https://study.163.com/provider/400000000398149/index.htm?share=2&shareId=400000000398149( 欢迎关注博主主页,学习python视频资源,还有大量免费python经典文章)
【强化学习】Q-Learning详解
1、算法思想
QLearning是强化学习算法中值迭代的算法,Q即为Q(s,a)就是在某一时刻的 s 状态下(s∈S),采取 a (a∈A)动作能够获得收益的期望,环境会根据agent的动作反馈相应的回报reward r,所以算法的主要思想就是将State与Action构建成一张Q-table来存储Q值,然后根据Q值来选取动作获得较大的收益。
2、公式推导
举个例子如图有一个GridWorld的游戏从起点出发到达终点为胜利掉进陷阱为失败。智能体(Agent)、环境状态(environment)、奖励(reward)、动作(action)可以将问题抽象成一个马尔科夫决策过程,我们在每个格子都算是一个状态 $s_t $ , π(a|s)在s状态下采取动作a a∈A 。 P(s’|s,a)为在s状态下选择a动作转换到下一个状态s’的概率。R(s’|s,a)表示在s状态下采取a动作转移到s’的奖励reward,我们的目的很明确就是找到一条能够到达终点获得最大奖赏的策略。
所以目标就是求出累计奖赏最大的策略的期望:
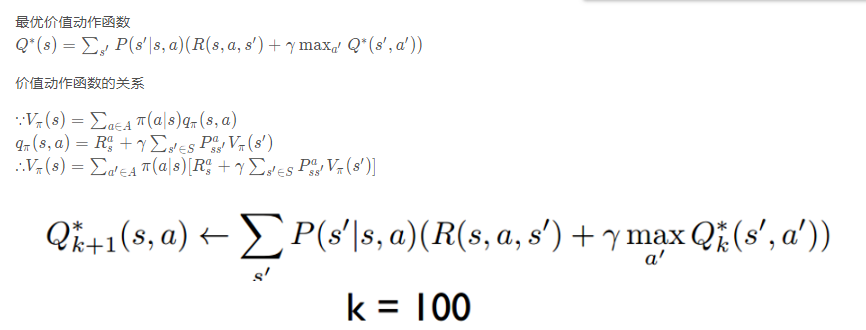
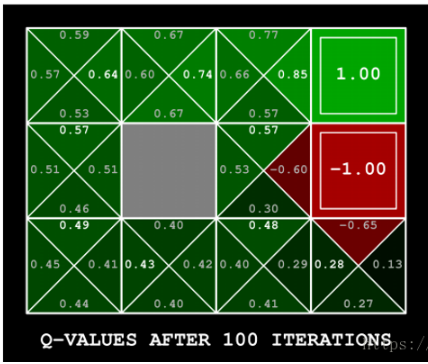
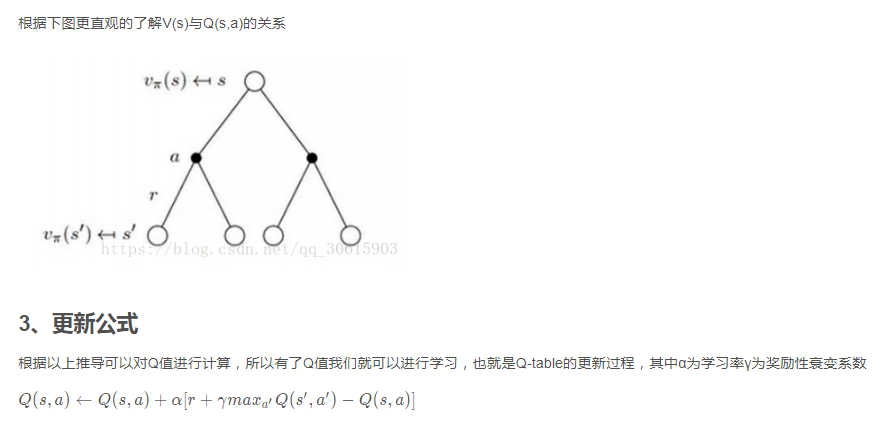
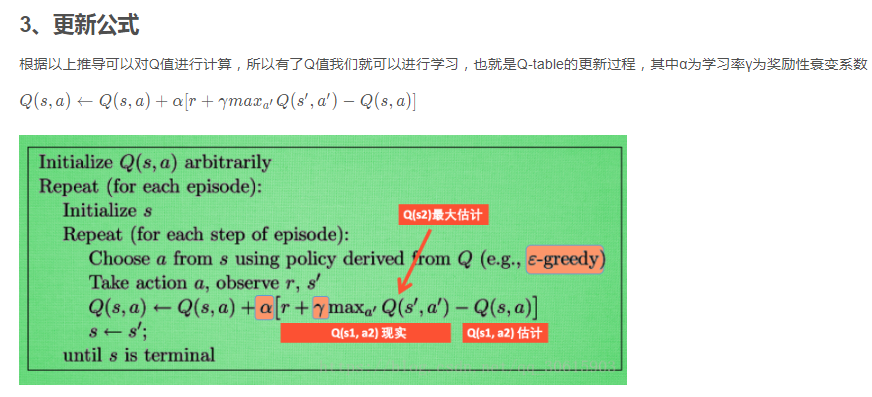
4、实现代码
值迭代部分
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from environment import GraphicDisplay, Env
class ValueIteration:
def __init__(self, env):
self.env = env
# 2-d list for the value function
self.value_table = [[0.0] * env.width for _ in range(env.height)]
self.discount_factor = 0.9
# get next value function table from the current value function table
def value_iteration(self):
next_value_table = [[0.0] * self.env.width
for _ in range(self.env.height)]
for state in self.env.get_all_states():
if state == [2, 2]:
next_value_table[state[0]][state[1]] = 0.0
continue
value_list = []
for action in self.env.possible_actions:
next_state = self.env.state_after_action(state, action)
reward = self.env.get_reward(state, action)
next_value = self.get_value(next_state)
value_list.append((reward + self.discount_factor * next_value))
# return the maximum value(it is the optimality equation!!)
next_value_table[state[0]][state[1]] = round(max(value_list), 2)
self.value_table = next_value_table
# get action according to the current value function table
def get_action(self, state):
action_list = []
max_value = -99999
if state == [2, 2]:
return []
# calculating q values for the all actions and
# append the action to action list which has maximum q value
for action in self.env.possible_actions:
next_state = self.env.state_after_action(state, action)
reward = self.env.get_reward(state, action)
next_value = self.get_value(next_state)
value = (reward + self.discount_factor * next_value)
if value > max_value:
action_list.clear()
action_list.append(action)
max_value = value
elif value == max_value:
action_list.append(action)
return action_list
def get_value(self, state):
return round(self.value_table[state[0]][state[1]], 2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
env = Env()
value_iteration = ValueIteration(env)
grid_world = GraphicDisplay(value_iteration)
grid_world.mainloop()
动态环境部分
import tkinter as tk
import time
import numpy as np
import random
from PIL import ImageTk, Image
PhotoImage = ImageTk.PhotoImage
UNIT = 100 # pixels
HEIGHT = 5 # grid height
WIDTH = 5 # grid width
TRANSITION_PROB = 1
POSSIBLE_ACTIONS = [0, 1, 2, 3] # up, down, left, right
ACTIONS = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)] # actions in coordinates
REWARDS = []
class GraphicDisplay(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self, value_iteration):
super(GraphicDisplay, self).__init__()
self.title('Value Iteration')
self.geometry('{0}x{1}'.format(HEIGHT * UNIT, HEIGHT * UNIT + 50))
self.texts = []
self.arrows = []
self.env = Env()
self.agent = value_iteration
self.iteration_count = 0
self.improvement_count = 0
self.is_moving = 0
(self.up, self.down, self.left,
self.right), self.shapes = self.load_images()
self.canvas = self._build_canvas()
self.text_reward(2, 2, "R : 1.0")
self.text_reward(1, 2, "R : -1.0")
self.text_reward(2, 1, "R : -1.0")
def _build_canvas(self):
canvas = tk.Canvas(self, bg='white',
height=HEIGHT * UNIT,
width=WIDTH * UNIT)
# buttons
iteration_button = tk.Button(self, text="Calculate",
command=self.calculate_value)
iteration_button.configure(width=10, activebackground="#33B5E5")
canvas.create_window(WIDTH * UNIT * 0.13, (HEIGHT * UNIT) + 10,
window=iteration_button)
policy_button = tk.Button(self, text="Print Policy",
command=self.print_optimal_policy)
policy_button.configure(width=10, activebackground="#33B5E5")
canvas.create_window(WIDTH * UNIT * 0.37, (HEIGHT * UNIT) + 10,
window=policy_button)
policy_button = tk.Button(self, text="Move",
command=self.move_by_policy)
policy_button.configure(width=10, activebackground="#33B5E5")
canvas.create_window(WIDTH * UNIT * 0.62, (HEIGHT * UNIT) + 10,
window=policy_button)
policy_button = tk.Button(self, text="Clear", command=self.clear)
policy_button.configure(width=10, activebackground="#33B5E5")
canvas.create_window(WIDTH * UNIT * 0.87, (HEIGHT * UNIT) + 10,
window=policy_button)
# create grids
for col in range(0, WIDTH * UNIT, UNIT): # 0~400 by 80
x0, y0, x1, y1 = col, 0, col, HEIGHT * UNIT
canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1)
for row in range(0, HEIGHT * UNIT, UNIT): # 0~400 by 80
x0, y0, x1, y1 = 0, row, HEIGHT * UNIT, row
canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x1, y1)
# add img to canvas
self.rectangle = canvas.create_image(50, 50, image=self.shapes[0])
canvas.create_image(250, 150, image=self.shapes[1])
canvas.create_image(150, 250, image=self.shapes[1])
canvas.create_image(250, 250, image=self.shapes[2])
# pack all
canvas.pack()
return canvas
def load_images(self):
PhotoImage = ImageTk.PhotoImage
up = PhotoImage(Image.open("../img/up.png").resize((13, 13)))
right = PhotoImage(Image.open("../img/right.png").resize((13, 13)))
left = PhotoImage(Image.open("../img/left.png").resize((13, 13)))
down = PhotoImage(Image.open("../img/down.png").resize((13, 13)))
rectangle = PhotoImage(
Image.open("../img/rectangle.png").resize((65, 65)))
triangle = PhotoImage(
Image.open("../img/triangle.png").resize((65, 65)))
circle = PhotoImage(Image.open("../img/circle.png").resize((65, 65)))
return (up, down, left, right), (rectangle, triangle, circle)
def clear(self):
if self.is_moving == 0:
self.iteration_count = 0
self.improvement_count = 0
for i in self.texts:
self.canvas.delete(i)
for i in self.arrows:
self.canvas.delete(i)
self.agent.value_table = [[0.0] * WIDTH for _ in range(HEIGHT)]
x, y = self.canvas.coords(self.rectangle)
self.canvas.move(self.rectangle, UNIT / 2 - x, UNIT / 2 - y)
def reset(self):
self.update()
time.sleep(0.5)
self.canvas.delete(self.rectangle)
return self.canvas.coords(self.rectangle)
def text_value(self, row, col, contents, font='Helvetica', size=12,
style='normal', anchor="nw"):
origin_x, origin_y = 85, 70
x, y = origin_y + (UNIT * col), origin_x + (UNIT * row)
font = (font, str(size), style)
text = self.canvas.create_text(x, y, fill="black", text=contents,
font=font, anchor=anchor)
return self.texts.append(text)
def text_reward(self, row, col, contents, font='Helvetica', size=12,
style='normal', anchor="nw"):
origin_x, origin_y = 5, 5
x, y = origin_y + (UNIT * col), origin_x + (UNIT * row)
font = (font, str(size), style)
text = self.canvas.create_text(x, y, fill="black", text=contents,
font=font, anchor=anchor)
return self.texts.append(text)
def rectangle_move(self, action):
base_action = np.array([0, 0])
location = self.find_rectangle()
self.render()
if action == 0 and location[0] > 0: # up
base_action[1] -= UNIT
elif action == 1 and location[0] < HEIGHT - 1: # down
base_action[1] += UNIT
elif action == 2 and location[1] > 0: # left
base_action[0] -= UNIT
elif action == 3 and location[1] < WIDTH - 1: # right
base_action[0] += UNIT
self.canvas.move(self.rectangle, base_action[0],
base_action[1]) # move agent
def find_rectangle(self):
temp = self.canvas.coords(self.rectangle)
x = (temp[0] / 100) - 0.5
y = (temp[1] / 100) - 0.5
return int(y), int(x)
def move_by_policy(self):
if self.improvement_count != 0 and self.is_moving != 1:
self.is_moving = 1
x, y = self.canvas.coords(self.rectangle)
self.canvas.move(self.rectangle, UNIT / 2 - x, UNIT / 2 - y)
x, y = self.find_rectangle()
while len(self.agent.get_action([x, y])) != 0:
action = random.sample(self.agent.get_action([x, y]), 1)[0]
self.after(100, self.rectangle_move(action))
x, y = self.find_rectangle()
self.is_moving = 0
def draw_one_arrow(self, col, row, action):
if col == 2 and row == 2:
return
if action == 0: # up
origin_x, origin_y = 50 + (UNIT * row), 10 + (UNIT * col)
self.arrows.append(self.canvas.create_image(origin_x, origin_y,
image=self.up))
elif action == 1: # down
origin_x, origin_y = 50 + (UNIT * row), 90 + (UNIT * col)
self.arrows.append(self.canvas.create_image(origin_x, origin_y,
image=self.down))
elif action == 3: # right
origin_x, origin_y = 90 + (UNIT * row), 50 + (UNIT * col)
self.arrows.append(self.canvas.create_image(origin_x, origin_y,
image=self.right))
elif action == 2: # left
origin_x, origin_y = 10 + (UNIT * row), 50 + (UNIT * col)
self.arrows.append(self.canvas.create_image(origin_x, origin_y,
image=self.left))
def draw_from_values(self, state, action_list):
i = state[0]
j = state[1]
for action in action_list:
self.draw_one_arrow(i, j, action)
def print_values(self, values):
for i in range(WIDTH):
for j in range(HEIGHT):
self.text_value(i, j, values[i][j])
def render(self):
time.sleep(0.1)
self.canvas.tag_raise(self.rectangle)
self.update()
def calculate_value(self):
self.iteration_count += 1
for i in self.texts:
self.canvas.delete(i)
self.agent.value_iteration()
self.print_values(self.agent.value_table)
def print_optimal_policy(self):
self.improvement_count += 1
for i in self.arrows:
self.canvas.delete(i)
for state in self.env.get_all_states():
action = self.agent.get_action(state)
self.draw_from_values(state, action)
class Env:
def __init__(self):
self.transition_probability = TRANSITION_PROB
self.width = WIDTH # Width of Grid World
self.height = HEIGHT # Height of GridWorld
self.reward = [[0] * WIDTH for _ in range(HEIGHT)]
self.possible_actions = POSSIBLE_ACTIONS
self.reward[2][2] = 1 # reward 1 for circle
self.reward[1][2] = -1 # reward -1 for triangle
self.reward[2][1] = -1 # reward -1 for triangle
self.all_state = []
for x in range(WIDTH):
for y in range(HEIGHT):
state = [x, y]
self.all_state.append(state)
def get_reward(self, state, action):
next_state = self.state_after_action(state, action)
return self.reward[next_state[0]][next_state[1]]
def state_after_action(self, state, action_index):
action = ACTIONS[action_index]
return self.check_boundary([state[0] + action[0], state[1] + action[1]])
@staticmethod
def check_boundary(state):
state[0] = (0 if state[0] < 0 else WIDTH - 1
if state[0] > WIDTH - 1 else state[0])
state[1] = (0 if state[1] < 0 else HEIGHT - 1
if state[1] > HEIGHT - 1 else state[1])
return state
def get_transition_prob(self, state, action):
return self.transition_probability
def get_all_states(self):
return self.all_state
转载https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30615903/article/details/80739243