Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.
Example:
Given a binary tree
1
/
2 3
/
4 5
Return 3, which is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
Note: The length of path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
class Solution { public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { int[] res = new int[1]; help(root, res); return res[0]; } public int help(TreeNode root, int[] res) { if(root == null) return 0; int lh = help(root.left, res); int rh = help(root.right, res); res[0] = Math.max(res[0], lh + rh); return Math.max(lh, rh) + 1; } }
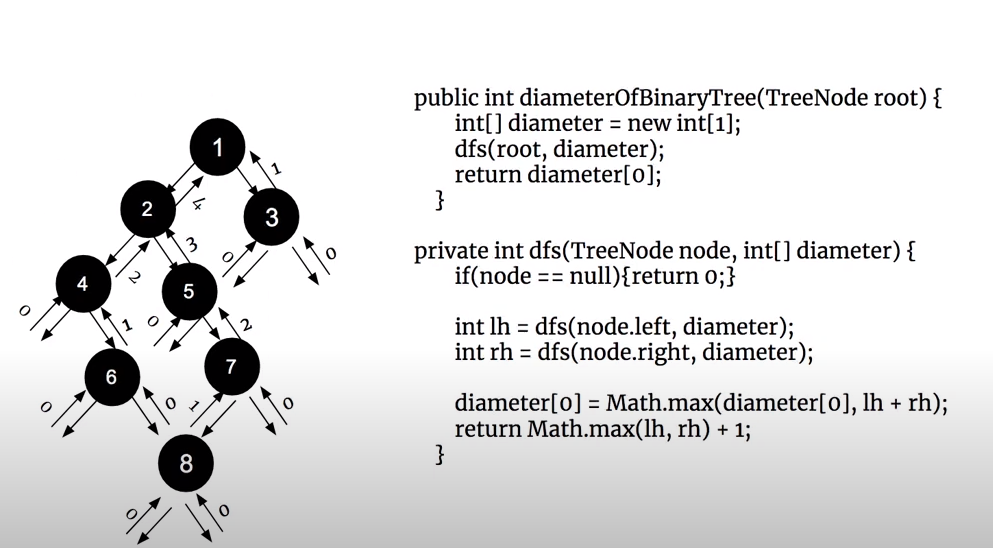
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3vZV-6qPDmE 看了一姐的视频恍然大悟。
res[0], 以这个点为root的左子树路径长度+右子树路径长度
return: 如果父亲节点往当前节点走,当前节点最多能提供的路径长度。也就是说,返回当前节点的左子树和右子树路径长度中大的一方(因为要最长,所以不能返回lh+rh而只能返回一边),然后+1,这个+1是指当前节点走到它的父亲节点的长度是1
整体来说,每个节点遍历完左右子树后,都会尝试更新res by comparing current res and (lh + rh), and return a number represent the longest path the left subtree or rightsubtree can give plus it goes back to root.