Ansible 介绍
运维工具分类:
- agent: puppet, func
这类都需要在客户端上安装agent客户端
- agentless: ansible, fabric
这类是不需要在客户端上安装agent,只需要知道客户端的用户密码或者是秘钥验证就可以管理。
Ansible 特性:
- Minimal learning curve, auditability
入门很平滑,简单
- No bootstrapping
无需在客户端安装agent
- No DAG ordering, Fails Fast
无序,只需要按照自定义设定即可
- No agents (other than sshd) - 0 resourcee consumption when not in use
- No server
没有代理同时也没有服务器端,用户只需要手动发起命令来运行就可以了。
- No additional PKI
因为依赖于SSH工作,所以无序SSL证书的功能,
- Modules in any language
- SSH by default
模块化工作,模块可以是任何语言来编写,只需要遵循ansible的调用风格就可以。
- YAML, NOT code
简化的html或者json格式来定义文档或文本格式,非常容易学习
- Strong multi-tier solution
支持非常强大的多级的解决方案
Ansible的架构
下图:
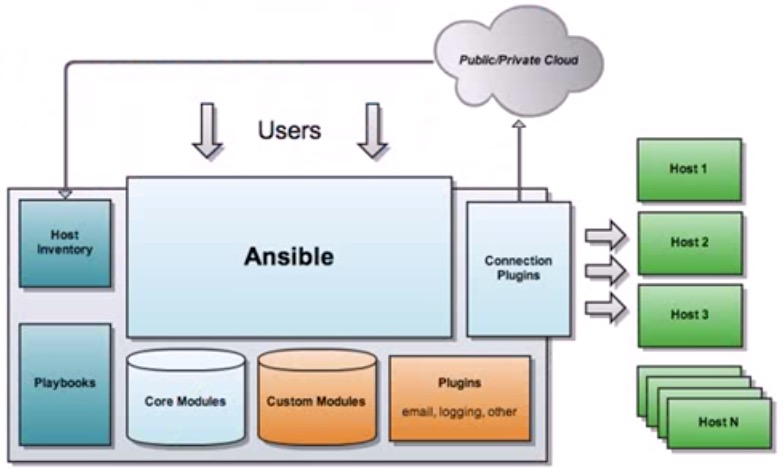
Ansible工作原理
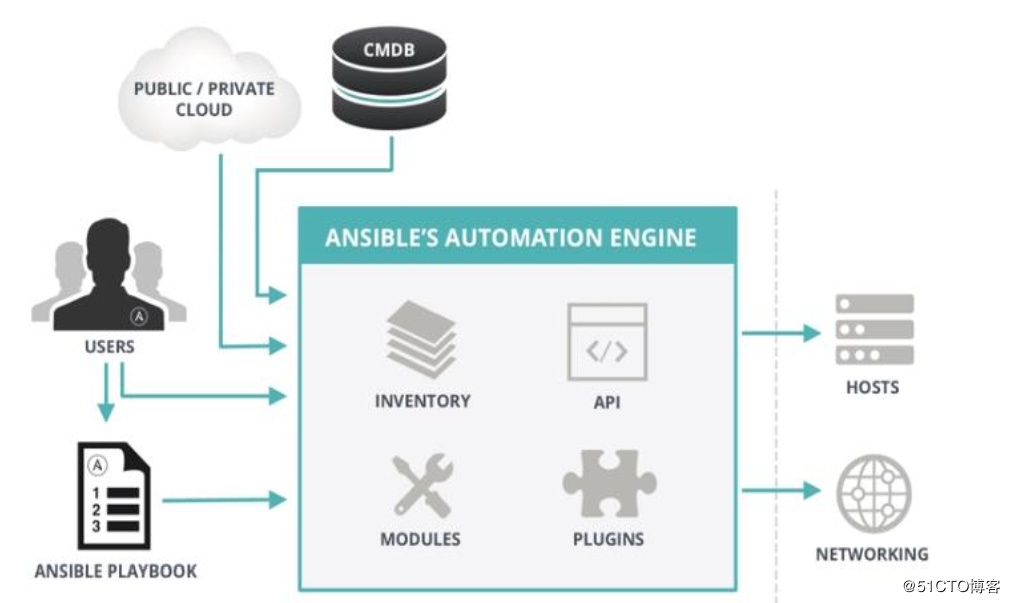
- ANSIBLE:
- 组合INVENTORY、 API、 MODULES、PLUGINS的绿框,可以理解为是ansible命令工具,其为核心执行工具
- PLAYBOOKS:
- 任务剧本(任务集),编排定义Ansible任务集的配置文件,由Ansible顺序依次执行,通常是JSON格式的YML文件
- INVENTORY:
- Ansible管理主机的清单/etc/anaible/hosts
- MODULES:
- Ansible执行命令的功能模块,多数为内置的核心模块,也可自定义,ansible-doc –l 可查看模块
- PLUGINS:
- 模块功能的补充,如连接类型插件、循环插件、变量插件、过滤插件等,该功能不常用
- API:
- 供第三方程序调用的应用程序编程接口
Ansible 特性:
- 基于Python语言实现,由Paramiko库实现连接管理主机,PyYAML和Jinjia2 三个关键模块。
- 部署简单,被管理节点无需安装agent
- 默认使用SSH协议
- 1 能够让管理机能够通过秘钥认证到每一台被管理的主机上
- 2 可以在inventory文件中指定被管理的用户密码,要确保该文件的安全
- 支持自定义模块: 支持各种编程语言
- 支持Playbook
- 基于“模块”完成各种“任务”
tasks
环境准备
| 系统版本 | 内核版本 | IP地址 |
|---|---|---|
| Centos 7.5 | 4.18.9-1.el7.elrepo.x86_64 | 10.0.0.3 |
| 角色 | IP | 用户 | 密码 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 管理节点 | 10.0.0.9 | root | 123456 |
| node-1 | 10.0.0.65 | root | 123456 |
| node-2 | 10.0.0.66 | root | 123456 |
备注 该系统采用MINI最小化安装,安装之后对系统进行了最基础的优化操作,操作过程点击这里
Ansible安装
可以使用编译安装和yum安装,本次使用较为简洁的yum安装,需要有
epel源,没有的可以在mirrors.aliyun.com上使用阿里云的epel源
在管理节点上操作
[root@node01 ~]# yum install ansible -y
...
Installed:
ansible.noarch 0:2.7.0-1.el7
Dependency Installed:
PyYAML.x86_64 0:3.10-11.el7 libtomcrypt.x86_64 0:1.17-26.el7 libtommath.x86_64 0:0.42.0-6.el7 libyaml.x86_64 0:0.1.4-11.el7_0
python-babel.noarch 0:0.9.6-8.el7 python-backports.x86_64 0:1.0-8.el7 python-backports-ssl_match_hostname.noarch 0:3.5.0.1-1.el7 python-cffi.x86_64 0:1.6.0-5.el7
python-enum34.noarch 0:1.0.4-1.el7 python-httplib2.noarch 0:0.9.2-1.el7 python-idna.noarch 0:2.4-1.el7 python-ipaddress.noarch 0:1.0.16-2.el7
python-jinja2.noarch 0:2.7.2-2.el7 python-keyczar.noarch 0:0.71c-2.el7 python-markupsafe.x86_64 0:0.11-10.el7 python-paramiko.noarch 0:2.1.1-4.el7
python-ply.noarch 0:3.4-11.el7 python-pycparser.noarch 0:2.14-1.el7 python-setuptools.noarch 0:0.9.8-7.el7 python-six.noarch 0:1.9.0-2.el7
python2-crypto.x86_64 0:2.6.1-15.el7 python2-cryptography.x86_64 0:1.7.2-2.el7 python2-jmespath.noarch 0:0.9.0-3.el7 python2-pyasn1.noarch 0:0.1.9-7.el7
sshpass.x86_64 0:1.06-2.el7
Complete!
[root@node02 ~]# yum info ansible
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirrors.aliyun.com
* extras: mirrors.aliyun.com
* updates: mirrors.aliyun.com
Available Packages
Name : ansible
Arch : noarch
Version : 2.7.0
Release : 1.el7
Size : 11 M
Repo : epel/x86_64
Summary : SSH-based configuration management, deployment, and task execution system
URL : http://ansible.com
License : GPLv3+
Description : Ansible is a radically simple model-driven configuration management,
: multi-node deployment, and remote task execution system. Ansible works
: over SSH and does not require any software or daemons to be installed
: on remote nodes. Extension modules can be written in any language and
: are transferred to managed machines automatically.
可以看到按装的ansible的版本是 2.7的版本
| 文件名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg | 主配置文件,配置ansible工作特性 |
| /etc/ansible/hosts | Inventory 被管理节点配置文件,主机清单 |
| /etc/ansible/roles | 存放角色的目录 |
| /usr/bin/ansible | 主程序,临时命令执行工具 |
| /etc/ansible/ansible-doc | 查看配置文档,模块功能查看工具 |
| /usr/bin/ansible-galaxy | 下载/上传优秀代码或Roles模块的官网平台 |
| /etc/ansible/ansible-playbook | 定制自动化任务,编排剧本工具 |
| /usr/bin/ansible-pull | 远程执行命令的工具 |
| /usr/bin/ansible-vault | 文件加密工具 |
配置秘钥管理
在管理节点上操作
生成密钥对,然后copy到node1 和nodde2 上使能够秘钥登陆
[root@node01 ~]# ssh-keygen -t rsa -P "" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:llhKseNPXM5O8O3M6lbz1sCj1p0eXtfED8d7Wrn/hRg root@node01
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| . |
| o |
| + o . |
| o * B . o |
| + S = E.. =|
| + o +oo+==|
| . ..==.OX|
| ..o =+X|
| oo. .o+=|
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@node01 ~]# ls -l .ssh/
total 8
-rw------- 1 root root 1675 Oct 15 13:27 id_rsa
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 393 Oct 15 13:27 id_rsa.pub
[root@node01 ~]# ssh-copy-id root@10.0.0.65
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '10.0.0.65 (10.0.0.65)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:Vu10B9+4iuvebISnNca1EPQtAaBJUjquSXY7AmfhRnc.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:a8:a0:32:f3:0a:07:25:1d:aa:0d:95:ec:cd:a8:c5:a0.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@10.0.0.65's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@10.0.0.65'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[root@node01 ~]# ssh-copy-id root@10.0.0.66
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '10.0.0.66 (10.0.0.66)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:Vu10B9+4iuvebISnNca1EPQtAaBJUjquSXY7AmfhRnc.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:a8:a0:32:f3:0a:07:25:1d:aa:0d:95:ec:cd:a8:c5:a0.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@10.0.0.66's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@10.0.0.66'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
# 测试连接10.0.0.65
[root@node01 ~]# ssh root@10.0.0.65
Last login: Fri Oct 12 14:15:30 2018 from 10.0.0.9
[root@node02 ~]# ip a | grep -w inet | tail -1 | awk '{print $2}'
10.0.0.65/24
# 测试连接10.0.0.66
[root@node01 ~]# ssh root@10.0.0.66
Last login: Fri Oct 12 14:15:29 2018 from 10.0.0.9
[root@node03 ~]# ip a | grep -w inet | tail -1 | awk '{print $2}'
10.0.0.66/24
配置Inventory文件
在/etc/ansible/hosts文件中,我们把65 和66 的两台机器配置成两个组
[root@node01 ~]# cd /etc/ansible/
[root@node01 ansible]# ls
ansible.cfg apache.yml cond.yml hosts nginx.retry nginx.yaml roles test.yml
[root@node01 ansible]# cp hosts hosts.bak
[root@node01 ansible]# cat hosts
# This is the default ansible 'hosts' file.
#
# It should live in /etc/ansible/hosts
#
# - Comments begin with the '#' character
# - Blank lines are ignored
# - Groups of hosts are delimited by [header] elements
# - You can enter hostnames or ip addresses
# - A hostname/ip can be a member of multiple groups
[webservs]
10.0.0.65
[dbservs]
10.0.0.66
这样,Inverteroy文件就配置完成
简单测试连通性
下面使用ansible演示连通性的测试
[root@node01 ansible]# ansible all -m ping
10.0.0.65 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
10.0.0.66 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
上面显示SUCCESS,表示都正常