一、原理
1、图解
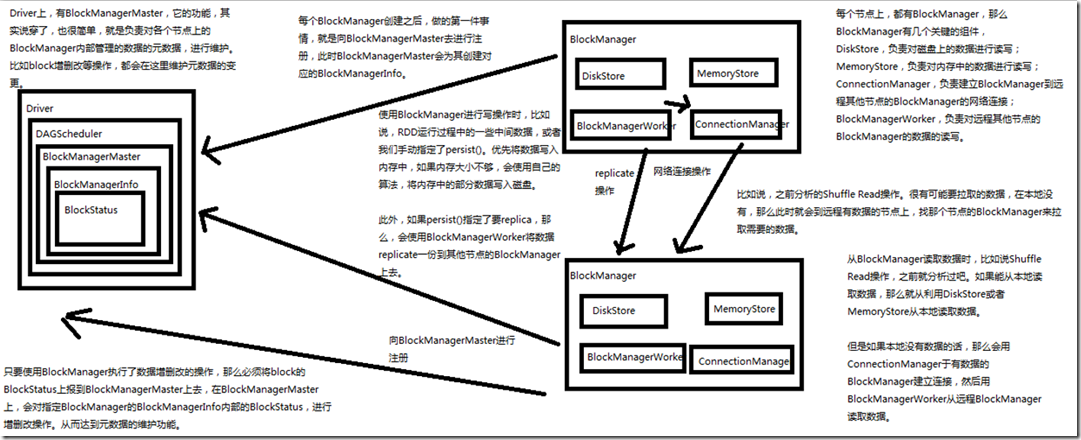
Driver上,有BlockManagerMaster,它的功能,就是负责对各个节点上的BlockManager内部管理的数据的元数据进行维护,
比如Block的增删改等操作,都会在这里维护元数据的变更;
每个节点上,都有BlockManager,BlockManager上有几个关键组件:
DiskStore,负责对磁盘上的数据进行读写;
MemoryStore,负责对内存中的数据进行读写;
ConnectionManager,负责建立BlockManager到远程其他节点的BlockManager的网络连接;
BlockTransferService,负责远程其他节点的BlockManager的数据的读写;
每个BlockManager创建之后,做的第一件事就是向BlockManagerMaster去进行注册,此时BlockManagerMaster会为其创建对应的BlockManagerInfo;
使用BlockManager进行写操作时,比如说,RDD运行过程中的一些中间数据,或者手动指定了persist(),优先将数据写入内存中,
内存大小不够用,会使用自己的算法,将内存中的部分数据写入磁盘;
此外,如果persist()指定了要replica,那么,会使用BlockTransferService将数据replicate一份到其他节点的BlockManager上去;
BlockTransferService会通过ConnectionManager连接其他BlockManager,BlockTransferService进行replicate操作;
从BlockManager读数据时,比如Shuffle Read操作,如果能从本地读取数据,那么利用DiskStore或者MemoryStore从本地读取数据,
如果本地没有数据的话,会用ConnectionManager与有数据的BlockManager建立连接,然后用BlockTransferService从远程BlockManager读取数据;
只要使用了BlockManager执行了数据增删改查的操作,那么必须将block的BlockStatus上报到BlockManagerMaster上去,在BlockManagerMaster上,
会对指定BlockManager的BlockManagerInfo内部的BlockStatus,进行增删改操作,从而达到元数据的维护功能;二、源码分析
1、BlockManager注册
首先看BlockManagerMasterActor,BlockManagerMasterActor就是负责维护各个executor的BlockManager的元数据,BlockManagerInfo,BlockStatus 首先看看BlockManagerMasterActor里面两个重要的map ###org.apache.spark.storage/BlockManagerMasterActor.scalal // Mapping from block manager id to the block manager's information. // 这个map,映射了block manager id 到 block manager的info // BlockManagerMaster要负责维护每个BlockManager的BlockManagerInfo private val blockManagerInfo = new mutable.HashMap[BlockManagerId, BlockManagerInfo] // Mapping from executor ID to block manager ID. // 映射了每个ExecutorId到BlockManagerId,也就是说,每个executor是与一个BlockManager相关联的 private val blockManagerIdByExecutor = new mutable.HashMap[String, BlockManagerId] ###org.apache.spark.storage/BlockManagerMasterActor.scalal /** * 注册BlockManager */ private def register(id: BlockManagerId, maxMemSize: Long, slaveActor: ActorRef) { val time = System.currentTimeMillis() // 首先判断本地HashMap中没有指定的BlockManagerId,说明从来没有注册过,才会往下走,去注册这个BlockManager if (!blockManagerInfo.contains(id)) { // 根据BlockManager对应的executorId找到对应的BlockManagerInfo // 这里其实是做一个安全判断,因为如果blockManagerInfo map里面没有BlockManagerId // 那么同步的blockManagerIdByExecutor map里,也必须没有BlockManager对应的executor对应的BlockManagerId // 所以这里要判断一下,如果blockManagerIdByExecutor map里有BlockManageId,那么做一下清理 blockManagerIdByExecutor.get(id.executorId) match { case Some(oldId) => // A block manager of the same executor already exists, so remove it (assumed dead) logError("Got two different block manager registrations on same executor - " + s" will replace old one $oldId with new one $id") // 从内存中,移除该executorId相关的BlockManagerInfo removeExecutor(id.executorId) case None => } logInfo("Registering block manager %s with %s RAM, %s".format( id.hostPort, Utils.bytesToString(maxMemSize), id)) // 往blockManagerIdByExecutor map中保存一份executorId到BlockManagerId的映射 blockManagerIdByExecutor(id.executorId) = id // 为BlockManagerId创建一根BlockManagerInfo,并往blockManagerInfo map中,保存一份BlockManagerId到BlockManagerInfo的映射 blockManagerInfo(id) = new BlockManagerInfo( id, System.currentTimeMillis(), maxMemSize, slaveActor) } listenerBus.post(SparkListenerBlockManagerAdded(time, id, maxMemSize)) } ###org.apache.spark.storage/BlockManagerMasterActor.scalal private def removeExecutor(execId: String) { logInfo("Trying to remove executor " + execId + " from BlockManagerMaster.") // 获取executorId对应的BlockManagerInfo,对其调用removeBlockManager方法 blockManagerIdByExecutor.get(execId).foreach(removeBlockManager) } ###org.apache.spark.storage/BlockManagerMasterActor.scalal private def removeBlockManager(blockManagerId: BlockManagerId) { // 尝试根据blockManagerId获取到它对应的BlockManagerInfo val info = blockManagerInfo(blockManagerId) // Remove the block manager from blockManagerIdByExecutor. // 从blockManagerIdByExecutor map中移除executorId对应的BlockManagerInfo blockManagerIdByExecutor -= blockManagerId.executorId // Remove it from blockManagerInfo and remove all the blocks. // 从blockManagerInfo也移除对应的BlockManagerInfo blockManagerInfo.remove(blockManagerId) // 遍历BlockManagerInfo内部所有的block的blockId val iterator = info.blocks.keySet.iterator while (iterator.hasNext) { // 清空BlockManagerInfo内部的block的BlockStatus信息 val blockId = iterator.next val locations = blockLocations.get(blockId) locations -= blockManagerId if (locations.size == 0) { blockLocations.remove(blockId) } } listenerBus.post(SparkListenerBlockManagerRemoved(System.currentTimeMillis(), blockManagerId)) logInfo(s"Removing block manager $blockManagerId") }
2、更新BlockInfo
更新BlockInfo,也就是说,每个BlockManager上,如果block发生了变化,那么都要发送updateBlockInfo请求来BlockManagerMaster这里。来进行BlockInfo的更新
/** * 更新BlockInfo,也就是说,每个BlockManager上,如果block发生了变化,那么都要发送updateBlockInfo请求来BlockManagerMaster这里。来进行BlockInfo的更新 */ private def updateBlockInfo( blockManagerId: BlockManagerId, blockId: BlockId, storageLevel: StorageLevel, memSize: Long, diskSize: Long, tachyonSize: Long): Boolean = { if (!blockManagerInfo.contains(blockManagerId)) { if (blockManagerId.isDriver && !isLocal) { // We intentionally do not register the master (except in local mode), // so we should not indicate failure. return true } else { return false } } if (blockId == null) { blockManagerInfo(blockManagerId).updateLastSeenMs() return true } // 调用BlockManager的blockManagerInfo的updateBlockInfo()方法,更新block信息 blockManagerInfo(blockManagerId).updateBlockInfo( blockId, storageLevel, memSize, diskSize, tachyonSize) // 每一个block可能会在多个BlockManager上面,因为如果将StorageLevel设置成带着_2的这种,那么就需要将block replicate一份,放到其他 // BlockManager上,blockLocations map其实保存了blockId对应的BlockManagerId的set集合,所以,这里会更新blockLocations中的信息, // 因为是用set存储BlockManagerId,因此自动就去重了 var locations: mutable.HashSet[BlockManagerId] = null if (blockLocations.containsKey(blockId)) { locations = blockLocations.get(blockId) } else { locations = new mutable.HashSet[BlockManagerId] blockLocations.put(blockId, locations) } if (storageLevel.isValid) { locations.add(blockManagerId) } else { locations.remove(blockManagerId) } // Remove the block from master tracking if it has been removed on all slaves. if (locations.size == 0) { blockLocations.remove(blockId) } true }
3、BlockManager初始化
BlockManager运行在每个节点上,包括Driver和Executor,都会有一份,主要提供了在本地或者远程存取数据的功能,支持内存、磁盘、堆外存储(Tychyon) ###org.apache.spark.storage/BlockManager.scala // 每个BlockManager,都会自己维护一个map,这里维护的blockInfo map,可以代表一个block,blockInfo最大的作用,就是用于 // 多线程并发访问同一个block的同步监视器 private val blockInfo = new TimeStampedHashMap[BlockId, BlockInfo] ###org.apache.spark.storage/BlockManager.scala def initialize(appId: String): Unit = { // 首先初始化,用于进行远程block数据传输的blockTransferService blockTransferService.init(this) shuffleClient.init(appId) // 为当前这个BlockManager创建一个唯一的BlockManagerId // 使用executorId(每个BlockManager都关联一个Executor),blockTransferService的hostname,blockTransferService的port // 所以,从BlockManagerId的初始化即可看出,一个BlockManager是通过一个节点上的Executor来唯一标识的 blockManagerId = BlockManagerId( executorId, blockTransferService.hostName, blockTransferService.port) shuffleServerId = if (externalShuffleServiceEnabled) { BlockManagerId(executorId, blockTransferService.hostName, externalShuffleServicePort) } else { blockManagerId } // 使用BlockManagerMasterActor的引用,进行BlockManager的注册,发送消息到BlockManagerMasterActor master.registerBlockManager(blockManagerId, maxMemory, slaveActor) // Register Executors' configuration with the local shuffle service, if one should exist. if (externalShuffleServiceEnabled && !blockManagerId.isDriver) { registerWithExternalShuffleServer() } }
4、BlockManager写数据
###org.apache.spark.storage/BlockManager.scala private def doPut( blockId: BlockId, data: BlockValues, level: StorageLevel, tellMaster: Boolean = true, effectiveStorageLevel: Option[StorageLevel] = None) : Seq[(BlockId, BlockStatus)] = { require(blockId != null, "BlockId is null") require(level != null && level.isValid, "StorageLevel is null or invalid") effectiveStorageLevel.foreach { level => require(level != null && level.isValid, "Effective StorageLevel is null or invalid") } // Return value val updatedBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, BlockStatus)] /* Remember the block's storage level so that we can correctly drop it to disk if it needs * to be dropped right after it got put into memory. Note, however, that other threads will * not be able to get() this block until we call markReady on its BlockInfo. */ // 为要写入的block,创建一个blockInfo,并将其放入blockinfo map中缓存起来 val putBlockInfo = { val tinfo = new BlockInfo(level, tellMaster) // Do atomically ! val oldBlockOpt = blockInfo.putIfAbsent(blockId, tinfo) if (oldBlockOpt.isDefined) { if (oldBlockOpt.get.waitForReady()) { logWarning(s"Block $blockId already exists on this machine; not re-adding it") return updatedBlocks } // TODO: So the block info exists - but previous attempt to load it (?) failed. // What do we do now ? Retry on it ? oldBlockOpt.get } else { tinfo } } val startTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis /* If we're storing values and we need to replicate the data, we'll want access to the values, * but because our put will read the whole iterator, there will be no values left. For the * case where the put serializes data, we'll remember the bytes, above; but for the case where * it doesn't, such as deserialized storage, let's rely on the put returning an Iterator. */ var valuesAfterPut: Iterator[Any] = null // Ditto for the bytes after the put var bytesAfterPut: ByteBuffer = null // Size of the block in bytes var size = 0L // The level we actually use to put the block val putLevel = effectiveStorageLevel.getOrElse(level) // If we're storing bytes, then initiate the replication before storing them locally. // This is faster as data is already serialized and ready to send. val replicationFuture = data match { case b: ByteBufferValues if putLevel.replication > 1 => // Duplicate doesn't copy the bytes, but just creates a wrapper val bufferView = b.buffer.duplicate() Future { replicate(blockId, bufferView, putLevel) } case _ => null } // 尝试对BlockInfo加锁,进行多线程并发访问同步 putBlockInfo.synchronized { logTrace("Put for block %s took %s to get into synchronized block" .format(blockId, Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTimeMs))) var marked = false try { // returnValues - Whether to return the values put // blockStore - The type of storage to put these values into // 首先根据持久化级别,选择一种BlockStore val (returnValues, blockStore: BlockStore) = { if (putLevel.useMemory) { // Put it in memory first, even if it also has useDisk set to true; // We will drop it to disk later if the memory store can't hold it. (true, memoryStore) } else if (putLevel.useOffHeap) { // Use tachyon for off-heap storage (false, tachyonStore) } else if (putLevel.useDisk) { // Don't get back the bytes from put unless we replicate them (putLevel.replication > 1, diskStore) } else { assert(putLevel == StorageLevel.NONE) throw new BlockException( blockId, s"Attempted to put block $blockId without specifying storage level!") } } // Actually put the values // 根据选择的BlockStore,然后根据数据的类型,将数据放入store中 val result = data match { case IteratorValues(iterator) => blockStore.putIterator(blockId, iterator, putLevel, returnValues) case ArrayValues(array) => blockStore.putArray(blockId, array, putLevel, returnValues) case ByteBufferValues(bytes) => bytes.rewind() blockStore.putBytes(blockId, bytes, putLevel) } size = result.size result.data match { case Left (newIterator) if putLevel.useMemory => valuesAfterPut = newIterator case Right (newBytes) => bytesAfterPut = newBytes case _ => } // Keep track of which blocks are dropped from memory if (putLevel.useMemory) { result.droppedBlocks.foreach { updatedBlocks += _ } } // 获取到一个Block对应的BlockStatus val putBlockStatus = getCurrentBlockStatus(blockId, putBlockInfo) if (putBlockStatus.storageLevel != StorageLevel.NONE) { // Now that the block is in either the memory, tachyon, or disk store, // let other threads read it, and tell the master about it. marked = true putBlockInfo.markReady(size) if (tellMaster) { // 调用reportBlockStatus()方法,将新写入的block数据,发送到BlockManagerMaster,以便于进行block元数据的同步和维护 reportBlockStatus(blockId, putBlockInfo, putBlockStatus) } updatedBlocks += ((blockId, putBlockStatus)) } } finally { // If we failed in putting the block to memory/disk, notify other possible readers // that it has failed, and then remove it from the block info map. if (!marked) { // Note that the remove must happen before markFailure otherwise another thread // could've inserted a new BlockInfo before we remove it. blockInfo.remove(blockId) putBlockInfo.markFailure() logWarning(s"Putting block $blockId failed") } } } logDebug("Put block %s locally took %s".format(blockId, Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTimeMs))) // Either we're storing bytes and we asynchronously started replication, or we're storing // values and need to serialize and replicate them now: // 如果持久化是定义了_2这种后缀,说明需要对block进行replica,然后传输到其他节点上 if (putLevel.replication > 1) { data match { case ByteBufferValues(bytes) => if (replicationFuture != null) { Await.ready(replicationFuture, Duration.Inf) } case _ => val remoteStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis // Serialize the block if not already done if (bytesAfterPut == null) { if (valuesAfterPut == null) { throw new SparkException( "Underlying put returned neither an Iterator nor bytes! This shouldn't happen.") } bytesAfterPut = dataSerialize(blockId, valuesAfterPut) } // 调用replicate()方法进行复制操作 replicate(blockId, bytesAfterPut, putLevel) logDebug("Put block %s remotely took %s" .format(blockId, Utils.getUsedTimeMs(remoteStartTime))) } } BlockManager.dispose(bytesAfterPut) if (putLevel.replication > 1) { logDebug("Putting block %s with replication took %s" .format(blockId, Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTimeMs))) } else { logDebug("Putting block %s without replication took %s" .format(blockId, Utils.getUsedTimeMs(startTimeMs))) } updatedBlocks } ###org.apache.spark.storage/DiskStore.scala override def putBytes(blockId: BlockId, _bytes: ByteBuffer, level: StorageLevel): PutResult = { // So that we do not modify the input offsets ! // duplicate does not copy buffer, so inexpensive val bytes = _bytes.duplicate() logDebug(s"Attempting to put block $blockId") val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis val file = diskManager.getFile(blockId) // 使用Java NIO将数据写入磁盘文件 val channel = new FileOutputStream(file).getChannel while (bytes.remaining > 0) { channel.write(bytes) } channel.close() val finishTime = System.currentTimeMillis logDebug("Block %s stored as %s file on disk in %d ms".format( file.getName, Utils.bytesToString(bytes.limit), finishTime - startTime)) PutResult(bytes.limit(), Right(bytes.duplicate())) } ###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala // MemoryStore中维护的entries map 其实就是真正存放每个block的数据 // 每个Block在内存中的数据,用MemoryEntry代表 private val entries = new LinkedHashMap[BlockId, MemoryEntry](32, 0.75f, true) ###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala override def putBytes(blockId: BlockId, _bytes: ByteBuffer, level: StorageLevel): PutResult = { // Work on a duplicate - since the original input might be used elsewhere. val bytes = _bytes.duplicate() bytes.rewind() if (level.deserialized) { val values = blockManager.dataDeserialize(blockId, bytes) putIterator(blockId, values, level, returnValues = true) } else { val putAttempt = tryToPut(blockId, bytes, bytes.limit, deserialized = false) PutResult(bytes.limit(), Right(bytes.duplicate()), putAttempt.droppedBlocks) } } ###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala override def putIterator( blockId: BlockId, values: Iterator[Any], level: StorageLevel, returnValues: Boolean): PutResult = { putIterator(blockId, values, level, returnValues, allowPersistToDisk = true) } ###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala private[storage] def putIterator( blockId: BlockId, values: Iterator[Any], level: StorageLevel, returnValues: Boolean, allowPersistToDisk: Boolean): PutResult = { val droppedBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, BlockStatus)] val unrolledValues = unrollSafely(blockId, values, droppedBlocks) unrolledValues match { case Left(arrayValues) => // Values are fully unrolled in memory, so store them as an array val res = putArray(blockId, arrayValues, level, returnValues) droppedBlocks ++= res.droppedBlocks PutResult(res.size, res.data, droppedBlocks) case Right(iteratorValues) => // Not enough space to unroll this block; drop to disk if applicable if (level.useDisk && allowPersistToDisk) { logWarning(s"Persisting block $blockId to disk instead.") val res = blockManager.diskStore.putIterator(blockId, iteratorValues, level, returnValues) PutResult(res.size, res.data, droppedBlocks) } else { PutResult(0, Left(iteratorValues), droppedBlocks) } } } ###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala override def putArray( blockId: BlockId, values: Array[Any], level: StorageLevel, returnValues: Boolean): PutResult = { if (level.deserialized) { val sizeEstimate = SizeEstimator.estimate(values.asInstanceOf[AnyRef]) val putAttempt = tryToPut(blockId, values, sizeEstimate, deserialized = true) PutResult(sizeEstimate, Left(values.iterator), putAttempt.droppedBlocks) } else { val bytes = blockManager.dataSerialize(blockId, values.iterator) val putAttempt = tryToPut(blockId, bytes, bytes.limit, deserialized = false) PutResult(bytes.limit(), Right(bytes.duplicate()), putAttempt.droppedBlocks) } } ###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala tryToPut()方法,优先放入内存,不行的话,尝试移除部分旧数据,再将block存入,真正存数据的方法; private def tryToPut( blockId: BlockId, value: Any, size: Long, deserialized: Boolean): ResultWithDroppedBlocks = { /* TODO: Its possible to optimize the locking by locking entries only when selecting blocks * to be dropped. Once the to-be-dropped blocks have been selected, and lock on entries has * been released, it must be ensured that those to-be-dropped blocks are not double counted * for freeing up more space for another block that needs to be put. Only then the actually * dropping of blocks (and writing to disk if necessary) can proceed in parallel. */ var putSuccess = false val droppedBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, BlockStatus)] // 进行多线程并发同步,这里必须进行多线程并发同步,因为可能你刚判断内存足够,但是其他线程就放入了数据,然后你往内存中放数据,直接OOM内存溢出 accountingLock.synchronized { // 调用ensureFreeSpace()方法,判断内存是否够用,如果不够用,此时会将部分数据用dropFromMemory()方法尝试写入磁盘,但是如果持久化级别不支持磁盘,那么数据丢失 val freeSpaceResult = ensureFreeSpace(blockId, size) val enoughFreeSpace = freeSpaceResult.success droppedBlocks ++= freeSpaceResult.droppedBlocks // 将数据写入内存的时候,首先调用enoughFreeSpace()方法,判断内存是否足够放入数据 if (enoughFreeSpace) { // 给数据创建一份MemoryEntry val entry = new MemoryEntry(value, size, deserialized) entries.synchronized { // 将数据放入内存的entries中 entries.put(blockId, entry) currentMemory += size } val valuesOrBytes = if (deserialized) "values" else "bytes" logInfo("Block %s stored as %s in memory (estimated size %s, free %s)".format( blockId, valuesOrBytes, Utils.bytesToString(size), Utils.bytesToString(freeMemory))) putSuccess = true } else { // Tell the block manager that we couldn't put it in memory so that it can drop it to // disk if the block allows disk storage. val data = if (deserialized) { Left(value.asInstanceOf[Array[Any]]) } else { Right(value.asInstanceOf[ByteBuffer].duplicate()) } val droppedBlockStatus = blockManager.dropFromMemory(blockId, data) droppedBlockStatus.foreach { status => droppedBlocks += ((blockId, status)) } } } ResultWithDroppedBlocks(putSuccess, droppedBlocks) } ###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala private def ensureFreeSpace( blockIdToAdd: BlockId, space: Long): ResultWithDroppedBlocks = { logInfo(s"ensureFreeSpace($space) called with curMem=$currentMemory, maxMem=$maxMemory") val droppedBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[(BlockId, BlockStatus)] if (space > maxMemory) { logInfo(s"Will not store $blockIdToAdd as it is larger than our memory limit") return ResultWithDroppedBlocks(success = false, droppedBlocks) } // Take into account the amount of memory currently occupied by unrolling blocks val actualFreeMemory = freeMemory - currentUnrollMemory // 如果当前内存不足够将这个block放入的话 if (actualFreeMemory < space) { val rddToAdd = getRddId(blockIdToAdd) val selectedBlocks = new ArrayBuffer[BlockId] var selectedMemory = 0L // This is synchronized to ensure that the set of entries is not changed // (because of getValue or getBytes) while traversing the iterator, as that // can lead to exceptions. // 同步entries entries.synchronized { val iterator = entries.entrySet().iterator() // 尝试从entries中,移除一部分数据 while (actualFreeMemory + selectedMemory < space && iterator.hasNext) { val pair = iterator.next() val blockId = pair.getKey if (rddToAdd.isEmpty || rddToAdd != getRddId(blockId)) { selectedBlocks += blockId selectedMemory += pair.getValue.size } } } // 判断,如果移除一部分数据,就可以存放新的block了 if (actualFreeMemory + selectedMemory >= space) { logInfo(s"${selectedBlocks.size} blocks selected for dropping") // 将之前选择要移除的block数据,遍历 for (blockId <- selectedBlocks) { val entry = entries.synchronized { entries.get(blockId) } // This should never be null as only one thread should be dropping // blocks and removing entries. However the check is still here for // future safety. if (entry != null) { val data = if (entry.deserialized) { Left(entry.value.asInstanceOf[Array[Any]]) } else { Right(entry.value.asInstanceOf[ByteBuffer].duplicate()) } // 调用dropFromMemory()方法,尝试将数据写入磁盘,但是如果block的持久化级别没有写入磁盘,那么这个数据就彻底丢了 val droppedBlockStatus = blockManager.dropFromMemory(blockId, data) droppedBlockStatus.foreach { status => droppedBlocks += ((blockId, status)) } } } return ResultWithDroppedBlocks(success = true, droppedBlocks) } else { logInfo(s"Will not store $blockIdToAdd as it would require dropping another block " + "from the same RDD") return ResultWithDroppedBlocks(success = false, droppedBlocks) } } ResultWithDroppedBlocks(success = true, droppedBlocks) }
6、BlockManager读数据
###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala /** * 从本地获取数据 */ private def doGetLocal(blockId: BlockId, asBlockResult: Boolean): Option[Any] = { // 尝试获取block对应的blockInfo的锁 val info = blockInfo.get(blockId).orNull if (info != null) { // 对所有的blockInfo,都会进行多线程并发访问的同步操作,所以BlockInfo,相当于是对一个Block,用于作为多线程并发访问的同步监视器 info.synchronized { // Double check to make sure the block is still there. There is a small chance that the // block has been removed by removeBlock (which also synchronizes on the blockInfo object). // Note that this only checks metadata tracking. If user intentionally deleted the block // on disk or from off heap storage without using removeBlock, this conditional check will // still pass but eventually we will get an exception because we can't find the block. if (blockInfo.get(blockId).isEmpty) { logWarning(s"Block $blockId had been removed") return None } // If another thread is writing the block, wait for it to become ready. // 如果其他线程在操作这个block,那么其实会卡住,等待,去获取BlockInfo的排他锁,如果始终没有获取到,返回false,就直接返回 if (!info.waitForReady()) { // If we get here, the block write failed. logWarning(s"Block $blockId was marked as failure.") return None } val level = info.level logDebug(s"Level for block $blockId is $level") // Look for the block in memory // 判断,如果持久化级别使用了内存,比如MEMORY_ONLY,MEMORY_AND_DISK,MEMORY_ONLY_SER,MEMORY_AND_DSK_SER等 // 尝试从MemoryStore中获取数据 if (level.useMemory) { logDebug(s"Getting block $blockId from memory") val result = if (asBlockResult) { memoryStore.getValues(blockId).map(new BlockResult(_, DataReadMethod.Memory, info.size)) } else { memoryStore.getBytes(blockId) } result match { case Some(values) => return result case None => logDebug(s"Block $blockId not found in memory") } } // Look for the block in Tachyon if (level.useOffHeap) { logDebug(s"Getting block $blockId from tachyon") if (tachyonStore.contains(blockId)) { tachyonStore.getBytes(blockId) match { case Some(bytes) => if (!asBlockResult) { return Some(bytes) } else { return Some(new BlockResult( dataDeserialize(blockId, bytes), DataReadMethod.Memory, info.size)) } case None => logDebug(s"Block $blockId not found in tachyon") } } } // Look for block on disk, potentially storing it back in memory if required // 判断,如果持久化级别使用了磁盘 if (level.useDisk) { logDebug(s"Getting block $blockId from disk") val bytes: ByteBuffer = diskStore.getBytes(blockId) match { case Some(b) => b case None => throw new BlockException( blockId, s"Block $blockId not found on disk, though it should be") } assert(0 == bytes.position()) if (!level.useMemory) { // If the block shouldn't be stored in memory, we can just return it if (asBlockResult) { return Some(new BlockResult(dataDeserialize(blockId, bytes), DataReadMethod.Disk, info.size)) } else { return Some(bytes) } } else { // Otherwise, we also have to store something in the memory store if (!level.deserialized || !asBlockResult) { /* We'll store the bytes in memory if the block's storage level includes * "memory serialized", or if it should be cached as objects in memory * but we only requested its serialized bytes. */ val copyForMemory = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.limit) copyForMemory.put(bytes) // 如果使用了Disk级别,也使用了Memory级别,那么从disk读取出来之后,其实会尝试将其放入MemoryStore中,也就是缓存到内存中 memoryStore.putBytes(blockId, copyForMemory, level) bytes.rewind() } if (!asBlockResult) { return Some(bytes) } else { val values = dataDeserialize(blockId, bytes) if (level.deserialized) { // Cache the values before returning them val putResult = memoryStore.putIterator( blockId, values, level, returnValues = true, allowPersistToDisk = false) // The put may or may not have succeeded, depending on whether there was enough // space to unroll the block. Either way, the put here should return an iterator. putResult.data match { case Left(it) => return Some(new BlockResult(it, DataReadMethod.Disk, info.size)) case _ => // This only happens if we dropped the values back to disk (which is never) throw new SparkException("Memory store did not return an iterator!") } } else { return Some(new BlockResult(values, DataReadMethod.Disk, info.size)) } } } } } } else { logDebug(s"Block $blockId not registered locally") } None } ###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala private def doGetRemote(blockId: BlockId, asBlockResult: Boolean): Option[Any] = { require(blockId != null, "BlockId is null") // 首先从BlockManagerMaster上,获取每个blockId对应的BlockManager的信息,然后会随机打乱 val locations = Random.shuffle(master.getLocations(blockId)) // 遍历每个BlockManager for (loc <- locations) { logDebug(s"Getting remote block $blockId from $loc") // 使用blockTransferService进行,异步的远程网络获取,将block数据传输过来 // 连接的时候,使用BlockManager的唯一标识,就是host,port,executorId val data = blockTransferService.fetchBlockSync( loc.host, loc.port, loc.executorId, blockId.toString).nioByteBuffer() if (data != null) { if (asBlockResult) { return Some(new BlockResult( dataDeserialize(blockId, data), DataReadMethod.Network, data.limit())) } else { return Some(data) } } logDebug(s"The value of block $blockId is null") } logDebug(s"Block $blockId not found") None } ###org.apache.spark.storage/DiskStore.scala private def getBytes(file: File, offset: Long, length: Long): Option[ByteBuffer] = { // 底层使用的是java的nio进行文件的读写操作 val channel = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r").getChannel try { // For small files, directly read rather than memory map if (length < minMemoryMapBytes) { val buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(length.toInt) channel.position(offset) while (buf.remaining() != 0) { if (channel.read(buf) == -1) { throw new IOException("Reached EOF before filling buffer " + s"offset=$offset file=${file.getAbsolutePath} buf.remaining=${buf.remaining}") } } buf.flip() Some(buf) } else { Some(channel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, offset, length)) } } finally { channel.close() } ###org.apache.spark.storage/MemoryStore.scala MemoryStore的getBytes()和getValues()方法 override def getBytes(blockId: BlockId): Option[ByteBuffer] = { // entries也是多线程并发访问同步的 val entry = entries.synchronized { // 尝试从内存中获取block数据 entries.get(blockId) } if (entry == null) { // 如果没有获取到 就返回None None } else if (entry.deserialized) { // 如果读取到了非序列化的数据,调用BlockManager序列化方法,将数据序列化后返回 Some(blockManager.dataSerialize(blockId, entry.value.asInstanceOf[Array[Any]].iterator)) } else { // 否则,直接返回数据 Some(entry.value.asInstanceOf[ByteBuffer].duplicate()) // Doesn't actually copy the data } } override def getValues(blockId: BlockId): Option[Iterator[Any]] = { val entry = entries.synchronized { entries.get(blockId) } if (entry == null) { None } else if (entry.deserialized) { // 如果非序列化,直接返回 Some(entry.value.asInstanceOf[Array[Any]].iterator) } else { // 如果序列化了,那么用blockManager进行反序列化返回 val buffer = entry.value.asInstanceOf[ByteBuffer].duplicate() // Doesn't actually copy data Some(blockManager.dataDeserialize(blockId, buffer)) } }