SVG: scalable vector graphics
1、使用XML定义图形
2、图像可伸缩,尺寸更小,放大或者是改变尺寸时图片质量不会有所损失
3、除了IE需要安装插件,其他浏览器都支持SVG文件
4、svg文件需以.svg后缀保存
5、svg文件可以通过标签嵌入html文档:<embed>、<object>或者是<iframe>(注意使用object时不能使用脚本)
6、html5允许svg标签直接在HTML文件中使用
预定义形状:
<rect> : 矩形 x、y分别是距离左侧和顶端的位置;rx、ry用于产生圆角;fill-opacity和stroke-opacity分别定义填充颜色和笔触颜色的透明度 <circle>: cx、cy定义原点坐标(忽略时为0,0),r圆半径 <eclipse>:cx、cy原点坐标 rx、xy半径 <line>: x1、x2、y1、y2 x方向和开始和结束和y方向的开始和结束 <polyline>: points定义每个点的x左边和y坐标 <polygon>:多边形 同polyline用points定义坐标 <path> : 路径,稍微有点复杂如下: 大写表示绝对定位、小写表示相对定位
M = moveto L = lineto H = horizontal lineto V = vertical lineto C = curveto S = smooth curveto Q = quadratic Belzier curve T = smooth quadratic Belzier curveto A = elliptical Arc Z = closepath
滤镜:
1、可在每个svg元素上定义多个滤镜,
2、需在<defs>标签中嵌套定义svg滤镜,将filter标签嵌套在defs中eg:
<defs>
<filter id = "gaus_blur">
<feGaussianBlur in="SourceGraphic" stdDeviation="3"/> //in定义由整个图像创建效果
</filter>
</defs>
3、用filter定义的同一滤镜可以被多个元素使用,使用时filter:url方式eg:引用上面的滤镜<filter="url(#gaus_blur)">
4、支持的滤镜如下:
feBlend
feColorMatrix
feComponentTransfer
feComposite
feConvolveMatrix
feDiffuseLighting
feDisplacementMap
feFlood
feGaussianBlur
feImage
feMerge
feMorphology
feOffset
feSpecularLighting
feTile
feTurbulence
feDistantLight
fePointLight
feSpotLight
渐变: 支持线性渐变和放射渐变
<linearGradient>:线性渐变,也是必须嵌套在<defs>标签中,x1,x2,y1,y2定义渐变的开始和结束
eg:
<defs>
<linearGradient id="orange_red" x1="0%" y1="0%" x2="100%" y2="0%">
<stop offset="0%" style="stop-color:rgb(255,255,0);stop-opacity:1"/>
<stop offset="100%" style="stop-color:rgb(255,0,0);stop-opacity:1"/>
</linearGradient>
</defs>
<ellipse cx="200" cy="190" rx="85" ry="55"
style="fill:url(#orange_red)"/>
<radialGradient>: 放射性渐变,也是必须嵌套在<defs>标签中
eg:
<defs> <radialGradient id="grey_blue" cx="50%" cy="50%" r="50%" fx="50%" fy="50%"> <stop offset="0%" style="stop-color:rgb(200,200,200); stop-opacity:0"/> <stop offset="100%" style="stop-color:rgb(0,0,255); stop-opacity:1"/> </radialGradient> </defs> <ellipse cx="230" cy="200" rx="110" ry="100" style="fill:url(#grey_blue)"/>
例子:
eg1:svg文件形式
<?xml version="1.0"> <svg width="100%" height="100%" version="1.1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"> <circle cx="100" cy="50" r="40" stroke="black" stroke-width="2" fill="red"/> </svg>
//stroke控制轮廓
结果:红色圆,边线为黑色
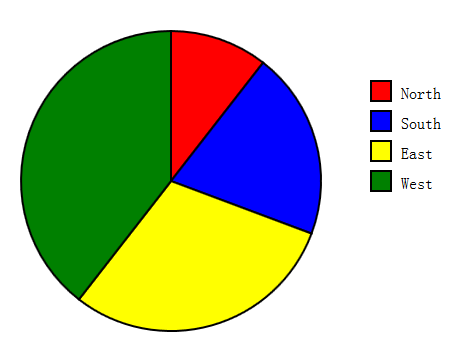
eg2:饼图:
/* 创建一个svg元素,并在其中绘制一个饼图 参数: data:用于绘制的数字类型的数组,数组的每一项都表示饼状图的一个栔 width,height: SVG图形的高和宽,单位为像素 cx、cy、r:饼状图的圆心及半径 colors:包含html颜色信息的数组,每种颜色代表饼状图的每一个栔的颜色 labels:标签数组,说明饼状图的每一个栔代表的含义 lx、ly:饼状图的左上角 */ function pieChart(data, width, height, cx, cy, r, colors, labels, lx, ly){ //svg元素的xml命名空间 var svgns = "http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"; //创建svg元素 var chart = document.createElementNS(svgns, "svg:svg"); chart.setAttribute("width", width); chart.setAttribute("height", height); chart.setAttribute("viewBox", "0 0 " + width + " " + height); //viewBox为坐标系 //累加data的值,以便于知道饼状图的大小 var total = 0; for(var i = 0; i < data.length; i++){ total += data[i]; } //计算饼状图的每个分片的大小,角度以弧度制计算 var angles = []; for(var i = 0; i < data.length; i++){ angles[i] = data[i]/total*Math.PI*2; } //栔的开始位置和结束位置以及和圆交汇的两个点的坐标位置,12点钟放 var startAngle = 0, endAngle, x1, y1, x2, y2; for(var i = 0; i < data.length; i++){ endAngle = startAngle + angles[i]; x1 = cx + r*Math.sin(startAngle); y1 = cy - r*Math.cos(startAngle); x2 = cx + r*Math.sin(endAngle); y2 = cy - r*Math.cos(endAngle); //判断角度是否大于半圆 var big = 0; if(endAngle - startAngle > Math.PI){ big = 1; } //使用<svg:path>描述栔,使用createElementNS创建该元素 var path = document.createElementNS(svgns, "path"); //设置路径 var d = "M " + cx + "," + cy + " L " + x1 + "," + y1 + " A " + r + "," + r + " 0 " + big + " 1 " + x2 + "," + y2 + " Z"; path.setAttribute("d", d); path.setAttribute("fill", colors[i]); path.setAttribute("stroke", "black"); path.setAttribute("stroke-width", "2"); chart.appendChild(path); //下一个栔从此处开始 startAngle = endAngle; //绘制小方格表示图例 var icon = document.createElementNS(svgns, "rect"); icon.setAttribute("x", lx); icon.setAttribute("y", ly + 30*i); icon.setAttribute("width", 20); icon.setAttribute("height", 20); icon.setAttribute("fill", colors[i]); icon.setAttribute("stroke", "black"); icon.setAttribute("stroke-width", "2"); chart.appendChild(icon); //为右边的小方格添加标签 var label = document.createElementNS(svgns, "text"); label.setAttribute("x", lx + 30); label.setAttribute("y", ly + 30*i + 18); label.setAttribute("font-family", "sans-serif"); label.setAttribute("font-size", "16"); label.appendChild(document.createTextNode(labels[i])); chart.appendChild(label); } return chart; }
<body onload = "document.body.appendChild(pieChart([12,23,34,45], 640, 400, 200, 200, 150,['red', 'blue', 'yellow', 'green'],['North', 'South', 'East', 'West'],400,100))">
结果:
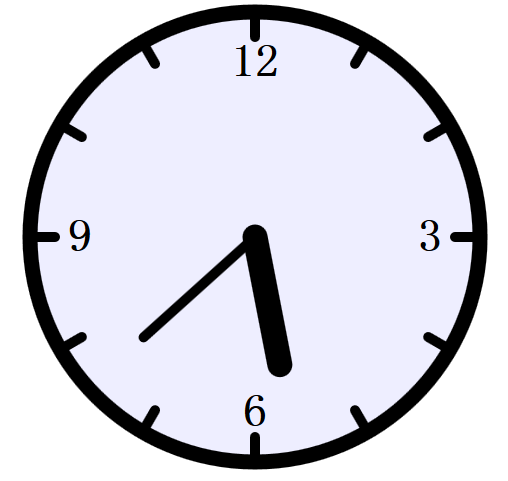
eg3:时钟:
function svgClock(){ var now = new Date(); var min = now.getMinutes(); var hour = (now.getHours() % 12) + min/60; var minAngle = min * 6; //每6度一分钟 var hourAngle = hour * 30; //每30度一小时 var minHand = document.getElementById("minuteHand"); var hourHand = document.getElementById("hourHand"); var clock = document.getElementById("clock"); minHand.setAttribute("transform", "rotate(" + minAngle + ",50,50)"); hourHand.setAttribute("transform", "rotate(" + hourAngle + ",50,50)"); clock.setAttribute("fill","#eef" ); //每一分钟更新下时间 setTimeout(svgClock, 60000); }
#clock { stroke: black; /*stroke定义轮廓颜色*/ stroke-linecap: round; /*圆角*/ fill: #eef; /*浅蓝色背景*/ } #face { stroke-width : 3px; /*时钟的外边框*/ } #ticks { stroke-width: 2; /*标记每个小时的线段*/ } #hourHand { stroke-width: 5px;. } #minuteHand { stoke-width: 3px; } #numbers { font-family: sans-resif; font-size: 7pt; font-weight: bold; text-anchor: middle; stroke: none; fill: black; }
<body onload="svgClock()"> <svg id="clock" viewBox="0 0 100 100" width="500" height="500"> <defs> <filter id="shadow" x="-50%" y="-50%" width="500" height="500"> <feGaussianBlur in="SourceAlpha" stdDeviation="1" result="blur"> <!-- 设置滤镜 --> <feOffset in="blur" dx="1" dy="1" result="shadow"/> <feMerge> <feMergeNode in="SourceGraphic"/> <feMergeNode in="shadow"/> </feMerge> </filter> </defs> <circle id="face" cx="50" cy="50" r="45"/> <!-- 钟面 --> <g id="ticks"> <!-- 12小时的刻度 g用于将元素组合 --> <line x1="50" y1="5.000" x2="50.00" y2="10.00"/> <line x1="72.50" y1="11.03" x2="70.00" y2="15.36"/> <line x1="88.97" y1="27.50" x2="84.64" y2="30.00"/> <line x1="95.00" y1="50.00" x2="90.00" y2="50.00"/> <line x1="88.97" y1="72.50" x2="84.64" y2="70.00"/> <line x1="72.50" y1="88.97" x2="70.00" y2="84.64"/> <line x1="50.00" y1="95.00" x2="50.00" y2="90.00"/> <line x1="27.50" y1="88.97" x2="30.00" y2="84.64"/> <line x1="11.03" y1="72.50" x2="15.36" y2="70.00"/> <line x1="5.000" y1="50.00" x2="10.00" y2="50.00"/> <line x1="11.03" y1="27.50" x2="15.36" y2="30.00"/> <line x1="27.50" y1="11.03" x2="30.00" y2="15.36"/> <g/> <g id="numbers"> <!-- 标记重要的刻度值,3,6,9,12等 --> <text x="50" y="18">12</text> <text x="85" y="53">3</text> <text x="50" y="88">6</text> <text x="15" y="53">9</text> </g> <g id="hands" > <!-- 初始绘制成竖直的指针,之后通js旋转,并且给指针加上阴影 --> <line id="hourHand" x1="50" y1="50" x2="50" y2="24"/> <line id="minuteHand" x1="50" y1="50" x2="50" y2="20"/> </g> </svg> </body>
结果: