书籍名称:HTML5-Animation-with-JavaScript
书籍源码:https://github.com/lamberta/html5-animation1
1.释放
现在假设我们写一个动画,将它运动到指定的地方,先设置一个速度,运用三角函数,我们计算x的速度,计算y的速度,判断距离。到达终点时停止。
这种方法在有些情况适用,但某些情况下,我们想让物体运动的自然一些。
在一些运动,我们知道目标,且一开始速度很快,后面逐渐变慢。也就是说,它的速度和距离是成正比的。看下图。
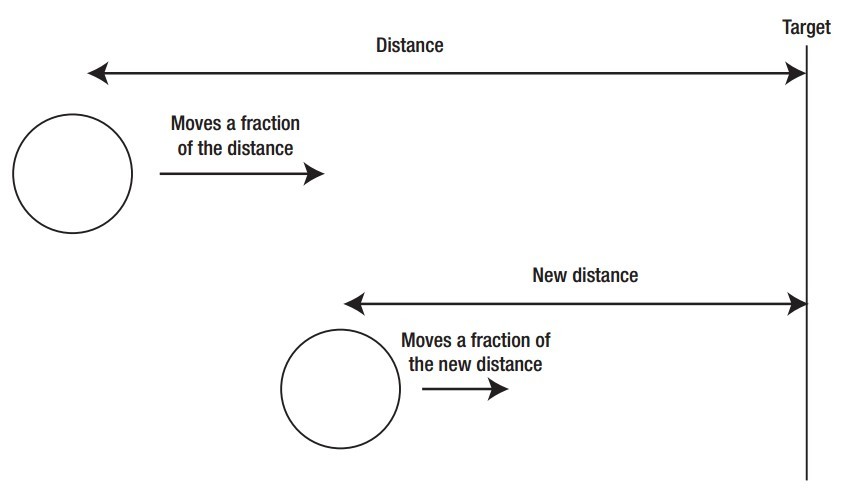
01-easing-1.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Easing 1</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), ball = new Ball(), easing = 0.05, targetX = canvas.width / 2, targetY = canvas.height / 2; (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); var vx = (targetX - ball.x) * easing, vy = (targetY - ball.y) * easing; ball.x += vx; ball.y += vy; ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
增加拖拽
02-easing-2.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Easing 2</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <aside>Press and drag circle with mouse.</aside> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), mouse = utils.captureMouse(canvas), ball = new Ball(), easing = 0.05, targetX = canvas.width / 2, targetY = canvas.height / 2, isMouseDown = false; canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', function () { if (utils.containsPoint(ball.getBounds(), mouse.x, mouse.y)) { isMouseDown = true; canvas.addEventListener('mouseup', onMouseUp, false); canvas.addEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove, false); } }, false); function onMouseUp () { isMouseDown = false; canvas.removeEventListener('mouseup', onMouseUp, false); canvas.removeEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove, false); } function onMouseMove () { ball.x = mouse.x; ball.y = mouse.y; } (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); if (!isMouseDown) { var vx = (targetX - ball.x) * easing, vy = (targetY - ball.y) * easing; ball.x += vx; ball.y += vy; } ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
按之前的想法速度是接近0的但不会为了,我们要加一个停止条件
03-easing-off.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Easing Off</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <textarea id="log"></textarea> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), log = document.getElementById('log'), ball = new Ball(), easing = 0.05, targetX = canvas.width / 2, animRequest; ball.y = canvas.height / 2; (function drawFrame () { animRequest = window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); var dx = targetX - ball.x; if (Math.abs(dx) < 1) { ball.x = targetX; /* ERRATA: 'cancelRequestAnimationFrame' renamed to 'cancelAnimationFrame' to reflect an update to the W3C Animation-Timing Spec. * See utils.js for the update to check for cross-browser compatibility. */ window.cancelAnimationFrame(animRequest); log.value = "Animation done!"; } else { var vx = dx * easing; ball.x += vx; } ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
移动到鼠标,是先获取鼠标的位置,并作为运动的目标点。
04-ease-to-mouse.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Ease to Mouse</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <aside>Move mouse on canvas element.</aside> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), mouse = utils.captureMouse(canvas), ball = new Ball(), easing = 0.05; (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); var vx = (mouse.x - ball.x) * easing, vy = (mouse.y - ball.y) * easing; ball.x += vx; ball.y += vy; ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
补充一下,释放(easing)不只是使用与运动,它是一种由快变慢的效果,还适用于旋转(如大转盘),颜色等。
2.弹性
一维弹簧效果
弹簧效果离中心点的距离和加速度成正比。实际的加速度应该是距离*系数。
05-spring-1.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Spring 1</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), ball = new Ball(), spring = 0.03, targetX = canvas.width / 2, vx = 0; ball.y = canvas.height / 2; (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); var dx = targetX - ball.x, ax = dx * spring; vx += ax; ball.x += vx; ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
比较真实的弹簧效果
在实际生活有摩擦力或是阻力,物体不会无休止的运动,下面将阻力的考虑在内。
06-spring-2.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Spring 2</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), ball = new Ball(), spring = 0.03, friction = 0.95, targetX = canvas.width / 2, vx = 0; ball.y = canvas.height / 2; (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); var dx = targetX - ball.x, ax = dx * spring; vx += ax; vx *= friction; ball.x += vx; ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
这里只是简单的用阻力来控制速度无限接近0,需要补充一个到目标停止计算的条件类似如下
if (Math.abs(vx) > 0.001) {
vx += ax;
vx *= friction;
ball.x += vx;
}
二维考虑y方向
07-spring-3.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Spring 3</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), ball = new Ball(), spring = 0.03, friction = 0.95, targetX = canvas.width / 2, targetY = canvas.height / 2, vx = 0, vy = 0; (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); var dx = targetX - ball.x, dy = targetY - ball.y, ax = dx * spring, ay = dy * spring; vx += ax; vy += ay; vx *= friction; vy *= friction; ball.x += vx; ball.y += vy; ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
在目标移动的情况
考虑移动到鼠标位置的弹簧效果,将目标设置为鼠标位置即可。
08-spring-4.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Spring 4</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <aside>Move mouse on canvas element.</aside> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), mouse = utils.captureMouse(canvas), ball = new Ball(), spring = 0.03, friction = 0.95, vx = 0, vy = 0; (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); var dx = mouse.x - ball.x, dy = mouse.y - ball.y, ax = dx * spring, ay = dy * spring; vx += ax; vy += ay; vx *= friction; vy *= friction; ball.x += vx; ball.y += vy; ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
考虑弹簧线
给弹簧效果加条弹簧线,让其更真实一点。
用api画一条圆心到鼠标位置的线就可以了。
考虑重力时,只需再加上重力加速度。
09-spring-5.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Spring 5</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <aside>Move mouse on canvas element.</aside> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), mouse = utils.captureMouse(canvas), ball = new Ball(), spring = 0.03, friction = 0.9, gravity = 2, vx = 0, vy = 0; (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); var dx = mouse.x - ball.x, dy = mouse.y - ball.y, ax = dx * spring, ay = dy * spring; vx += ax; vy += ay; vy += gravity; vx *= friction; vy *= friction; ball.x += vx; ball.y += vy; context.beginPath(); context.moveTo(ball.x, ball.y); context.lineTo(mouse.x, mouse.y); context.stroke(); ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
链式效果
链式效果的是对单个效果的发散,第一个球的目标为鼠标,第二个球的目标为第一个球的中心,依次类推。
10-chain.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Chain</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <aside>Move mouse on canvas element.</aside> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), mouse = utils.captureMouse(canvas), ball0 = new Ball(), ball1 = new Ball(), ball2 = new Ball(), spring = 0.03, friction = 0.9, gravity = 2; function move (ball, targetX, targetY) { ball.vx += (targetX - ball.x) * spring; ball.vy += (targetY - ball.y) * spring; ball.vy += gravity; ball.vx *= friction; ball.vy *= friction; ball.x += ball.vx; ball.y += ball.vy; } (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); move(ball0, mouse.x, mouse.y); move(ball1, ball0.x, ball0.y); move(ball2, ball1.x, ball1.y); //draw spring context.beginPath(); context.moveTo(mouse.x, mouse.y); context.lineTo(ball0.x, ball0.y); context.lineTo(ball1.x, ball1.y); context.lineTo(ball2.x, ball2.y); context.stroke(); //draw balls ball0.draw(context); ball1.draw(context); ball2.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
用数组管理

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Chain Array</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <aside>Move mouse on canvas element.</aside> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), mouse = utils.captureMouse(canvas), balls = [], numBalls = 10, spring = 0.03, friction = 0.9, gravity = 2; while (numBalls--) { balls.push(new Ball(20)); } function move (ball, targetX, targetY) { ball.vx += (targetX - ball.x) * spring; ball.vy += (targetY - ball.y) * spring; ball.vy += gravity; ball.vx *= friction; ball.vy *= friction; ball.x += ball.vx; ball.y += ball.vy; } function draw (ballB, i) { //if first ball, move to mouse if (i === 0) { move(ballB, mouse.x, mouse.y); context.moveTo(mouse.x, mouse.y); } else { var ballA = balls[i-1]; move(ballB, ballA.x, ballA.y); context.moveTo(ballA.x, ballA.y); } context.lineTo(ballB.x, ballB.y); context.stroke(); ballB.draw(context); } (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); context.beginPath(); balls.forEach(draw); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
多个弹簧
12-multi-spring.html

12-multi-spring.html
与目标保持一定距离
利用三角函数,根据鼠标位置计算出将要运动到的目标。之后同上。
13-offset-spring.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Offset Spring</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <aside>Move mouse on canvas element.</aside> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), mouse = utils.captureMouse(canvas), ball = new Ball(), spring = 0.03, friction = 0.9, springLength = 100, vx = 0, vy = 0; (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); var dx = ball.x - mouse.x, dy = ball.y - mouse.y, angle = Math.atan2(dy, dx), targetX = mouse.x + Math.cos(angle) * springLength, targetY = mouse.y + Math.sin(angle) * springLength; vx += (targetX - ball.x) * spring; vy += (targetY - ball.y) * spring; vx *= friction; vy *= friction; ball.x += vx; ball.y += vy; context.beginPath(); context.moveTo(ball.x, ball.y); context.lineTo(mouse.x, mouse.y); context.stroke(); ball.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
双重弹簧
综合运用:用到保持距离,一般弹簧效果,移动目标等
14-double-spring.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Double Spring</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <aside>Press and drag circles with mouse.</aside> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), mouse = utils.captureMouse(canvas), ball0 = new Ball(20), ball1 = new Ball(20), ball0_dragging = false, ball1_dragging = false, spring = 0.03, friction = 0.9, springLength = 100, vx = 0, vy = 0; ball0.x = Math.random() * canvas.width; ball0.y = Math.random() * canvas.height; ball1.x = Math.random() * canvas.width; ball1.y = Math.random() * canvas.height; canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', function () { if (utils.containsPoint(ball0.getBounds(), mouse.x, mouse.y)) { ball0_dragging = true; } if (utils.containsPoint(ball1.getBounds(), mouse.x, mouse.y)) { ball1_dragging = true; } }, false); canvas.addEventListener('mouseup', function () { if (ball0_dragging || ball1_dragging) { ball0_dragging = false; ball1_dragging = false; } }, false); canvas.addEventListener('mousemove', function () { if (ball0_dragging) { ball0.x = mouse.x; ball0.y = mouse.y; } if (ball1_dragging) { ball1.x = mouse.x; ball1.y = mouse.y; } }, false); function springTo (ballA, ballB) { var dx = ballB.x - ballA.x, dy = ballB.y - ballA.y, angle = Math.atan2(dy, dx), targetX = ballB.x - Math.cos(angle) * springLength, targetY = ballB.y - Math.sin(angle) * springLength; ballA.vx += (targetX - ballA.x) * spring; ballA.vy += (targetY - ballA.y) * spring; ballA.vx *= friction; ballA.vy *= friction; ballA.x += ballA.vx; ballA.y += ballA.vy; } (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); if (!ball0_dragging) { springTo(ball0, ball1); } if (!ball1_dragging) { springTo(ball1, ball0); } context.beginPath(); context.moveTo(ball0.x, ball0.y); context.lineTo(ball1.x, ball1.y); context.stroke(); ball0.draw(context); ball1.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
三重
好复杂……
15-triple-spring.html

<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>Triple Spring</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="../include/style.css"> </head> <body> <header> Example from <a href="http://amzn.com/1430236655?tag=html5anim-20"><em>Foundation HTML5 Animation with JavaScript</em></a> </header> <canvas id="canvas" width="400" height="400"></canvas> <aside>Press and drag circles with mouse.</aside> <script src="../include/utils.js"></script> <script src="./classes/ball.js"></script> <script> window.onload = function () { var canvas = document.getElementById('canvas'), context = canvas.getContext('2d'), mouse = utils.captureMouse(canvas), ball0 = new Ball(20), ball1 = new Ball(20), ball2 = new Ball(20), ball0_dragging = false, ball1_dragging = false, ball2_dragging = false, spring = 0.03, friction = 0.9, springLength = 100, vx = 0, vy = 0; ball0.x = Math.random() * canvas.width; ball0.y = Math.random() * canvas.height; ball1.x = Math.random() * canvas.width; ball1.y = Math.random() * canvas.height; ball2.x = Math.random() * canvas.width; ball2.y = Math.random() * canvas.height; canvas.addEventListener('mousedown', function () { if (utils.containsPoint(ball0.getBounds(), mouse.x, mouse.y)) { ball0_dragging = true; } if (utils.containsPoint(ball1.getBounds(), mouse.x, mouse.y)) { ball1_dragging = true; } if (utils.containsPoint(ball2.getBounds(), mouse.x, mouse.y)) { ball2_dragging = true; } }, false); canvas.addEventListener('mouseup', function () { if (ball0_dragging || ball1_dragging || ball2_dragging) { ball0_dragging = false; ball1_dragging = false; ball2_dragging = false; } }, false); canvas.addEventListener('mousemove', function () { if (ball0_dragging) { ball0.x = mouse.x; ball0.y = mouse.y; } if (ball1_dragging) { ball1.x = mouse.x; ball1.y = mouse.y; } if (ball2_dragging) { ball2.x = mouse.x; ball2.y = mouse.y; } }, false); function springTo (ballA, ballB) { var dx = ballB.x - ballA.x, dy = ballB.y - ballA.y, angle = Math.atan2(dy, dx), targetX = ballB.x - Math.cos(angle) * springLength, targetY = ballB.y - Math.sin(angle) * springLength; ballA.vx += (targetX - ballA.x) * spring; ballA.vy += (targetY - ballA.y) * spring; ballA.vx *= friction; ballA.vy *= friction; ballA.x += ballA.vx; ballA.y += ballA.vy; } (function drawFrame () { window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame, canvas); context.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height); if (!ball0_dragging) { springTo(ball0, ball1); springTo(ball0, ball2); } if (!ball1_dragging) { springTo(ball1, ball0); springTo(ball1, ball2); } if (!ball2_dragging) { springTo(ball2, ball0); springTo(ball2, ball1); } context.beginPath(); context.moveTo(ball0.x, ball0.y); context.lineTo(ball1.x, ball1.y); context.lineTo(ball2.x, ball2.y); context.lineTo(ball0.x, ball0.y); context.stroke(); ball0.draw(context); ball1.draw(context); ball2.draw(context); }()); }; </script> </body> </html>
