页面调度控制器的方法有几种?
控制器向视图传递数据的方法有几种?
生成视图、页面的方法有几种?
静态页面、动态页面、部分页面几种?
将页面放入母版的方法有几种?
局部刷新页面的方法有几种?
view不能同时引用多个model,controller中的方法也不能同时传多个类到view中??
0、控制器向视图传递Model数据
SysUser是Model类,对应数据库表
控制器代码:
public ActionResult Index() { return View(db.SysUsers.ToList());
}
视图代码
@model IEnumerable<WMS.Models.SysUser> @{ Layout = null; } <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <title>Index</title> </head> <body> <p> @Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create") </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.UserName) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.accountName) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Password) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.DepartID) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.RoleName) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Remark) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.IsDelete) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.LoginCount) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.LastLoginDate) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.CreateUser) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.CreateTime) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.UpdateUser) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.UpdateTime) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Email) </th> <th></th> </tr> @foreach (var item in Model) { <tr> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.UserName) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.accountName) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Password) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.DepartID) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.RoleName) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Remark) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.IsDelete) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.LoginCount) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.LastLoginDate) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.CreateUser) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.CreateTime) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.UpdateUser) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.UpdateTime) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Email) </td> <td> @Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id=item.ID }) | @Html.ActionLink("Details", "Details", new { id=item.ID }) | @Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id=item.ID }) </td> </tr> } </table> </body> </html>
1、控制器向视图传递定制的ViewModel数据
定制的ViewModel类
public class ViewModel
{
public IEnumerable<Task> task
{
get; set;
}
public IEnumerable<Teacher> teacher
{
get; set;
}
public IEnumerable<Grade> grade
{
get; set;
}
...
}
控制器部分代码:
var grades = gradeSer.GetModels(b => b.Grade_id !=0);
var tasks = taskSer.GetAll().Take(5);
ViewModel vm= new ViewModel;
vm.grade = grades;
vm.task = tasks;
return View(vm);
视图代码:
@model ~.Models.ViewModel
@ foreach( item in model.task) {
@item.~
}
又例如控制器:
public ActionResult Index() { DateTime date = DateTime.Now;//一个对象作为View方法的参数传递给视图 return View(date); }
视图代码:
第1种方法:
@model DateTime
@Model.Day
第2种方法:
@(((DateTime)Model).Day)
2、利用数据库的导航属性视图传递定制的ViewModel数据
例如控制器向视图传递了家教单数据(来自task表),视图需要显示学员姓名(学员姓名在student表中,student是task的主键表,通过student_id关联,task主要存储了哪个学生需要上哪门课程信息),这时控制器主要查task表,不需要查学员student表,前台可通过导航属性获得学员数据。
@foreach(var item in Model.task) { <div> <div> <div>@item.Student.Suser_name 急需家教</div> Student是导航属性 , 需要注意的是task-->subject是 N:1关系 <div>辅导 @item.Subject</div> <div> <strong>面议</strong> </div> </div> ... </div> }
3、利用数据库视图传递数据
例如控制器向视图传递了家教单数据(来自task表),视图需要显示学员姓名(学员姓名在student表中,student是task的主键表,通过student_id关联,task主要存储了哪个学生需要上哪门课程信息),这时控制器主要查task表,不需要查学员student表,前台可通过导航属性获得学员数据。
4、通过ViewData、ViewBag、TempData向视图传递数据
三者都是保存控制器中的数据,在视图中使用。
string[] items = new string[] { "one", "two", "three" }; ViewBag.Items = items; ViewData["Items"] = items;
有调试可以看到:
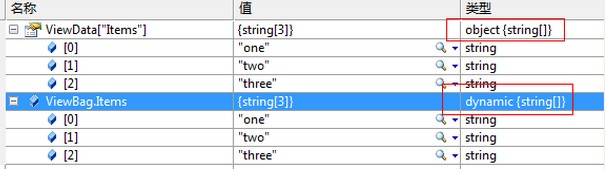
ViewBag中用的是dynamic类型,因此可以自动根据数据类型转换。
<ul> @foreach (dynamic p in ViewBag.Items) { <li>The item is: @p</li> } </ul>
而ViewData中用的是object对象,要自己去强制转换类型才可以遍历使用。
<ul> @foreach (string a in (string[])ViewData["Items"]) { <li>The item is: @a</li> } </ul>
ViewBag的使用方法
后台代码
public ActionResult Index() { Dictionary<string, string> address = new Dictionary<string, string>(); address.Add("Lng", "12.353535"); address.Add("Lat", "28.262626"); address.Add("Location", "唐宁街十号"); List<string> modules = new List<string>(); modules.Add("Admin module"); modules.Add("Recursive module"); modules.Add("Consistent module"); ViewBag.Name = "蝈蝈"; ViewBag.Age = "18"; ViewBag.Phone = "18233199999"; ViewBag.Address = address; ViewBag.Modules = modules; return View(); }
前台代码:
后台用ViewBag存值,前台既可以通过ViewBag取值,也可以通过ViewData取值。使用ViewData取值时,必须将数据转换成合适的类型;使用ViewBag取值时不需要转换数据类型。
@ViewData["Name"] @ViewData["Age"] @ViewData["Phone"] @{ Dictionary<string, string> dict = ViewData["Address"] as Dictionary<string, string>; } @if (dict != null) { @dict["Lng"] @dict["Lat"] @dict["Location"] } @{ List<string> list = ViewData["Modules"] as List<string>; } @if (list != null) { @list[0] @list[1] @list[2] } <br/> @ViewBag.Name @ViewBag.Age @ViewBag.Phone @ViewBag.Address @ViewBag.Address["Lng"] @ViewBag.Address["Lat"] @ViewBag.Address["Location"] @ViewBag.Modules @ViewBag.Modules[0] @ViewBag.Modules[1] @ViewBag.Modules[2]
ViewData的使用方法
后台代码:
public ActionResult Index() { Dictionary<string, string> address = new Dictionary<string, string>(); address.Add("Lng", "12.353535"); address.Add("Lat", "28.262626"); address.Add("Location", "唐宁街十号"); List<string> modules = new List<string>(); modules.Add("Admin module"); modules.Add("Recursive module"); modules.Add("Consistent module"); ViewData["Name"] = "蝈蝈"; ViewData["Age"] = "18"; ViewData["Phone"] = "18233199999"; ViewData["Address"]=address; ViewData["Modules"] = modules; return View(); }
前台代码:
后台用ViewData存值,前台既可以通过ViewBag取值,也可以通过ViewData取值。使用ViewData取值时,必须将数据转换成合适的类型;使用ViewBag取值时不需要转换数据类型。
@ViewData["Name"] @ViewData["Age"] @ViewData["Phone"] @{ Dictionary<string, string> dict = ViewData["Address"] as Dictionary<string, string>; } @if (dict != null) { @dict["Lng"] @dict["Lat"] @dict["Location"] } @{ List<string> list = ViewData["Modules"] as List<string>; } @if (list != null) { @list[0] @list[1] @list[2] } <br/> @ViewBag.Name @ViewBag.Age @ViewBag.Phone @ViewBag.Address @ViewBag.Address["Lng"] @ViewBag.Address["Lat"] @ViewBag.Address["Location"] @ViewBag.Modules @ViewBag.Modules[0] @ViewBag.Modules[1] @ViewBag.Modules[2]
两者的定义:
public dynamic ViewBag { get { if (_dynamicViewData == null) { _dynamicViewData = new DynamicViewDataDictionary(() => ViewData); } return _dynamicViewData; } }
public ViewDataDictionary ViewData { get { if (_viewData == null) { SetViewData(new ViewDataDictionary()); } return _viewData; } set { SetViewData(value); } }
通过定义我们可以看出ViewBag是ViewData的动态封装器,相当于在ViewData的基础上进行了封装处理。
两者的区别
ViewData是字典类型,赋值方式用字典方式,通过key值读取对应的value,ViewData[“myName”]
ViewBag是动态类型,使用时直接通过属性赋值即可,ViewBag.myName
ViewData和ViewBag只在当前Action中有效,等同于View
ViewData和ViewBag中的值可以互相访问
注意:
1、只有当关键字是有效的C#标识符时,ViewBag才起作用。
例如:如果在ViewData[“Key With Space”]中存放一个值,那么就不能使用ViewBag访问,因为这样根本无法通过编译。
2、动态值不能作为一个参数传递给扩展方法,因为C#编译器为了选择正确的扩展方法,在编译时必须知道每一个参数的真正类型。如果其中任何一个参数是动态的,那么就不会通过编译。
例如:@Html.TextBox(“name”,ViewBag.Name) 就会编译失败。
要使这行代码通过编译有两种方法:
@Html.TextBox(“name”,(string)ViewBag.Name)
@Html.TextBox(“name”,ViewData[“Name”])
TempData的使用方法
两个Action
public ActionResult Index() { this.TempData["Name"] = "Julian"; return View(); }
public ActionResult Index2() { string name = this.TempData["Name"] as string; return View(); }
Index()中,给TempData添加了一个键值对。假设请求了这个Action后,接着请求Index2这个Action。则可以在Index2中,获取到TempData的键值对的信息。
有趣的是,如果再一次请求Index2,那么从TempData中读取到的Name的值为Null。