python金融风控评分卡模型和数据分析微专业课(博主亲自录制视频):http://dwz.date/b9vv
Lemmatizing with NLTK
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Spyder Editor author 231469242@qq.com
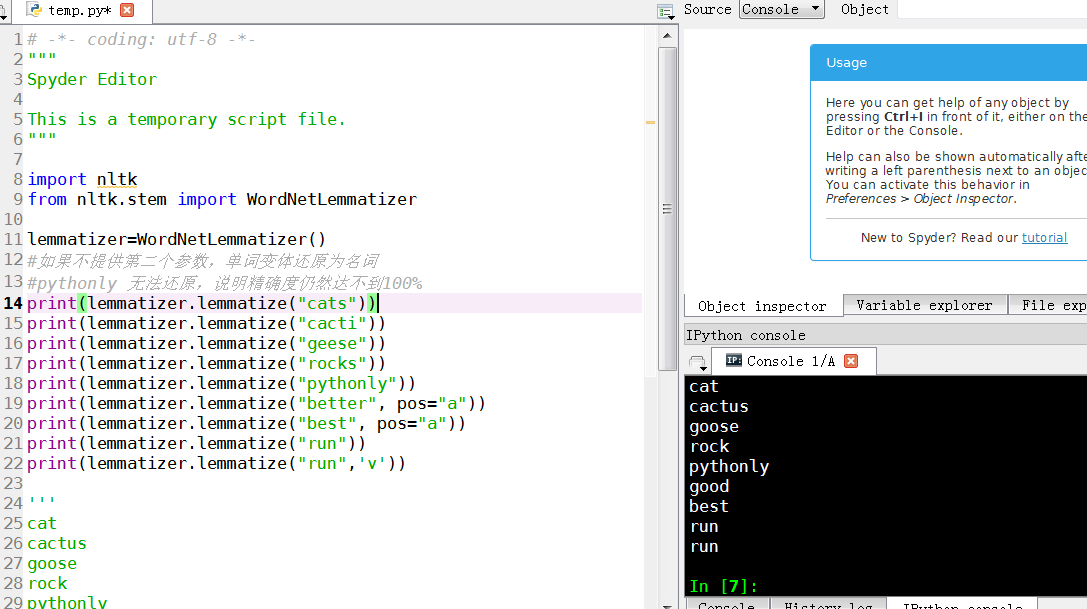
微信公众号:pythonEducation """ import nltk from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer lemmatizer=WordNetLemmatizer() #如果不提供第二个参数,单词变体还原为名词 #pythonly 无法还原,说明精确度仍然达不到100% print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("cats")) print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("cacti")) print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("geese")) print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("rocks")) print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("pythonly")) print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("better", pos="a")) print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("best", pos="a")) print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("run")) print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("run",'v')) ''' cat cactus goose rock pythonly good best run run '''
A very similar operation to stemming is called lemmatizing. The major difference between these is, as you saw earlier, stemming can often create non-existent words, whereas lemmas are actual words.
So, your root stem, meaning the word you end up with, is not something you can just look up in a dictionary, but you can look up a lemma.
Some times you will wind up with a very similar word, but sometimes, you will wind up with a completely different word. Let's see some examples.
from nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer
lemmatizer = WordNetLemmatizer()
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("cats"))
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("cacti"))
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("geese"))
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("rocks"))
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("python"))
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("better", pos="a"))
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("best", pos="a"))
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("run"))
print(lemmatizer.lemmatize("run",'v'))
Here, we've got a bunch of examples of the lemma for the words that we use. The only major thing to note is that lemmatize takes a part of speech parameter, "pos." If not supplied, the default is "noun." This means that an attempt will be made to find the closest noun, which can create trouble for you. Keep this in mind if you use lemmatizing!
In the next tutorial, we're going to dive into the NTLK corpus that came with the module, looking at all of the awesome documents they have waiting for us there.