2019面向对象程序设计(Java)第4周学习指导及要求
|
项目 |
内容 |
|
这个作业属于哪个课程 |
<任课教师博客主页链接>https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ |
|
这个作业的要求在哪里 |
<作业链接地址>https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/11552848.html |
|
作业学习目标 |
<填写具体目标>
|
第一部分:总结第四章理论知识(20分)
第四章主要讲述了对象与类的概念,有十小节内容,而这章内容也是非常重要的一章,学起来也是很困难的,如果课后不认真看书,不多加练习,那么这一章的内容就什么也学不下,这会影响后面的学习。
1. 面向对象程序设计(Object Oriented Programming,OOP)是一种计算机编程架构。OOP的一条基本原则是计算机程序由单个能够起到子程序作用的单元或对象组合而成。OOP达到了软件工程的三个主要目标:重用性、灵活性和扩展性。OOP=对象+类+继承+多态+消息,其中核心概念是类和对象。面向对象程序设计以对象为核心,该方法认为程序由一系列对象组成。类是对现实世界的抽象,包括表示静态属性的数据和对数据的操作,对象是类的实例化。对象间通过消息传递相互通信,来模拟现实世界中不同实体间的联系。在面向对象的程序设计中,对象是组成程序的基本模块。
面向对象程序设计中的概念主要包括:对象、类、数据抽象、继承、动态绑定、数据封装、多态性、消息传递。通过这些概念面向对象的思想得到了具体的体现。
在Java程序设计语言中,使用构造器构造新实例。 构造器是一种特殊的方法,用来构造并初始化对象。构造器的名字应该与类名相同
1.2对象和对象变量的区别:
变量不是个对象,实际上对象变量的初始化只是对对象的引用,Java中,任何对象变量的值都是对存储在另外一个地方的一个对象的引用。新的操作符的返回值也是一个引用
C ++中没有空引用 Date b; // Java的, 实际上,等同于Date* b; // C ++
的Java中的空引用对应于C ++中的空指针
所有的Java的对象都存储在堆中
clone方法获得对象的完整拷贝
1.3.LocalDate类:
Java的类库分别包含了两个类:一个是用来表示时间点的Date类;另一个是用来表示大家熟悉的日历表示法的LocalDate类
不要使用构造器来构造LocalDate类的对象,应当使用静态工厂方法代表你调用构造器,如下:
LocalDate.now()会构造一个新对象,表示构造这个对象时的日期
可以提供年,月和日来构造对应一个特定日期的对象:LocalDate.of(1999,12,31)
3. 静态域与静态方法:Java 中被static 修饰的域或方法常被称作静态的。
1)静态域:如果将静态域定义为static,那么每个类中只有这样一个域,而每一个对象对于所有的实例域都有自己的一份拷贝本。
2)静态常量 静态变量使用的比较少,但是静态常量却使用的比较多(在实际的开发中,静态常量可以做到:该改一处而改全处作用,大大的减少修改和出错的地方),在使用的时候,我们就可以跟使用静态变量、静态方法方法一样使用静态常量(用静态static修饰的都是可以直接用类名来使用) Math.PI来使用这个常量。如果关键字static被省略,那么PI就变成Math类的一个实例域,需要通过Math类的对象访问PI,并且每一个Math对象都有它自己的一个PI复制本。另外一个多次使用的静态常量是Java中System.out. 它在System类中声明。 我们都知道每个类对象都可以对公有域进行修改,所以,最好不要将域设计成为public ,然而,公有常量(即final域)却没有问题,因为out被声明为final, 所以,不允许再将其他的打印流赋值给它
3)静态方法:静态方法是一种不能由对象操作的方法, 例如Math类中的求取一个数的次方的pow()方法就是一个静态方法。表达式是: Math.pow(x, a),在运算时,不使用任何Math对象,换句话说,没有隐式的参数。可以认为静态方法是没有this参数的方法(在一个非静态的方法中,this参数表示这个方法的隐式参数)。
Student 类的静态方法不能访问Id实例域,因为Id它不是静态的,Student的静态方法它不能操作对象,但是静态方法可以访问自身类中的静态域。总之就是常说的:静态方法中只能调用静态的东西,非静态的是不能使用的。
4.包作用域:
1)类中标记为public的部分可以被任意类使用;
2)类中标记为private的部分只能在类中使用;
3)如果没有为类、方法或实例域指定访问控制修饰符public或private,这部分可以被同一包中的所有方法访问;
4)如果实例域不标记为private,将默认为包可见,这样做会破坏类的封装性。
5. 类路径:
1)类存储在文件系统的子目录中,类得路径必须与包名匹配;
2)在命令行方式下,设置类路径,使用-classpath选项指定类路径。
第二部分:实验部分
实验名称:实验三 类与对象的定义及使用
1. 实验目的:
(1) 熟悉PTA平台线上测试环境;
(2) 理解用户自定义类的定义;
(3) 掌握对象的声明;
(4) 学会使用构造函数初始化对象;
(5) 使用类属性与方法的使用掌握使用;
(6) 掌握package和import语句的用途。
3. 实验步骤与内容:
实验1 任务1(10分)
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 6 String s1 = in.nextLine(); 7 String s2,s3,s4; 8 s2 = s1.substring(6,10); 9 s3 = s1.substring(10,12); 10 s4 = s1.substring(12,14); 11 System.out.println(s2+"-"+s3+"-"+s4); 12 } 13 14 }
运行结果如图:
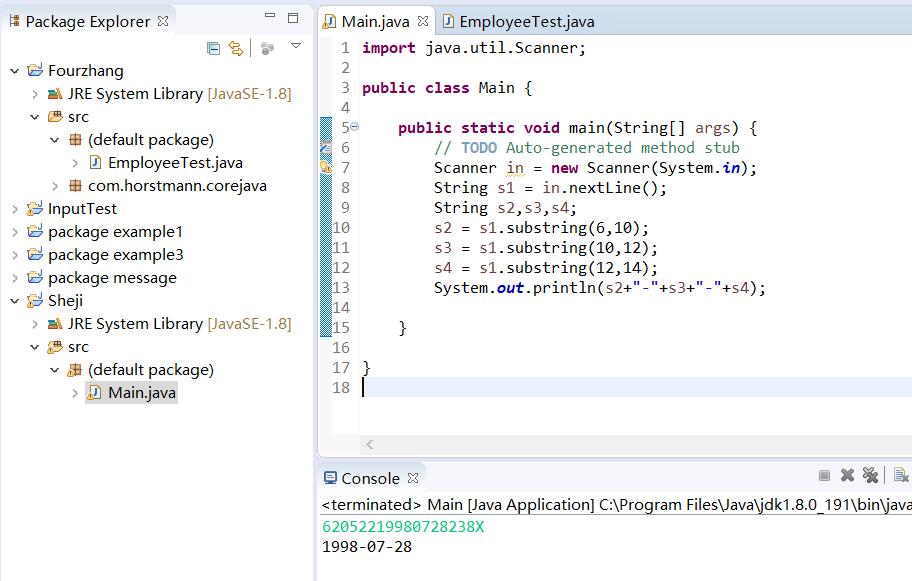
实验1 任务2(25分)
1 import java.io.BufferedReader; 2 3 import java.io.FileReader; 4 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 import java.util.ArrayList; 8 9 import java.util.Scanner; 10 11 public class students { 12 13 private static ArrayList<Student> list; 14 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 17 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 18 19 list = new ArrayList<>(); 20 21 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 22 23 try { 24 25 readFile("studentfile.txt"); //读如文件 studentfile.txt的信息 26 27 System.out.println("请选择操作,1按姓名,2按学号,3退出"); //首先在控制台输出 :请选择操作,1按姓名,2按学号,3退出 28 29 int i; 30 31 while ((i = in.nextInt()) != 3) //读出并转换下一个表示整型的字符序列 32 33 { 34 35 switch (i) //switch语句控制菜单 36 37 { 38 39 case 1: //按学生的姓名查找 40 41 System.out.println("请输入姓名"); //在控制台上输出:请输入姓名 42 43 String name = in.next(); //定义一个String类对象name,表示下一行字符串 44 45 Student student = findStudentByName(name); //通过姓名查找学生的信息 46 47 if (student == null) { 48 49 System.out.println("没找到"); //if语句判断,如果学生的信息为空,则在控制台输出: 没找到 50 51 } else { 52 53 System.out.println(student.toString()); //否则,调用toString方法输出学生的信息 54 55 } 56 57 System.out.println("请选择操作,1按姓名,2按学号,3退出"); 58 59 break; //退出当前的循环 60 61 case 2: 62 63 System.out.println("请输入学号"); //按学生的学号查找 64 65 String id = in.next(); //定义一个String类对象id,表示下一行字符串 66 67 Student student1 = findStudentById(id); //通过学号查找学生的信息 68 69 if (student1 == null) { ////if语句判断,如果学生的信息为空,则在控制台输出: 没找到 70 71 System.out.println("没找到"); 72 73 } else { 74 75 System.out.println(student1.toString()); //否则,调用toString方法输出学生的信息 76 77 78 79 } 80 81 System.out.println("请选择操作,1按姓名,2按学号,3退出"); 82 83 break; 84 85 86 87 default: 88 89 System.out.println("输入有误"); 90 91 System.out.println("请选择操作,1按姓名,2按学号,3退出"); 92 93 break; 94 95 } 96 97 98 99 } 100 101 } catch (IOException e) { 102 103 // TODO 自动生成的 catch 块 104 105 e.printStackTrace(); 106 107 }finally { 108 109 in.close(); //最后关闭0 110 111 } 112 113 114 115 } 116 117 118 119 public static void readFile(String path) throws IOException { 120 121 FileReader reader = new FileReader(path); // 122 123 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader); 124 125 String result; //定义一个String类对象 result 126 127 while ((result = br.readLine()) != null) { //while循环 128 129 Student student = new Student(); 130 131 student.setName(result.substring(13)); 132 133 student.setID(result.substring(0,12)); //从第十三位开始,调用result对象的substring方法得到一个新的字符串 134 135 list.add(student); 136 137 } 138 139 br.close(); 140 141 } 142 143 144 145 public static Student findStudentByName(String name) { //通过姓名找学生的信息 146 147 for (Student student : list) { 148 149 if (student.getName().equals(name)) { //用equals方法检测两个字符串是否相等 150 151 return student; 152 153 } 154 155 } 156 157 return null; 158 159 160 161 } 162 163 164 165 public static Student findStudentById(String Id) { //通过学号查找学生的信息 166 167 for (Student student : list) { 168 169 if (student.getID().equals(Id)) { //用equals方法检测两个字符串是否相等 170 171 return student; 172 173 } 174 175 } 176 177 return null; 178 179 180 181 } 182 183 } 184 185 186 187 class Student { 188 189 private String name; //String类对象name的私有的实例域 190 191 private String ID; //String类对象ID的私有的实例域 192 193 194 195 public String getName() { 196 197 return name; 198 199 } 200 201 202 203 public void setName(String name) { 204 205 this.name = name; 206 207 } 208 209 210 211 public String getID() { 212 213 return ID; 214 215 } 216 217 218 219 public void setID(String iD) { 220 221 ID = iD; 222 223 } 224 225 226 227 @Override 228 229 public String toString() { 230 231 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 232 233 return "姓名是:" + name + "学号是:" + ID; //得到查找学生的信息 234 235 } 236 237 }
运行结果:
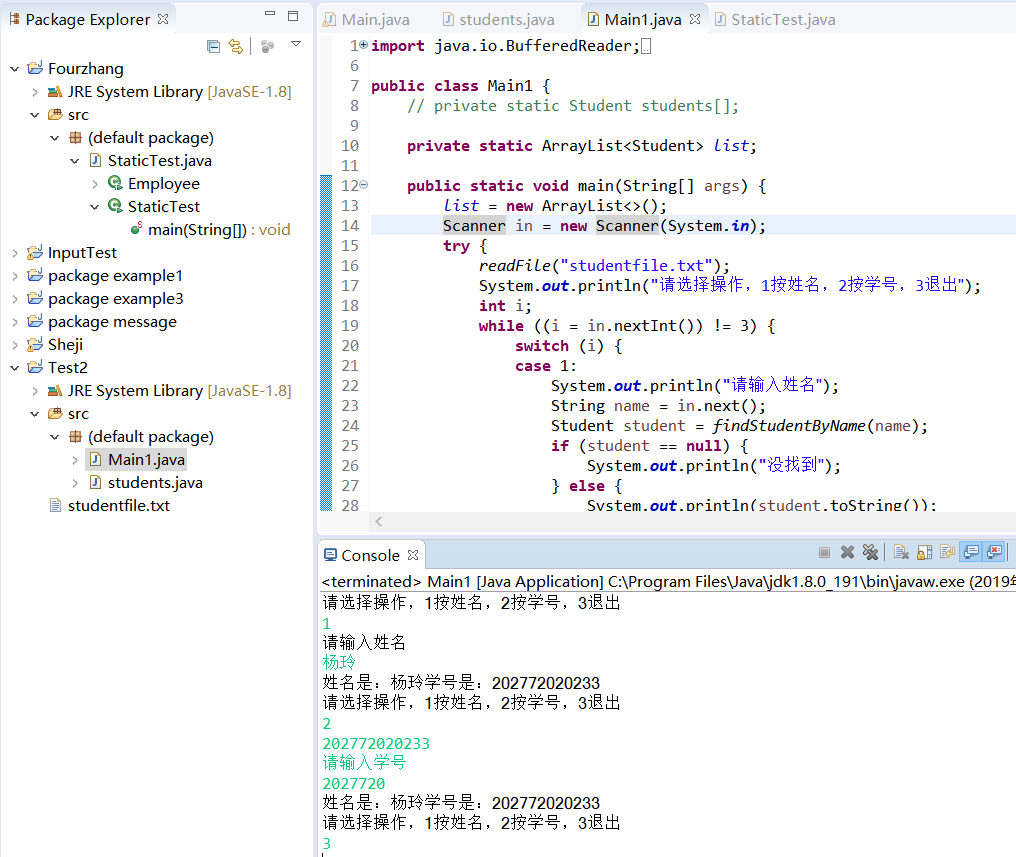
实验2 测试程序1(10分)导入第4章示例程序并测试。
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-2(教材104页);
l 结合程序运行结果,掌握类的定义与类对象的用法,并在程序代码中添加类与对象知识应用的注释;
l 尝试在项目中编辑两个类文件(Employee.java、 EmployeeTest.java ),编译并运行程序。
l 参考教材104页EmployeeTest.java,设计StudentTest.java,定义Student类,包含name(姓名)、sex(性别)、javascore(java成绩)三个字段,编写程序,从键盘输入学生人数,输入学生信息,并按以下表头输出学生信息表:
姓名 性别 java成绩
1 import java.time.*; 2 3 /** 4 * This program tests the Employee class. 5 * @version 1.13 2018-04-10 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class EmployeeTest 9 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) 11 { 12 // fill the staff array with three Employee objects 13 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; 14 15 staff[0] = new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); 16 staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); 17 staff[2] = new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15); 18 19 // raise everyone's salary by 5% 20 for (Employee e : staff) 21 e.raiseSalary(5); 22 23 // print out information about all Employee objects 24 for (Employee e : staff) 25 System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" 26 + e.getHireDay()); 27 } 28 } 29 30 class Employee 31 { 32 private String name; 33 private double salary; 34 private LocalDate hireDay; 35 36 public Employee(String n, double s, int year, int month, int day) 37 { 38 name = n; 39 salary = s; 40 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); 41 } 42 43 public String getName() 44 { 45 return name; 46 } 47 48 public double getSalary() 49 { 50 return salary; 51 } 52 53 public LocalDate getHireDay() 54 { 55 return hireDay; 56 } 57 58 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 59 { 60 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 61 salary += raise; 62 } 63 }
运行结果:
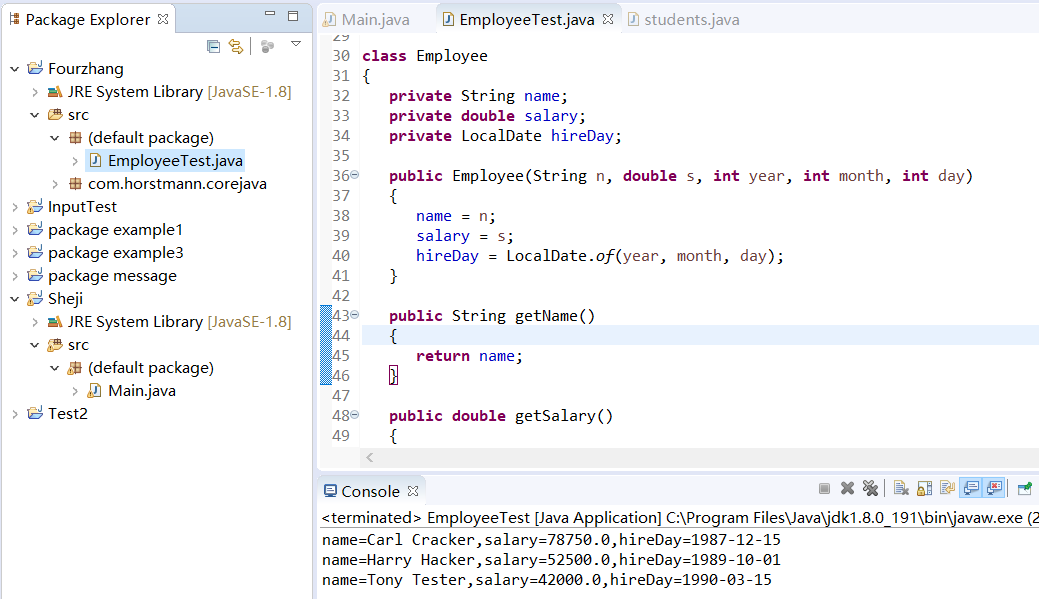
(2)Employee:
class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String n, double s, int year, int month, int day) { name = n; salary = s; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; }
运行结果:
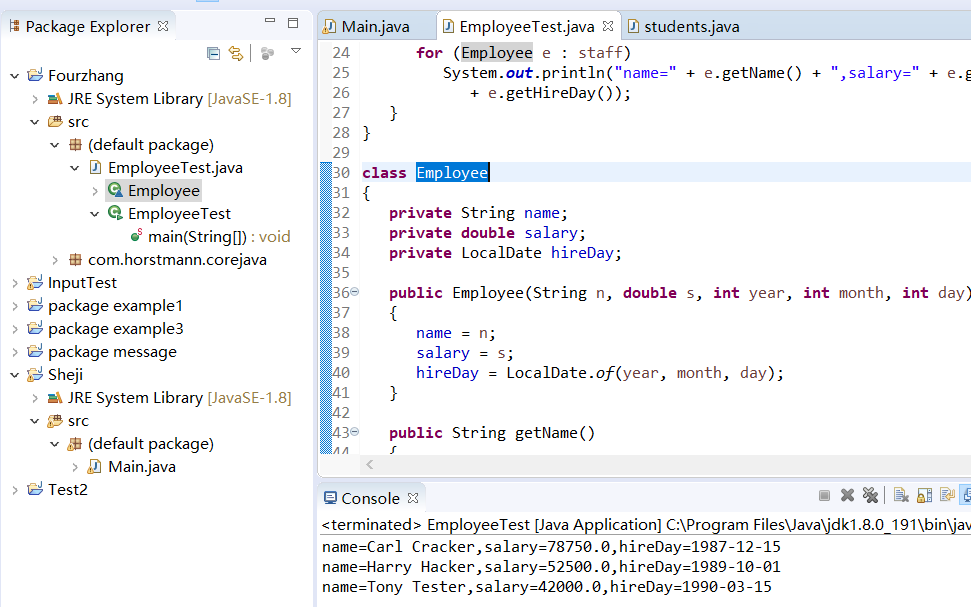
(3)代码如下(EmployeeTest):
public class EmployeeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array with three Employee objects Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; staff[0] = new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); staff[2] = new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15); // raise everyone's salary by 5% for (Employee e : staff) e.raiseSalary(5); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } }
运行结果:
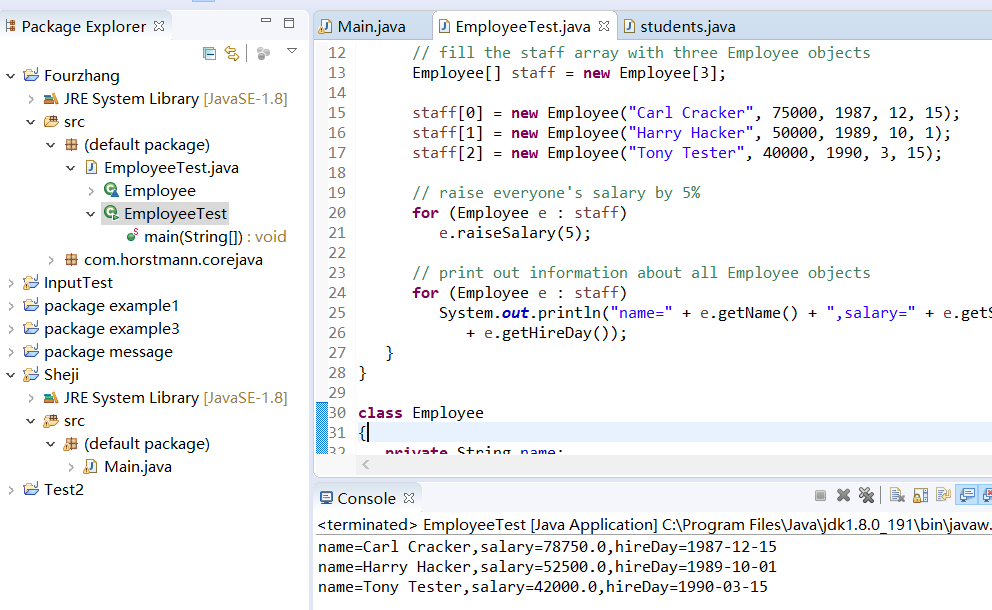
实验2 测试程序2(5分)
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-3(教材116);
l 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握静态域(netxtId)与静态方法(getNextId)的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
l 理解Java单元(类)测试的技巧。
代码如下:
1 /** 2 * This program demonstrates static methods. 3 * @version 1.02 2008-04-10 4 * @author Cay Horstmann 5 */ 6 public class StaticTest 7 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) 9 { 10 // fill the staff array with three Employee objects //用三个employee对象填充staff数组 11 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; 12 13 staff[0] = new Employee("Tom", 40000); 14 staff[1] = new Employee("Dick", 60000);////构造Employee数组,并有三个雇员对象; 15 staff[2] = new Employee("Harry", 65000); 16 17 // print out information about all Employee objects 18 for (Employee e : staff) 19 { 20 e.setId(); //打印每个雇员的信息; 21 System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",id=" + e.getId() + ",salary=" 22 + e.getSalary()); 23 } 24 25 int n = Employee.getNextId(); // calls static method (通过类名调用静态方法) 26 System.out.println("Next available id=" + n); 27 } 28 } 29 30 class Employee //定义Employee类; 31 { 32 private static int nextId = 1; 33 34 private String name; 35 private double salary; 36 private int id; //进行实例域定义来存放的需要操作的数据; 37 38 public Employee(String n, double s) 39 { 40 name = n; 41 salary = s; 42 id = 0; //构造Employee类的对象,并声明局部变量name,salary,hireday; 43 } 44 45 public String getName() 46 { 47 return name; //实例域name的访问器方法 48 } 49 50 public double getSalary() 51 { 52 return salary; 53 } 54 55 public int getId() 56 { 57 return id; 58 } 59 60 public void setId() 61 { 62 id = nextId; // set id to next available id 63 nextId++; 64 } 65 66 public static int getNextId() 67 { 68 return nextId; // returns static field 69 } 70 71 public static void main(String[] args) // unit test 72 { 73 Employee e = new Employee("Harry", 50000); 74 System.out.println(e.getName() + " " + e.getSalary()); 75 } 76 }
运行结果:

实验2 测试程序3(5分)
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-4(教材121);
结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java方法参数的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
代码如下:
1 /** 2 * This program demonstrates parameter passing in Java. 3 * @version 1.01 2018-04-10 4 * @author Cay Horstmann 5 */ 6 public class ParamTest 7 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) 9 { 10 /* 11 * Test 1: Methods can't modify numeric parameters 12 */ //测试方法不能修改数值参数 13 System.out.println("Testing tripleValue:"); 14 double percent = 10; 15 System.out.println("Before: percent=" + percent); 16 tripleValue(percent); //调用 tripleValue 17 System.out.println("After: percent=" + percent); 18 19 /* 20 * Test 2: Methods can change the state of object parameters 21 */ //测试方法可以更改对象参数的状态 22 System.out.println("\nTesting tripleSalary:"); 23 Employee harry = new Employee("Harry", 50000); 24 System.out.println("Before: salary=" + harry.getSalary()); 25 tripleSalary(harry); //调用tripleSalary 26 System.out.println("After: salary=" + harry.getSalary()); 27 28 /* 29 * Test 3: Methods can't attach new objects to object parameters 30 */ //方法可以将新对象附加到对象参数 31 System.out.println("\nTesting swap:"); 32 Employee a = new Employee("Alice", 70000); 33 Employee b = new Employee("Bob", 60000); 34 System.out.println("Before: a=" + a.getName()); 35 System.out.println("Before: b=" + b.getName()); 36 swap(a, b); //用交换函数交换a,b 37 System.out.println("After: a=" + a.getName()); 38 System.out.println("After: b=" + b.getName()); 39 } 40 41 public static void tripleValue(double x) // doesn't work 42 { 43 x = 3 * x; 44 System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x); 45 } 46 47 public static void tripleSalary(Employee x) // works 48 { 49 x.raiseSalary(200); 50 System.out.println("End of method: salary=" + x.getSalary()); 51 } 52 53 public static void swap(Employee x, Employee y) 54 { 55 Employee temp = x; 56 x = y; 57 y = temp; 58 System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x.getName()); 59 System.out.println("End of method: y=" + y.getName()); 60 } 61 } 62 63 class Employee // simplified Employee class 64 { 65 private String name; 66 private double salary; //类的实例域定义来存放的需要操作的数据; 67 68 public Employee(String n, double s) 69 { 70 name = n; 71 salary = s; 72 } 73 74 public String getName() 75 { 76 return name; 77 } 78 79 public double getSalary() 80 { 81 return salary; 82 } 83 84 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 85 { 86 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 87 salary += raise; 88 } 89 }
其运行结果:
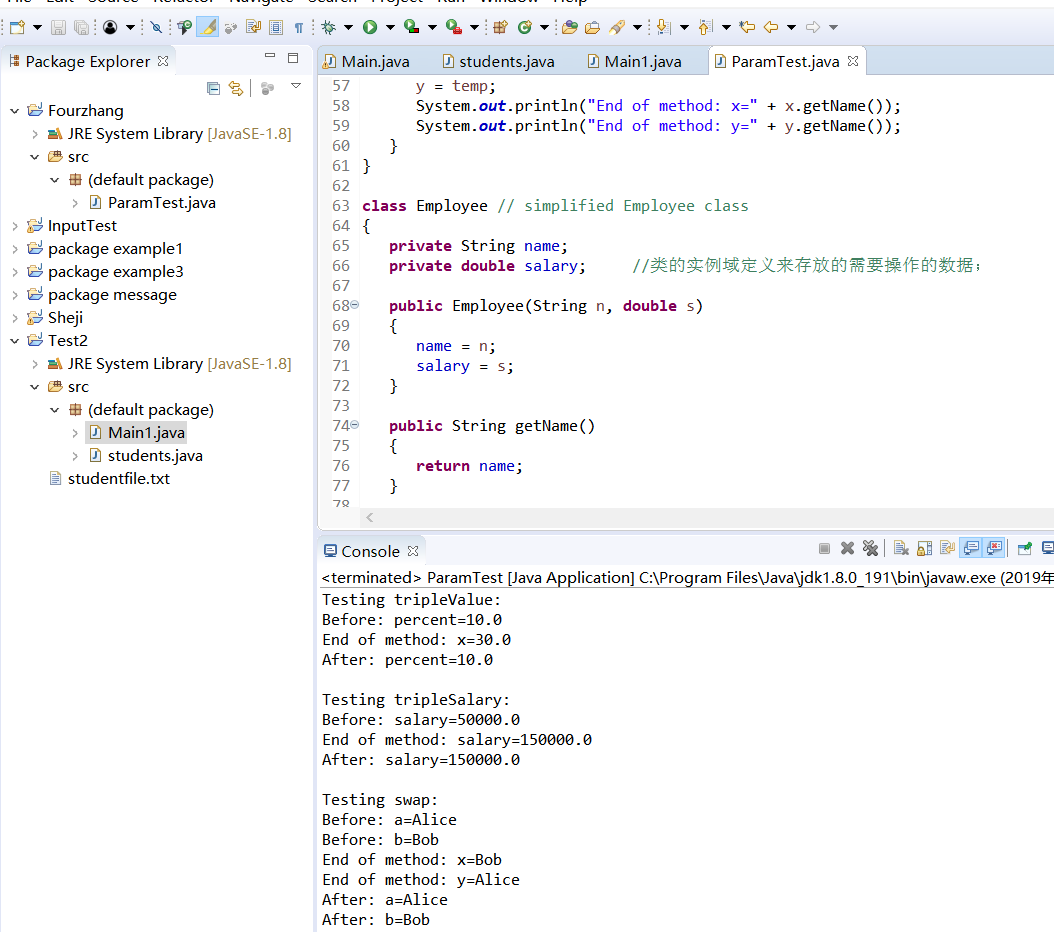
实验2 测试程序4(5分)
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-5(教材129);
l 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java用户自定义类的用法,掌握对象构造方法及对象使用方法,在相关代码后添加注释。
代码如下:
1 import java.util.*; 2 3 /** 4 * This program demonstrates object construction. 5 * @version 1.02 2018-04-10 6 * @author Cay Horstmann 7 */ 8 public class ConstructorTest 9 { 10 public static void main(String[] args) 11 { 12 // fill the staff array with three Employee objects 用三个employee对象填充staff数组 13 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; 14 15 staff[0] = new Employee("Harry", 40000); 16 staff[1] = new Employee(60000); //构造Employee数组,并有三个雇员对象; 17 staff[2] = new Employee(); 18 19 // print out information about all Employee objects 20 for (Employee e : staff) //打印每个雇员的信息 21 System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",id=" + e.getId() + ",salary=" 22 + e.getSalary()); 23 } 24 } 25 26 class Employee 27 { 28 private static int nextId; 29 30 private int id; 31 private String name = ""; // instance field initialization 实例字段初始化 32 private double salary; 33 34 // static initialization block 35 static 36 { 37 Random generator = new Random(); 38 // set nextId to a random number between 0 and 9999 将nextId设置为0到999之间的随机值 39 nextId = generator.nextInt(10000); 40 } 41 42 // object initialization block 对象 initialization块 43 { 44 id = nextId; 45 nextId++; 46 } 47 48 // three overloaded constructors //三个重载的构造 49 public Employee(String n, double s) 50 { 51 name = n; 52 salary = s; 53 } 54 55 public Employee(double s) 56 { 57 // calls the Employee(String, double) constructor 58 this("Employee #" + nextId, s); 59 } 60 61 // the default constructor 错误的构造器 62 public Employee() 63 { 64 // name initialized to ""--see above 名称初始化为同上 65 // salary not explicitly set--initialized to 0 工资未显示设置,初始化为0 66 // id initialized in initialization block id初始化 67 } 68 69 public String getName() 70 { 71 return name; //实例域name的访问器方法 72 } 73 74 public double getSalary() 75 { 76 return salary; //实例域salary的访问器方法 77 } 78 79 public int getId() 80 { 81 return id; //实例域id的访问器方法 82 } 83 }
运行结果:
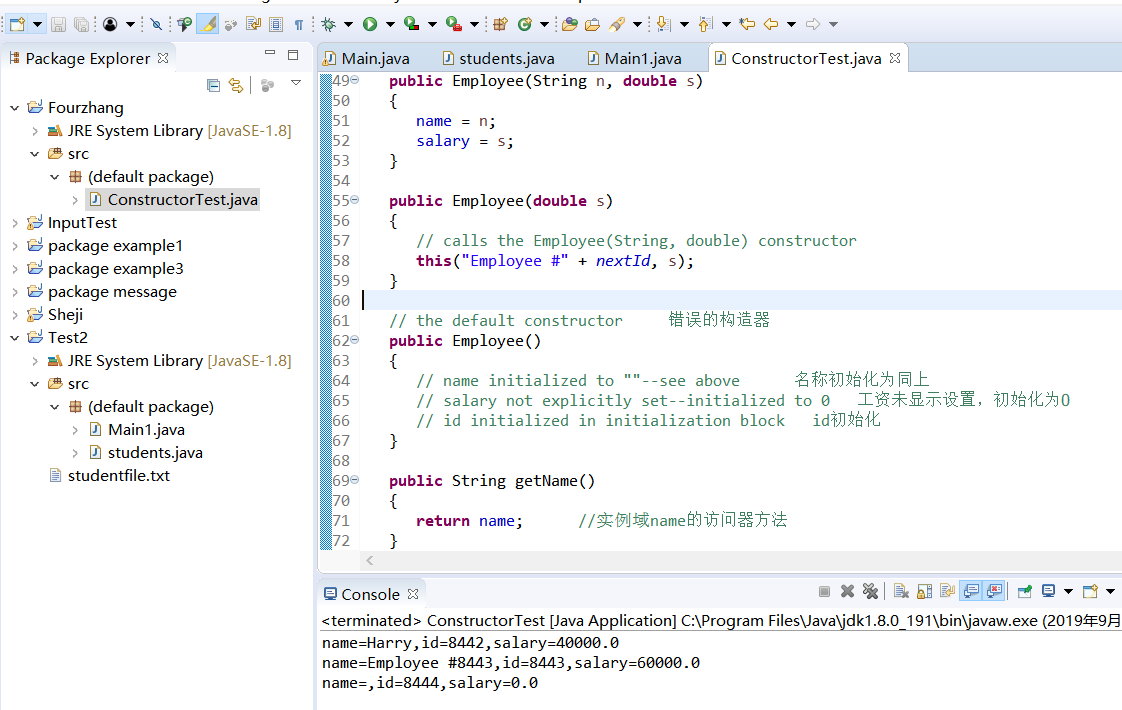
实验2 测试程序5(5分)
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-6、4-7(教材135);
结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java包的定义及用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
4-6 代码如下:
1 import com.horstmann.corejava.*; 2 // the Employee class is defined in that package 3 4 import static java.lang.System.*; 5 6 /** 7 * This program demonstrates the use of packages. 8 * @version 1.11 2004-02-19 9 * @author Cay Horstmann 10 */ 11 public class PackageTest 12 { 13 public static void main(String[] args) 14 { 15 // because of the import statement, we don't have to use 16 // com.horstmann.corejava.Employee here 因为import语句,不需要使用com.horstmann.corejava 17 Employee harry = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); 18 19 harry.raiseSalary(5); 20 21 // because of the static import statement, we don't have to use System.out here 22 out.println("name=" + harry.getName() + ",salary=" + harry.getSalary()); 23 } //由于使用了静态导入语句,在这里不需要使用System.out 24 }
运行结果:
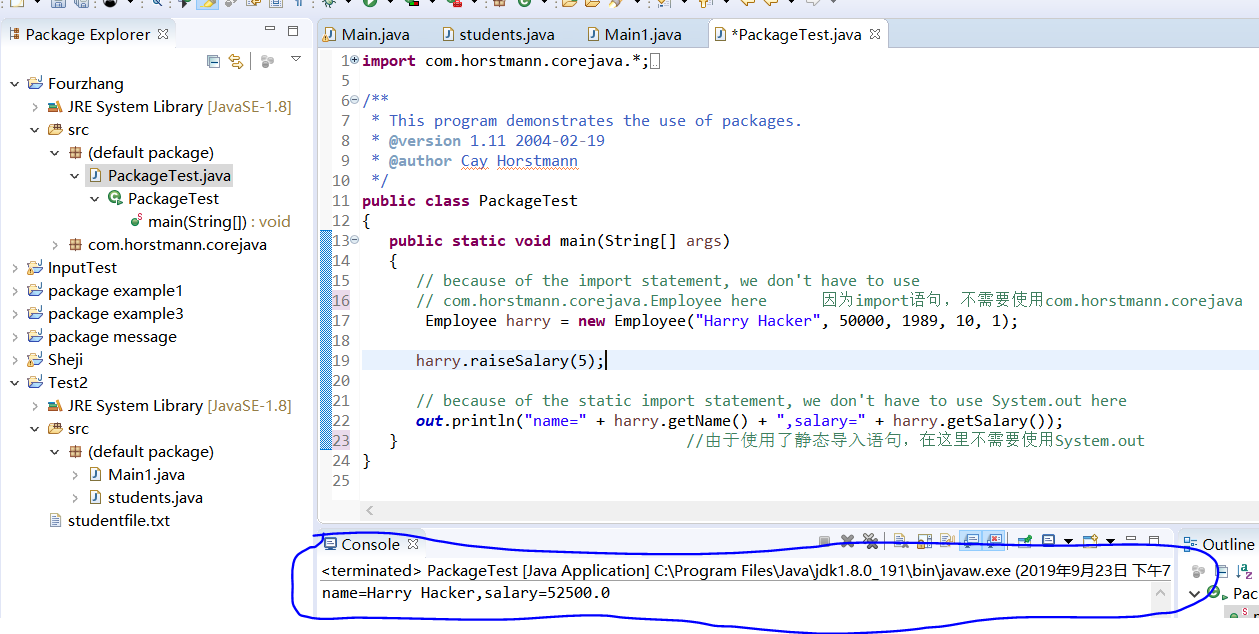
4-7 代码如下:
1 package com.horstmann.corejava; //将类放入包中 2 3 // the classes in this file are part of this package 这个文件中的类是这个包的一部分 4 5 import java.time.*; //java.time包的导入 6 7 // import statements come after the package statement 导入语句位于PACKAGE语句之后 8 9 /** 10 * @version 1.11 2015-05-08 11 * @author Cay Horstmann 12 */ 13 public class Employee 14 { 15 private String name; 16 private double salary; 17 private LocalDate hireDay; 18 19 public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) 20 { 21 this.name = name; //this用来引用当前对象 22 this.salary = salary; 23 hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); 24 } 25 26 public String getName() 27 { 28 return name; 29 } 30 31 public double getSalary() 32 { 33 return salary; 34 } 35 36 public LocalDate getHireDay() 37 { 38 return hireDay; 39 } 40 41 public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) 42 { 43 double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; 44 salary += raise; 45 } 46 }
其结果如图:
4. 实验总结:(10分)
这一章的学习内容很是重要,但同时学起来也比较困难复杂。在这一章里面,主要讲述的是对象与类,在第一小节里,是对面向对象程序设计的概述在这一节里,具体解释了什么是类,什么是对象等一系列内容,我根据老师在课堂上讲的,按照实验步骤进行程序的运行,在这一过程中,我遇到了很大的困难,我就觉得,要把学到的知识运用在实验中是非常困难的,辛亏在实验课上,有老师和助教的帮助,我解决了遇到的困难,但我同时也认识到,我的操作能力很是差,应该多加练习,为后续的学习做好准备。