有的时候我们需要为非input类型的元素添加ng-model来实现双向的数据绑定,从而减少冗余代码,那么可以尝试一下的方式
例如:我页面中使用了contenteditable这个属性来实现用户可直接编译的div元素
html:
<style> .text{ margin:0 auto; 100px; height:50px; border:1px solid red; } </style> </head> <body> <div ng-controller="selectController"> <div ng-repeat="pop in citylist"> <div class="text" contenteditable="true" ng-model="pop.pop"></div> </div> <button ng-click="cs()">输出新数据</button> </div> </body>
但是直接绑定ng-model是肯定得不到数据的,这时就需要为其增加自定义的属性,如下所示。
js:
<script>
var app = angular.module('app', []);
app.controller('selectController', function ($scope) {
$scope.citylist=[{id:1,pop:"北京"},{id:1,pop:"上海"},{id:1,pop:"广州"}];
$scope.p={};
$scope.cs=function(){
console.log($scope.citylist);
}
}).directive('contenteditable', function() {//自定义ngModel的属性可以用在div等其他元素中
return {
restrict: 'A', // 作为属性使用
require: '?ngModel', // 此指令所代替的函数
link: function(scope, element, attrs, ngModel) {
if (!ngModel) {
return;
} // do nothing if no ng-model
// Specify how UI should be updated
ngModel.$render = function() {
element.html(ngModel.$viewValue || '');
};
// Listen for change events to enable binding
element.on('blur keyup change', function() {
scope.$apply(readViewText);
});
// No need to initialize, AngularJS will initialize the text based on ng-model attribute
// Write data to the model
function readViewText() {
var html = element.html();
// When we clear the content editable the browser leaves a <br> behind
// If strip-br attribute is provided then we strip this out
if (attrs.stripBr && html === '<br>') {
html = '';
}
ngModel.$setViewValue(html);
}
}
};
})
</script>
其中参数类别如下:
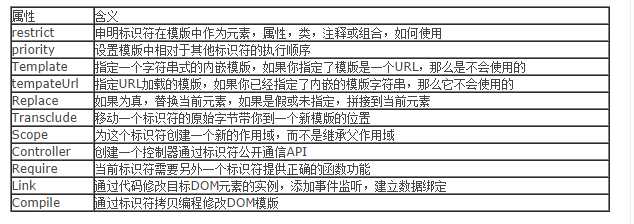
部分参数解释
restrict:
(字符串)可选参数,指明指令在DOM里面以什么形式被声明;
取值有:E(元素),A(属性),C(类),M(注释),其中默认值为A;
E(元素):<directiveName></directiveName>
A(属性):<div directiveName='expression'></div>
C(类): <div class='directiveName'></div>
M(注释):<--directive:directiveName expression-->
2.require
字符串代表另一个指令的名字,它将会作为link函数的第四个参数
具体用法我们可以举个例子说明
假设现在我们要编写两个指令,两个指令中的link链接函数中(link函数后面会讲)存在有很多重合的方法,
这时候我们就可以将这些重复的方法写在第三个指令的controller中(上面也讲到controller经常用来提供指令间的复用行为)
然后在这两个指令中,require这个拥有controller字段的的指令(第三个指令),
最后通过link链接函数的第四个参数就可以引用这些重合的方法了。
<!doctype html>
<html ng-app="myApp">
<head>
<script src="http://cdn.staticfile.org/angular.js/1.2.10/angular.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<outer-directive>
<inner-directive></inner-directive>
<inner-directive2></inner-directive2>
</outer-directive>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.directive('outerDirective', function() {
return {
scope: {},
restrict: 'AE',
controller: function($scope) {
this.say = function(someDirective) {
console.log('Got:' + someDirective.message);
};
}
};
});
app.directive('innerDirective', function() {
return {
scope: {},
restrict: 'AE',
require: '^outerDirective',
link: function(scope, elem, attrs, controllerInstance) {
scope.message = "Hi,leifeng";
controllerInstance.say(scope);
}
};
});
app.directive('innerDirective2', function() {
return {
scope: {},
restrict: 'AE',
require: '^outerDirective',
link: function(scope, elem, attrs, controllerInstance) {
scope.message = "Hi,shushu";
controllerInstance.say(scope);
}
};
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
上面例子中的指令innerDirective和指令innerDirective2复用了定义在指令outerDirective的controller中的方法
也进一步说明了,指令中的controller是用来让不同指令间通信用的。
另外我们可以在require的参数值加上下面的某个前缀,这会改变查找控制器的行为:
(1)没有前缀,指令会在自身提供的控制器中进行查找,如果找不到任何控制器,则会抛出一个error
(2)?如果在当前的指令没有找到所需的控制器,则会将null传给link连接函数的第四个参数
(3)^如果在当前的指令没有找到所需的控制器,则会查找父元素的控制器
(4)?^组合