Equations are given in the format A / B = k, where A and B are variables represented as strings, and k is a real number (floating point number). Given some queries, return the answers. If the answer does not exist, return -1.0.
Example:
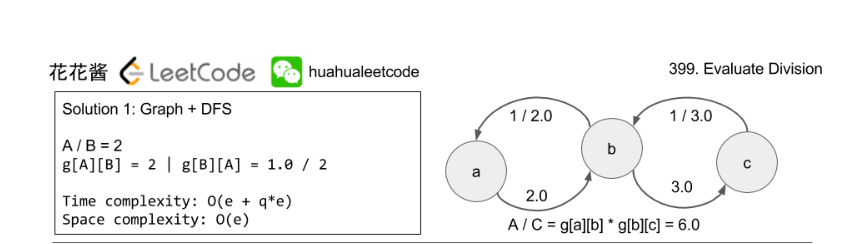
Given a / b = 2.0, b / c = 3.0.
queries are: a / c = ?, b / a = ?, a / e = ?, a / a = ?, x / x = ? .
return [6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0 ].
The input is: vector<pair<string, string>> equations, vector<double>& values, vector<pair<string, string>> queries , where equations.size() == values.size(), and the values are positive. This represents the equations. Return vector<double>.
According to the example above:
equations = [ ["a", "b"], ["b", "c"] ], values = [2.0, 3.0], queries = [ ["a", "c"], ["b", "a"], ["a", "e"], ["a", "a"], ["x", "x"] ].
class Solution { Map<String, Map<String, Double>> g = new HashMap(); public double[] calcEquation(List<List<String>> equations, double[] values, List<List<String>> queries) { for(int i = 0; i < equations.size(); i++){ String fir = equations.get(i).get(0); String sec = equations.get(i).get(1); double val = values[i]; g.putIfAbsent(fir, new HashMap()); g.putIfAbsent(sec, new HashMap()); g.get(fir).putIfAbsent(sec, val); g.get(sec).putIfAbsent(fir, 1.0/val); //map.get(fir).put(sec, val); } double[] ans = new double[queries.size()]; for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); ++i) { String x = queries.get(i).get(0); String y = queries.get(i).get(1); if (!g.containsKey(x) || !g.containsKey(y)) { ans[i] = -1.0; } else { ans[i] = divide(x, y, new HashSet<String>()); } } return ans; //return new double[]{}; } private double divide(String x, String y, Set<String> visited) { if (x.equals(y)) return 1.0; visited.add(x); if (!g.containsKey(x)) return -1.0; for (String n : g.get(x).keySet()) { if (visited.contains(n)) continue; visited.add(n); double d = divide(n, y, visited); if (d > 0) return d * g.get(x).get(n); } return -1.0; } }
1. 阳间方法,graph + dfs
http://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/graph/leetcode-399-evaluate-division/花哥讲解
看着代码长其实挺好理解,先用Map<String, Map<String, Double>>来表示有向图,注意权重值不同,每条路径唯一
然后iterate queries,如果graph中没有这个key说明要返回-1,否则进入dfs中,
dfs参数是分子,分母,visited(确保不进入死循环)
如果这一步了找不到分子了就直接返回-1,找到x的话遍历它的邻居们n,如果邻居能牵线搭桥到y,说明此路通,否则此路不通
2. 阴间方法,union find
挖个坑