示例程序1
1 public class CatchWho { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 try { 4 try { 5 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); 6 } 7 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 8 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); 9 } 10 11 throw new ArithmeticException(); 12 } 13 catch(ArithmeticException e) { 14 System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); 15 } 16 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 17 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); 18 } 19 } 20 }
结果截图
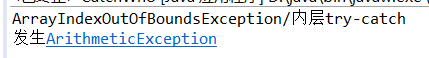
结果分析:程序运行到第五行时抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();该异常被第16行的catch语句捕获,
示例程序2
1 public class CatchWho2 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 try { 4 try { 5 throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(); 6 } 7 catch(ArithmeticException e) { 8 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch"); 9 } 10 throw new ArithmeticException(); 11 } 12 catch(ArithmeticException e) { 13 System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException"); 14 } 15 catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { 16 System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch"); 17 } 18 } 19 }
结果截图
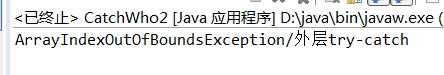
结果分析:程序运行到第5行时抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();该异常被第15行的catch语句捕获,
分析
1.异常捕获时可以有多个catch语句块,每个代码块捕获一种异常。
2.在某个try块后有两个不同的catch 块捕获两个相同类型的异常是语法错误。
3.使用catch语句,只能捕获Exception类及其子类的对象。因此,一个捕获Exception对象的catch语句块可以捕获所有“可捕获”的异常。
4.将catch(Exception e)放在别的catch块前面会使这些catch块都不执行,因此Java不会编译这个程序。