For an undirected graph with tree characteristics, we can choose any node as the root. The result graph is then a rooted tree. Among all possible rooted trees, those with minimum height are called minimum height trees (MHTs). Given such a graph, write a function to find all the MHTs and return a list of their root labels.
Format
The graph contains n nodes which are labeled from 0 to n - 1. You will be given the number n and a list of undirected edges (each edge is a pair of labels).
You can assume that no duplicate edges will appear in edges. Since all edges are undirected, [0, 1] is the same as [1, 0] and thus will not appear together in edges.
Example 1 :
Input:n = 4,edges = [[1, 0], [1, 2], [1, 3]]0 | 1 / 2 3 Output:[1]
Example 2 :
Input:n = 6,edges = [[0, 3], [1, 3], [2, 3], [4, 3], [5, 4]]0 1 2 | / 3 | 4 | 5 Output:[3, 4]
Note:
- According to the definition of tree on Wikipedia: “a tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. In other words, any connected graph without simple cycles is a tree.”
- The height of a rooted tree is the number of edges on the longest downward path between the root and a leaf.
class Solution { public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges) { if(n == 1) return Collections.singletonList(0); List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[n]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) g[i] = new ArrayList(); for(int[] e: edges){ g[e[0]].add(e[1]); g[e[1]].add(e[0]); } List<Integer> leaves = new ArrayList(); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ if(g[i].size() == 1) leaves.add(i); } while(n > 2){ n -= leaves.size(); List<Integer> newleaves = new ArrayList(); for(int i: leaves){ int j = g[i].get(0); g[j].remove((Integer) i); if(g[j].size() == 1) newleaves.add(j); } leaves = newleaves; } return leaves; } }
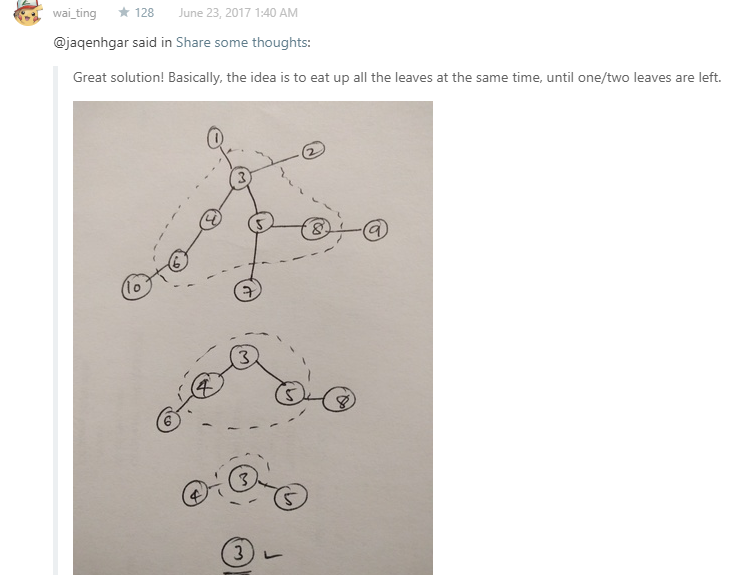
每次把leaves(只有1个邻居)踢掉,最后剩下1或2个就是答案。
具体做法是先用arraylist数组存图,然后把leaves存起来,
进入循环后通过前一个leaves数组遍历找到他们相连的其他潜在leaves,通过remove除掉前一个leaves,判断是否成为了新的leaves并存到newleaves中,完事leaves = newleaves
为什么是n > 2呢?
因为是图,不存在circle,那说明最多有两个点能当根(偶数n),一个点当根(奇数n)。或者想想n个点,只有它的根在中点时,height才能minimum
class Solution { public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges) { if(n == 1) return Collections.singletonList(0); Set<Integer>[] g = new HashSet[n]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) g[i] = new HashSet(); for(int[] e: edges){ g[e[0]].add(e[1]); g[e[1]].add(e[0]); } List<Integer> leaves = new ArrayList(); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ if(g[i].size() == 1) leaves.add(i); } while(n > 2){ n -= leaves.size(); List<Integer> newleaves = new ArrayList(); for(int i: leaves){ int j = g[i].iterator().next(); g[j].remove(i); if(g[j].size() == 1) newleaves.add(j); } leaves = newleaves; } return leaves; } }
将arraylist替换成hashset能提高运算速度