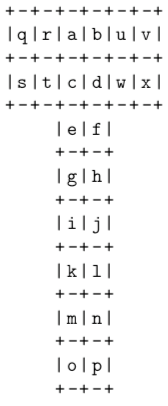- 1000ms
- 262144K
The Pocket Cube, also known as the Mini Cube or the Ice Cube, is the 2×2×22 imes 2 imes 22×2×2 equivalence of a Rubik’s Cube. The cube consists of 888 pieces, all corners.
Each piece is labeled by a three dimensional coordinate (h,k,l)(h, k, l)(h,k,l) where hhh, kkk, l∈0,1l in {0, 1}l∈0,1. Each of the six faces owns four small faces filled with a positive integer.
For each step, you can choose a certain face and turn the face ninety degrees clockwise or counterclockwise.
You should judge that if one can restore the pocket cube in one step. We say a pocket cube has been restored if each face owns four same integers.
Input
The first line of input contains one integer N(N≤30)N(N le 30)N(N≤30) which is the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line describes the top face of the pocket cube, which is the common 2×22 imes 22×2 face of pieceslabelled by (0,0,1)(0, 0, 1)(0,0,1), (0,1,1)(0, 1, 1)(0,1,1), (1,0,1)(1, 0, 1)(1,0,1), (1,1,1)(1, 1, 1)(1,1,1). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
The second line describes the front face, the common face of (1,0,1)(1,0,1)(1,0,1), (1,1,1)(1,1,1)(1,1,1), (1,0,0)(1,0,0)(1,0,0), (1,1,0)(1,1,0)(1,1,0). Four integers aregiven corresponding to the above pieces.
The third line describes the bottom face, the common face of (1,0,0)(1, 0, 0)(1,0,0), (1,1,0)(1, 1, 0)(1,1,0), (0,0,0)(0, 0, 0)(0,0,0), (0,1,0)(0, 1, 0)(0,1,0). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
The fourth line describes the back face, the common face of (0,0,0)(0,0,0)(0,0,0), (0,1,0)(0,1,0)(0,1,0), (0,0,1)(0,0,1)(0,0,1), (0,1,1)(0,1,1)(0,1,1). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
The fifth line describes the left face, the common face of (0,0,0)(0, 0, 0)(0,0,0), (0,0,1)(0, 0, 1)(0,0,1), (1,0,0)(1, 0, 0)(1,0,0), (1,0,1)(1, 0, 1)(1,0,1). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
The six line describes the right face, the common face of (0,1,1)(0, 1, 1)(0,1,1), (0,1,0)(0, 1, 0)(0,1,0), (1,1,1)(1, 1, 1)(1,1,1), (1,1,0)(1, 1, 0)(1,1,0). Four integers are given corresponding to the above pieces.
In other words, each test case contains 242424 integers aaa, bbb, ccc to xxx. You can flat the surface to get the surface development as follows.
Output
For each test case, output YES if can be restored in one step, otherwise output NO.
样例输入
4 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 5 5 5 5 4 4 4 4 1 4 1 4 2 1 2 1 3 2 3 2 4 3 4 3 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 1 3 1 3 2 4 2 4 3 1 3 1 4 2 4 2 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6
样例输出
YES YES YES NO
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int a[10][5]; 4 int main() 5 { 6 int n; 7 scanf("%d",&n); 8 while(n--) 9 { 10 for(int i=1; i<=6; i++) 11 { 12 for(int j=1; j<=4; j++) 13 { 14 scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); 15 } 16 } 17 int summ=0; 18 int sum=0; 19 for(int i=1; i<=6; i++) 20 { 21 if(a[i][1]==a[i][2] && a[i][2]==a[i][3] && a[i][3]==a[i][4]) 22 { 23 summ++; 24 } 25 } 26 if((a[1][1]==a[1][2] && a[1][2]==a[1][3] && a[1][3]==a[1][4]) && (a[3][1]==a[3][2] && a[3][2]==a[3][3] && a[3][3]==a[3][4])) 27 { 28 sum=1; 29 } 30 if((a[2][1]==a[2][2] && a[2][2]==a[2][3] && a[2][3]==a[2][4]) && (a[4][1]==a[4][2] && a[4][2]==a[4][3] && a[4][3]==a[4][4])) 31 { 32 sum=2; 33 } 34 if((a[5][1]==a[5][2] && a[5][2]==a[5][3] && a[5][3]==a[5][4]) && (a[6][1]==a[6][2] && a[6][2]==a[6][3] && a[6][3]==a[6][4])) 35 { 36 sum=3; 37 } 38 if(summ==6) 39 { 40 printf("YES "); 41 } 42 else if(sum==0) 43 { 44 printf("NO "); 45 } 46 else if(sum==1) 47 { 48 if(a[2][3]==a[2][4] &&a[2][3]==a[6][3] &&a[6][3]==a[6][1]&& 49 a[6][4]==a[6][2] &&a[6][4]==a[4][3] &&a[4][3]==a[4][4]&& 50 a[4][1]==a[4][2] &&a[4][1]==a[5][4] &&a[5][4]==a[5][2]&& 51 a[5][3]==a[5][1] &&a[5][3]==a[2][1] &&a[2][1]==a[2][2]) 52 printf("YES "); 53 else if(a[2][3]==a[2][4] &&a[2][3]==a[5][4] &&a[5][4]==a[5][2]&& 54 a[5][3]==a[5][1] &&a[5][3]==a[4][3] &&a[4][3]==a[4][4]&& 55 a[4][1]==a[4][2] &&a[4][1]==a[6][3] &&a[6][3]==a[6][1]&& 56 a[6][4]==a[6][2] &&a[6][4]==a[2][1] &&a[2][1]==a[2][2]) 57 printf("YES "); 58 else 59 printf("NO "); 60 } 61 else if(sum==2) 62 { 63 if(a[1][3]==a[1][4] &&a[1][3]==a[5][2] &&a[5][2]==a[5][1]&& 64 a[5][3]==a[5][4] &&a[5][3]==a[3][3] &&a[3][3]==a[3][4]&& 65 a[3][1]==a[3][2] &&a[3][1]==a[6][1] &&a[6][1]==a[6][2]&& 66 a[6][3]==a[6][4] &&a[6][4]==a[1][1] &&a[1][1]==a[1][2]) 67 printf("YES "); 68 else if(a[1][3]==a[1][4] &&a[1][3]==a[6][1] &&a[6][1]==a[6][2]&& 69 a[6][3]==a[6][4] &&a[6][4]==a[3][3] &&a[3][3]==a[3][4]&& 70 a[3][1]==a[3][2] &&a[3][1]==a[5][2] &&a[5][2]==a[5][1]&& 71 a[5][4]==a[5][3] &&a[5][3]==a[1][1] &&a[1][1]==a[1][2]) 72 printf("YES "); 73 else 74 printf("NO "); 75 76 } 77 else if(sum==3) 78 { 79 if(a[1][1]==a[1][3] &&a[1][3]==a[2][2] &&a[2][2]==a[2][4]&& 80 a[2][1]==a[2][3] &&a[2][1]==a[3][4] &&a[3][2]==a[3][4]&& 81 a[3][1]==a[3][3] &&a[3][3]==a[4][2] &&a[4][2]==a[4][4]&& 82 a[4][1]==a[4][3] &&a[4][3]==a[1][2] &&a[1][2]==a[1][4]) 83 printf("YES "); 84 else if(a[1][1]==a[1][3] &&a[1][3]==a[4][2] &&a[4][2]==a[4][4]&& 85 a[4][1]==a[4][3] &&a[4][1]==a[3][4] &&a[3][2]==a[3][4]&& 86 a[3][1]==a[3][3] &&a[3][3]==a[2][2] &&a[2][2]==a[2][4]&& 87 a[2][1]==a[2][3] &&a[2][3]==a[1][2] &&a[1][2]==a[1][4]) 88 printf("YES "); 89 else 90 printf("NO "); 91 } 92 else 93 { 94 printf("NO "); 95 } 96 } 97 return 0; 98 }
- 1000ms
- 262144K
Let’s talking about something of eating a pocky. Here is a Decorer Pocky, with colorful decorative stripes in the coating, of length LLL.
While the length of remaining pocky is longer than ddd, we perform the following procedure. We break the pocky at any point on it in an equal possibility and this will divide the remaining pocky into two parts. Take the left part and eat it. When it is not longer than ddd, we do not repeat this procedure.
Now we want to know the expected number of times we should repeat the procedure above. Round it to 666 decimal places behind the decimal point.
Input
The first line of input contains an integer NNN which is the number of test cases. Each of the NNN lines contains two float-numbers LLL and ddd respectively with at most 555 decimal places behind the decimal point where 1≤d,L≤1501 le d, L le 1501≤d,L≤150.
Output
For each test case, output the expected number of times rounded to 666 decimal places behind the decimal point in a line.
样例输入
6 1.0 1.0 2.0 1.0 4.0 1.0 8.0 1.0 16.0 1.0 7.00 3.00
样例输出
0.000000 1.693147 2.386294 3.079442 3.772589 1.847298
思路:微分。
代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 int n; 4 double l,d; 5 int main() 6 { 7 scanf("%d",&n); 8 while(n--) 9 { 10 scanf("%lf%lf",&l,&d); 11 if(l<=d) 12 { 13 printf("0.000000 "); 14 } 15 else 16 { 17 printf("%.6f ",1+log(l/d)); 18 } 19 } 20 return 0; 21 }