spray-json是一个轻量级的,简介的和高效的使用Scala实现的json
它拥有以下特征:
- 一个简单不可变的模型的json语言元素
- 一个高效的json解析器
- 可选择既紧凑又漂亮的json到string的打印(格式化输出)
- 基于类的自定义对象的(反)序列化(没有反射,没有入侵)
- 没有外部依赖包
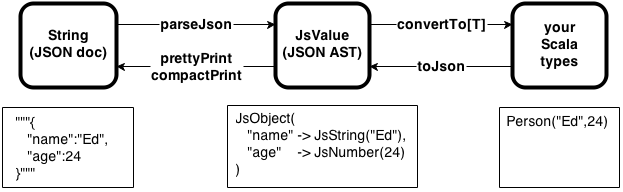
spray可以做以下转换:
*JSON字符串
*基于JsValue的JSON抽象语法树(JSON Abstract Syntax Tree(ASTs))
*任意的scala类型的实例
如下图描述
安装
spray-json 可以从 http://repo.spray.io/仓库获得
最终的发布版本是1.3.2 ,对应的构建在scala 2.10.5和scala 2.11.6
如果你使用SBT 使用下面方依赖将spray-json加入到你的项目中
libraryDependencies += "io.spray" %% "spray-json" % "1.3.2"
使用方法
spray-json 非常容易使用.
仅仅需要导入相关方法
import spray.json._ import DefaultJsonProtocol._ //如果你不提供自己的协议(见下文)
如下样例:
- 解析JSON字符串转换为树结构(Abstract Syntax Tree (AST))实例
val source = """{ "some": "JSON source" }"""
val jsonAst = source.parseJson // or JsonParser(source)
输出:
source: String = { "some": "JSON source" }
jsonAst: spray.json.JsValue = {"some":"JSON source"}
- 打印JSON AST 返回一个string既可以用CompactPrinter也可以用PrettyPrinter输出
val json = jsonAst.prettyPrint //格式化输出
val json1 = jsonAst.compactPrint //输出一行
输出:
json: String = {
"some": "JSON source"
}
json1: String = {"some":"JSON source"}
- 调用其toJson方法将scala的任意类型转换为一个Json AST
val jsonAst = List(1, 2, 3).toJson
输出:
jsonAst: spray.json.JsValue = [1,2,3]
- 调用convertTo方法将JSON AST 转换为Scala object
val jsonAst = List(1, 2, 3).toJson jsonAst.convertTo[List[Int]]
输出:
res0: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3)
为了使对象的步骤3和步骤4的工作你需要指定隐式类型的值的范围,提供JsonFormat[T]实例为T,T(直接或间接)所使用的所有类型。
JsonProtocol
spray-json使用的是SJSON(https://github.com/debasishg/sjs)基于类类型的scala习惯的方法连接一个已经存在的类型T,依据的逻辑为:怎样序列化实例到Json和从Json反序列化到实例。(事实上,spray-json甚至重新使用SJSON的代码,参照‘Credits’这一节)
这个方法有个优点就是不不需要改变(或者访问)T的资源代码。所有的(反)序列化都是"从外面"附加的.他没有涉及到反射,所以结果转换快。
Scala的优秀类型推断减小了冗余和引用,scala编辑器当确认编译时你必须提供所有的序列化和反序列化的逻辑。
在spray-json的术语中一个'JsonProtocol' 是没有任何东西的,但是一堆类型为JsonFormat[T]隐式(implicit)的值,其中每一个JsonFormat[T]包含怎样从JSON转换实例化的T。所有的JsonFormat 是一个协议需要是"mece"(相互排斥的,完全穷尽的(mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive)),例如:他们不需要重叠在一起,需要被应用程序跨越类型。
这些听起来比现在的更复杂。
spray-json来自一个DefaultJsonProtocol,已经封装了所有的Scala值类型,以及最重要的参考和集合类型。 只要你的代码没有超过这些内容就需要使用DefaultJsonProtocol
下面的类型已经被DefaultJsonProtocol使用:
- Byte, Short, Int, Long, Float, Double, Char, Unit, Boolean
- String, Symbol
- BigInt, BigDecimal
- Option, Either, Tuple1 - Tuple7
- List, Array
- immutable.{Map, Iterable, Seq, IndexedSeq, LinearSeq, Set, Vector}
- collection.{Iterable, Seq, IndexedSeq, LinearSeq, Set}
- JsValue
大多数情况下你也想不通过DefaultJsonProtocol转换类型,在这些情况下你需要提供JsonFormat[T]为您的自定义类型。这并不难。
提供 JsonFormats 的 Case 类
如果您的自定义类型T是一个case类,为DefaultJsonProtocol增加JsonFormat[T]很容易:
case class Color(name: String, red: Int, green: Int, blue: Int)
object MyJsonProtocol extends DefaultJsonProtocol {
implicit val colorFormat = jsonFormat4(Color)
}
import MyJsonProtocol._
import spray.json._
val json = Color("CadetBlue", 95, 158, 160).toJson
val color = json.convertTo[Color]
运行结果:
defined class Color
defined module MyJsonProtocol
import MyJsonProtocol._
import spray.json._
json: spray.json.JsValue = {"name":"CadetBlue","red":95,"green":158,"blue":160}
color: Color = Color(CadetBlue,95,158,160)
提供JsonFormat的case 类
如果你的自定义类型是一个case class 为JsonFormat[T]增加一个DefaultJsonProtocol是非常容易的:
case class Color(name: String, red: Int, green: Int, blue: Int)
object MyJsonProtocol extends DefaultJsonProtocol {
implicit val colorFormat = jsonFormat4(Color)
}
import MyJsonProtocol._
import spray.json._
val json = Color("CadetBlue", 95, 158, 160).toJson
val color = json.convertTo[Color]
运行结果:
import MyJsonProtocol._
import spray.json._
json: spray.json.JsValue = {"name":"CadetBlue","red":95,"green":158,"blue":160}
color: Color = Color(CadetBlue,95,158,160)
jsonFormatX方法将模板减小为最小,仅仅需要传递一个case class 的伴生对象,他就可以返回一个现成的JsonFormatle类型(正确的匹配参数的数量是你的case class 类例如:你的case class 有13个字段 你需要使用JsonFormat13 这个方法).
jsonFormatX 方法尝试多次调用JsonFormat的重载方法提取你的case class中定义的参数,这个你必须手动指定字段名。
假如spray-json无法确定字段类型,或者你的JSON Object 使用成员名称月case class中的名称不相同也能直接使用JsonFormat。
有一个其他的习惯:如果你明确的指明了clase class的伴生对象上面的操作将停止工作。你必须显式地引用伴生对象
case class Color(name: String, red: Int, green: Int, blue: Int)
object Color
object MyJsonProtocol extends DefaultJsonProtocol {
implicit val colorFormat = jsonFormat4(Color.apply)
}
运行结果:
import spray.json._ defined class Color defined module Color defined module MyJsonProtocol
如果你的case类是通用的,它需要类型参数本身jsonFormat方法也可以帮助你。
然而,有模板有一点要求,你需要为参数添加上下文和显示的引用case class类的apply方法,例如下面的例子:
case class NamedList[A](name: String, items: List[A])
object MyJsonProtocol extends DefaultJsonProtocol {
implicit def namedListFormat[A :JsonFormat] = jsonFormat2(NamedList.apply[A])
}
运行结果:
import spray.json._ defined class NamedList defined module MyJsonProtocol
NullOptions
NullOptions特征提供的另一种呈现模式可选的类成员。未定义的成员是无法提取出来的。
JsonProtocol为你定义了未定义程序最为null(主意这仅仅是JSON的写法,spray-json经常读取错误的操作程序作为null ).
为其他类型提供JsonFormat
当然你也能用序列化和反序列化的不是case class类的类型逻辑。
这是一个方法:
import spray.json._
import DefaultJsonProtocol._
class Color(val name: String, val red: Int, val green: Int, val blue: Int)
object MyJsonProtocol extends DefaultJsonProtocol {
implicit object ColorJsonFormat extends RootJsonFormat[Color] {
def write(c: Color) = JsArray(JsString(c.name), JsNumber(c.red), JsNumber(c.green), JsNumber(c.blue))
def read(value: JsValue) = value match {
case JsArray(Vector(JsString(name), JsNumber(red), JsNumber(green), JsNumber(blue))) =>
new Color(name, red.toInt, green.toInt, blue.toInt)
case _ => deserializationError("Color expected")
}
}
}
import MyJsonProtocol._
val json =new Color("CadetBlue", 95, 158, 160).toJson
val color = json.convertTo[Color]
color.blue
运行结果
import spray.json._ import spray.json.DefaultJsonProtocol._ defined class Color defined module MyJsonProtocol import MyJsonProtocol._ json: spray.json.JsValue = ["CadetBlue",95,158,160] color: Color = Color@74ba1505
res0: Int = 160
这个序列化的Color实例作为一个JSONArray,紧凑但语义元素不明确。
另一种方式将JSON对象序列化的Color:
import spray.json._
import DefaultJsonProtocol._
class Color(val name: String, val red: Int, val green: Int, val blue: Int)
object MyJsonProtocol extends DefaultJsonProtocol { implicit object ColorJsonFormat extends RootJsonFormat[Color] { def write(c: Color) = JsObject( "name" -> JsString(c.name), "red" -> JsNumber(c.red), "green" -> JsNumber(c.green), "blue" -> JsNumber(c.blue) ) def read(value: JsValue) = { value.asJsObject.getFields("name", "red", "green", "blue") match { case Seq(JsString(name), JsNumber(red), JsNumber(green), JsNumber(blue)) => new Color(name, red.toInt, green.toInt, blue.toInt) case _ => throw new DeserializationException("Color expected") } } } }
这是一个更详细的定义和生成的JSON但传输到该领域语义JSON。注意这个方法仅仅使用月spray-json对case class
JsonFormat 和 RootJsonFormat比较
根据JSON规范并不是所有允许定义JSON值类型的根级别的一个JSON文档。