|
项目 |
内容 |
||
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
||
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11435127.html |
||
|
作业学习目标 |
|
第一部分:总结第七章理论知识
1.异常(exception):
1)异常对象是派生于Throwable类的一个封装了错误信息的对象实例。
2)异常具有自己的语法和特定的继承结构。
3)所有的异常都是由Throwable继承而来,但在下一层分解为两个分支:Error 和 Exception
1.Error类层次结构描述了Java运行时系统的内部错误和资源耗尽错误。
2.Exception层次结构又分为两个分支: 由程序错误导致的异常属于RuntimeException,例如:错误的类型转换;数组访问越界;访问空指针。 另一个分支包含其他异常。
2.抛出(throws)异常:声明抛出异常在方法声明中用throws子句中来指明。
1)throws子句可以同时指明多个异常,说明该方法将不对这些异常进行处理,而是声明抛出它们。
2)一个方法必须声明该方法所有可能抛出的已检查异常,而未检查异常要么不可控制(Error),要么应该避免发生(RuntimeException)。
3)抛出异常对象通过throw语句来实现。 throws new EOFException
3.创建异常类
1)用于标准异常类不能充分描述清楚问题时。
2)基本与创建派生类相同,一般应包含默认的构造器和包含详细描述信息的构造器。
4.捕获异常
1)没有被捕获的异常会导致程序的终止。
2)捕获异常需要使用 try/catch语句块
1.如果try语句块中的代码抛出了异常,那么程序将跳过try语句块中的其他代码并执行catch子句中的处理器代码。
2.如何try语句块中的代码没有抛出异常,那么程序将跳过catch子句。
5.堆栈跟踪: 程序执行中一个方法调用过程的列表,它包含了程序执行过程中方法调用的特定位置。
6.使用异常机制的技巧:
1)异常处理不能代替简单的测试
2)不要过分地细化异常
3)利用异常层次结构
4)不要压制异常
5)在检测错误时,“苛刻”要比放任更好
6)不要羞于传递异常
7.断言(assert):
1)语法:assert 条件 或者 assert 条件:表达式
2)断言只应该用与在测试阶段确定程序内部的错误位置。
第二部分:实验部分
实验1:
命令行环境下:
程序1:
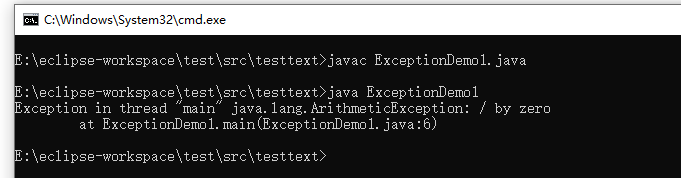
程序2:
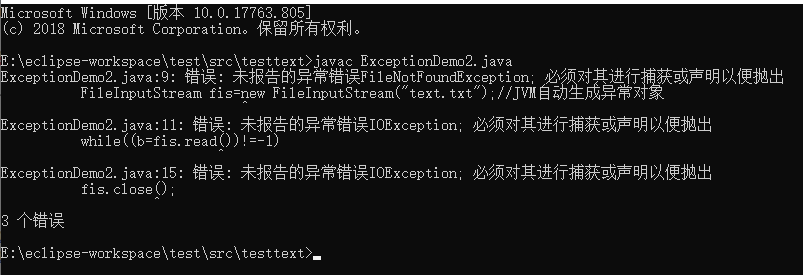
Eclipse环境下:
程序1:
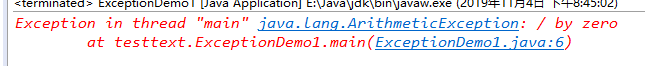
程序2:
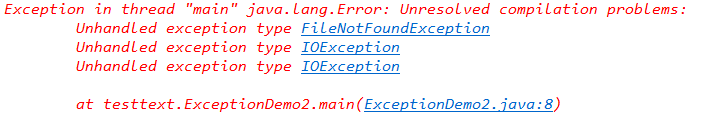
未被处理的未检查异常和已检查异常的区别在于报错的阶段不同。
实验2:
测试程序1:
代码:
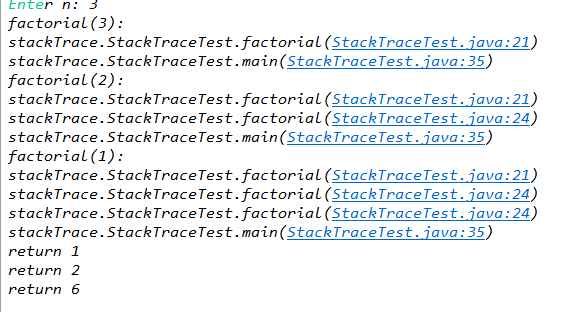
import java.util.*; public class StackTraceTest { /** * Computes the factorial of a number * @param n a non-negative integer * @return n! = 1 * 2 * . . . * n */ public static int factorial(int n) { System.out.println("factorial(" + n + "):"); var walker = StackWalker.getInstance(); //堆栈跟踪 walker.forEach(System.out::println); int r; if (n <= 1) r = 1; else r = n * factorial(n - 1); System.out.println("return " + r); return r; } public static void main(String[] args) { try (var in = new Scanner(System.in)) { System.out.print("Enter n: "); int n = in.nextInt(); factorial(n); } } }
结果:
测试程序2:
代码:
//积极的处理方式 import java.io.*; public class ExceptionTest { public static void main (String args[]) { try{ FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("身份证号.txt"); BufferedReader in =new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); String m=new String(); String n=new String(); while((m=in.readLine())!=null) { n+=m+" "; } in.close(); System.out.println(n); } catch(FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("文件未找到"); e.printStackTrace(); }catch(IOException e) { System.out.println("学生信息错误"); e.printStackTrace(); } } }
//消极的处理方式 import java.io.*; public class a { public static void main (String args[]) throws IOException { FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("身份证号.txt"); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); String m, n = new String(); while ((m = in.readLine()) != null) { n += m + " "; } in.close(); System.out.println(n); } }
结果:

实验3: 编程练习
代码:
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
PrintWriter output = null;
try {
output = new PrintWriter("题目.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int sum = 0;
int s = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3);
double a = (double) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
double b = (double) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
double c = 0;
int d;
String[] str = {"正确","错误"};
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
s = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3);
a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);
d=0;
switch(s)
{
case 0:
a = (double) Math.round(Math.random() * 20);
while (b == 0 || b > a) {
b = (double) Math.round(Math.random() * 20);
}
System.out.println( a + "/" + b + "=");
c = in.nextDouble();
if (c ==a/b) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("恭喜你,答对了!");
}
else {
System.out.println("遗憾,答错了!");
d=1;
}
output.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + c +"---"+str[d]);
break;
case 1:
System.out.println( a + "-" + b + "=");
c = in.nextDouble();
if (c == a-b) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("恭喜你,答对了!");
}
else {
System.out.println("遗憾,答错了!");
d=1;
}
output.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + c +"---"+str[d]);
break;
case 2:
a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 20);
b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 20);
System.out.println( a + "*" + b + "=");
c = in.nextDouble();
if (c == a*b) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("恭喜你,答对了!");
}
else {
System.out.println("遗憾,答错了!");
d=1;
}
output.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + c +"---"+str[d]);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println( a + "+" + b + "=");
c = in.nextDouble();
if (c == a+b) {
sum += 10;
System.out.println("恭喜你,答对了!");
}
else {
System.out.println("遗憾,答错了!");
d=1;
}
output.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + c +"---"+str[d]);
break;
}
}
in.close();
System.out.println("你的得分为:"+sum);
output.println("你的得分为:"+sum);
output.close();
}
}
结果:


实验4:断言、日志、程序调试技巧验证实验
实验程序1:
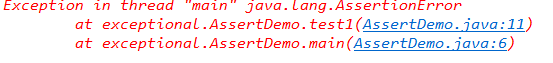
添加注释后:

实验程序2,实验程序3 :
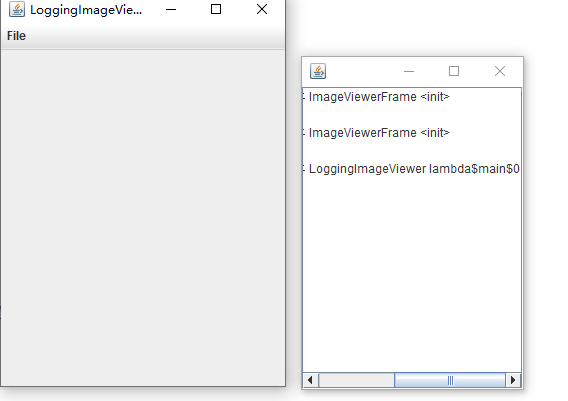
实验总结:
通过本周的学习,对理论知识异常、日志、断言和调试的理论知识有了进一步的掌握