1、准备工作
首先准备两台服务器,这里我们准备了两台虚拟机,ip 地址分别为 192.168.32.128 和 192.168.32.129,以此模拟两台服务器。
在这两台服务器上分别启动了 tomcat 服务器, 并且都在 tomcat 的 webapps 目录下新建 mySystem 目录,在该目录下新建 a.html,以此模拟在多台服务器上都部署了同一个项目。不过我们在不同服务器上的 a.html 文件的显示内容上做了一些不同修改,以便做负载均衡时能区分出来是不是请求发送到了不同服务器上(当然,实际生产时多台服务器上的资源应该是保持一致的)。
在 192.168.32.128 服务器上启动 Nginx,并在该服务器上的 Nginx 做负载均衡。
Nginx的安装可参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wenxuehai/p/14966724.html#autoid-h2-2-3-0
在Linux上安装启动tomcat可参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/wenxuehai/p/14974657.html#_label0
2、配置负载均衡
我们需要实现的效果如下:
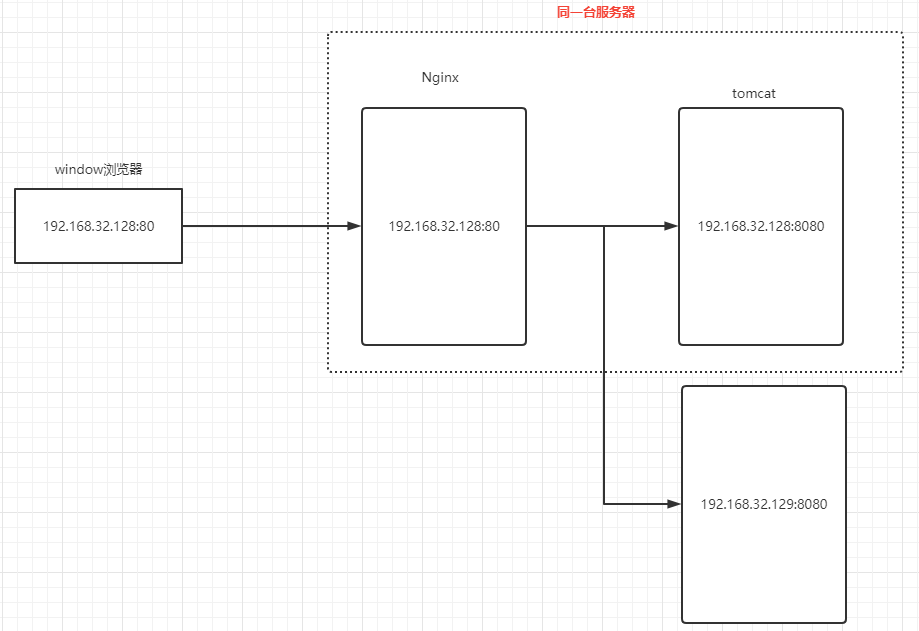
也就是通过 Nginx 将请求转发至两台服务器上。
打开 192.168.32.128 服务器的 Nginx 配置文件,即 /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf 文件,配置负载均衡。
修改内容如下:
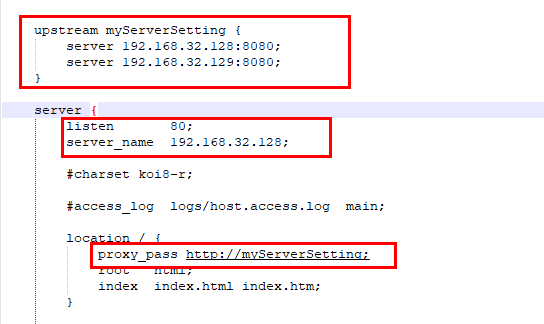
配置完成后,启动两台服务器的 tomcat ,并且启动 192.168.32.128 服务器的 Nginx。我们通过浏览器访问 http://192.168.32.128/mySystem/a.html ,多次刷新可以看到效果如下:
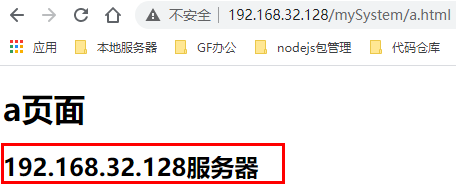
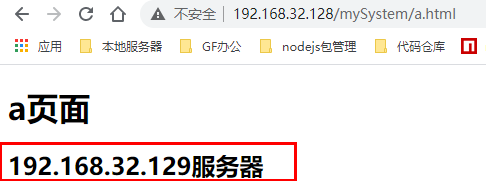
可以看到请求被平均分发到两台服务器上,也就是这一次请求的是 192.168.32.128 上的资源,下一次请求的就是 192.168.32.129 服务器上的资源。由此,我们就实现了负载均衡。
2.1、完整的Nginx配置文件
完整的 nginx.conf 配置文件如下:
#user nobody; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; #log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' # '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' # '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; #access_log logs/access.log main; sendfile on; #tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0; keepalive_timeout 65; #gzip on; upstream myServerSetting { server 192.168.32.128:8080; server 192.168.32.129:8080; } server { listen 80; server_name 192.168.32.128; #charset koi8-r; #access_log logs/host.access.log main; location / { proxy_pass http://myServerSetting; root html; index index.html index.htm; } #error_page 404 /404.html; # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html # error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 # #location ~ .php$ { # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; #} # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 # #location ~ .php$ { # root html; # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; # fastcgi_index index.php; # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; # include fastcgi_params; #} # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root # concurs with nginx's one # #location ~ /.ht { # deny all; #} } # another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration # #server { # listen 8000; # listen somename:8080; # server_name somename alias another.alias; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} # HTTPS server # #server { # listen 443 ssl; # server_name localhost; # ssl_certificate cert.pem; # ssl_certificate_key cert.key; # ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; # ssl_session_timeout 5m; # ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5; # ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # location / { # root html; # index index.html index.htm; # } #} }
3、Nginx负载均衡策略
3.1、轮询(默认)
轮询方式是 Nginx 负载均衡默认的方式。顾名思义,所有请求都按照时间顺序分配到不同的服务上。如果某个服务器 Down 掉,可以自动将该服务器剔除,不再分发请求到该服务器上。
我们上面的配置就是使用的默认即轮询策略进行分发:
upstream myServerSetting { server 192.168.32.128:8080; server 192.168.32.129:8080; }
3.2、权重(weight)
可以用 weight 关键字来指定每个服务器的权重比例,默认权重为 1,weight和访问比率成正比,权重越高被分发到的请求越多。通常用于后端服务机器性能不统一,将性能好的分配权重高来发挥服务器最大性能。
如下配置后10002服务的访问比率会是10001服务的二倍:
upstream dalaoyang-server { server localhost:10001 weight=1; server localhost:10002 weight=2; }
3.3、ip_hash(一个客户端访问固定服务器)
每个请求都根据访问 ip 的 hash 结果分配,经过这样的处理,每个访客固定访问一个后端服务,可以解决 session 的问题。
如下配置(ip_hash 可以和 weight 配合使用)。
upstream dalaoyang-server { ip_hash; server localhost:10001 weight=1; server localhost:10002 weight=2; }
3.4、fair(服务器响应快的优先分配)
按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。
upstream dalaoyang-server { server localhost:10001 weight=1; server localhost:10002 weight=2; fair; }