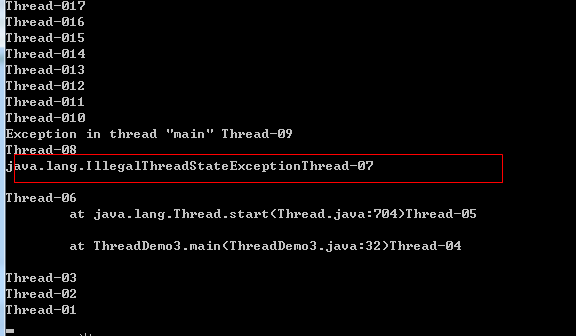
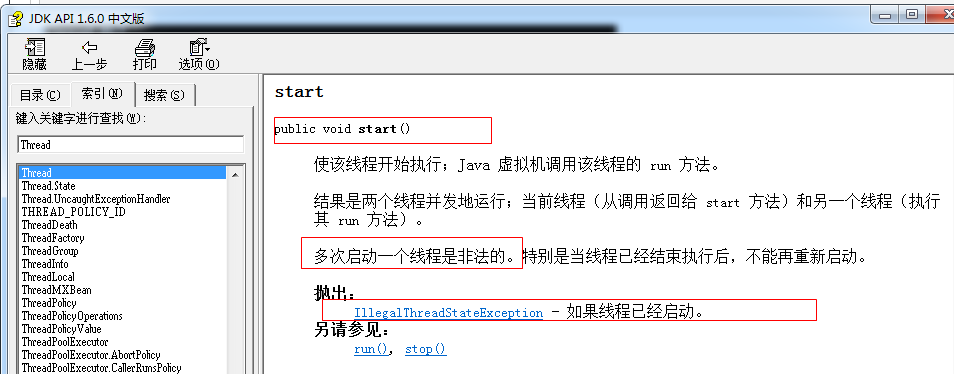
class Ticket implements Runnable { //1.描述票的数量 private int tickets = 100; //2.售票的动作,这个动作需要被多线程执行,那就是线程任务代码,需要定义run方法中 //线程任务中通常都有循环结构 public void run() { while (true) { if (tickets > 0) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + tickets--); } } } } public class ThreadDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.创建Runnable接口的子类对象 Ticket t = new Ticket(); //2创建4个线程对象,并将Runnable接口的子类对象作为参数传递给Thread的构造函数 Thread t1 = new Thread(t); //Thread t2 = new Thread(t); //Thread t3 = new Thread(t); //Thread t4 = new Thread(t); //3.开启4个线程 t1.start(); t1.start(); t1.start(); t1.start(); } }