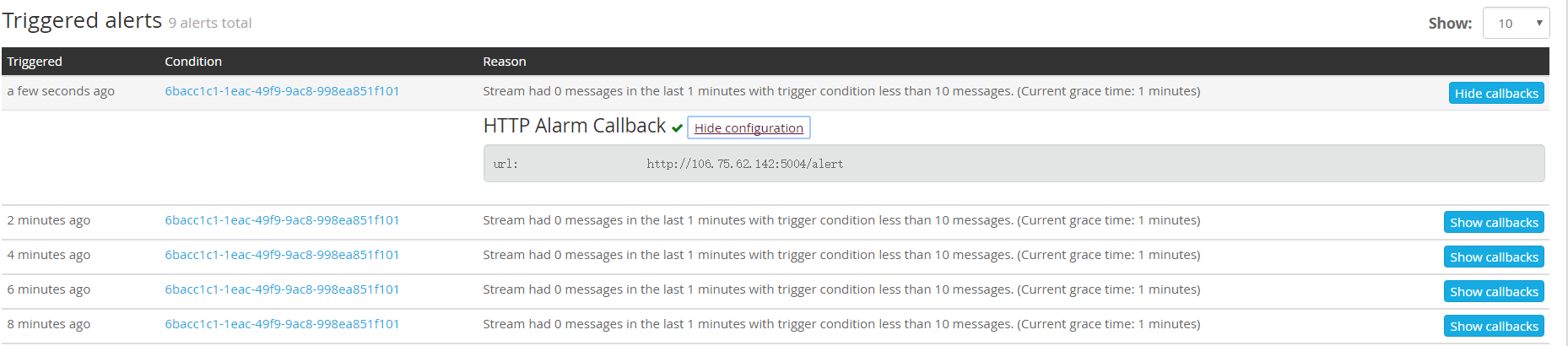
更多更好用的功能等待发现…
官方文档 : http://docs.graylog.org/en/2.3/index.html
