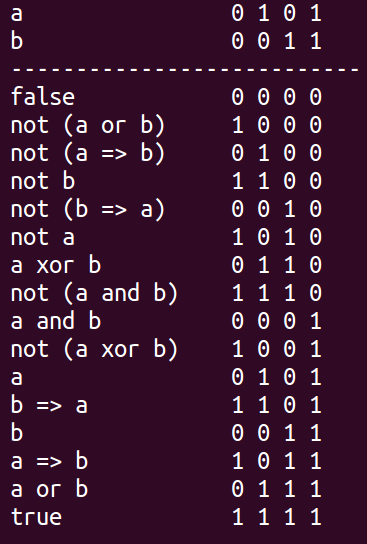
This is only ok in Binary Logic.
有17个最小联结词组(如果认为包含true和false的不是最小联结词组,那么最小联结词组只有11个)
not(or) |
not(=>) |not |
not(and) |
not |and |
not(=>) |not(xor) |
false |and |not(xor) |
xor |and |not(xor) |
false |=> |
not(=>) |=> |
not |=> |
xor |=> |
not |or |
false |not(xor) |or |
xor |not(xor) |or |
not(=>) |true |
xor |and |true |
xor |or |true |
整理一下
not(or)
not(and)
not,or
not,and
not,=>
not,not(=>)
not(=>),=>
not(=>),true
not(=>),not(xor)
=>,false
=>,xor
xor,and,not(xor)
xor,or,not(xor)
xor,and,true
xor,or,true
not(xor),and,false
not(xor),or,false
xor功能比false更丰富,因为false = a xor a,所以一切出现false的地方都可以用xor取代
I got this result by a violent method:If you run this program ,you can see more things.
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1 << 16;//There are 65536 probability.
bool a[16][4]; //A 10 B 12
const char *desc[16] = { "false", "not (a or b)",
"not (a => b)", "not b",
"not (b => a)", "not a",
"a xor b", "not (a and b)",
"a and b", "not (a xor b)",
"a", "b => a",
"b", "a => b",
"a or b", "true" };
const char*desc_simple[16] = { "false", "not(or)", "not(=>)", "not", "not(=>)", "not", "xor", "not(and)", "and", "not(xor)", "a", "=>", "b", "=>", "or", "true" };
/*
上表中,只有条件运算符和非条件运算符是不满足交换律,但是它们是等价的
也就是说:2,4等价,11,13等价,3,5等价
*/
int eq[] = { 2, 4, 11, 13, 3, 5 }, eq_size = 3;
void init(){//初始化16个逻辑词
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++){
int x = i;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++){
a[i][j] = x & 1;
x >>= 1;
}
}
}
void show(int n){
printf(" %-16s", desc[n]);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)printf("%2d", a[n][i]);
puts("");
}
void table(){
show(10), show(12);//10和12代表着原始的a和b
puts(" ---------------------------");
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)show(i);
}
int ans[N], ai = 0;//存储全部的答案
int book[N][16][3];//对于N中逻辑词组,16个逻辑词来源于三个人:a,b,操作
//判断集合set是否是完备的逻辑词组
bool ok(int n){
int temp = n;
n |= (1 << 10) | (1 << 12);
again:
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
if (n&(1 << i))
for (int j = 0; j < 16; j++)
if (n&(1 << j))
for (int k = 0; k < 16; k++)
if (n&(1 << k)){
//i,j分别操作数,k表示操作符,也就是k表示运算法则
int t = 0;//t表示运算结果
for (int l = 0; l < 4; l++)//将四位分别进行运算
t |= (a[k][a[i][l] + a[j][l] * 2] << l);
if ((n&(1 << t)) == 0){
n |= (1 << t);
book[temp][t][0] = i, book[temp][t][1] = j, book[temp][t][2] = k;
goto again;
}
}
return n == N - 1;
}
void print(bool detail){
for (int i = 0; i < ai; i++){
int n = ans[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 16; j++){
if (n&(1 << j)){
const char*des = detail ? desc[j] : desc_simple[j];
printf("%-15s|", des);
}
}
puts("");
if (detail){
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++){
if ((n&(1 << i)) || i == 10 || i == 12)continue;
printf(" %-15s = %-15s [%-15s] %-15s
", desc[i], desc[book[n][i][0]], desc[book[n][i][2]], desc[book[n][i][1]]);
}
puts("");
}
}
}
//根据eq数组去掉等价的元素
void simple(){
for (int i = 0; i < ai; i++){
int n = ans[i];
for (int j = 0; j < eq_size; j++){
if (n&(1 << eq[j << 1 | 1])){
n &= ~(1 << eq[j << 1 | 1]);
n |= (1 << eq[j << 1]);
}
}
ans[i] = n;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
if (ans[i] == ans[j])
ans[i] = -1;
}
int ind = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ai; i++)
if (ans[i] != -1)ans[ind++] = ans[i];
ai = ind;
}
bool visited(int x){
for (int i = 0; i < ai; i++)
if ((ans[i] & x) == ans[i])
return true;
return false;
}
int main(){
init();
table();//打印表,说清逻辑运算及其对应的编码
memset(book, -1, sizeof(book));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++){
//先判断i的某个子集是否已经是最小逻辑词组,如果是,则i必然不是最小逻辑词组
if (visited(i))continue;
if (ok(i)) ans[ai++] = i;
}
simple();
print(false);
return 0;
}