声明:本文转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/litianxiang_kaola/article/details/79481422
这里介绍两种整合SpringBoot和Mybatis的模式,分别是“全注解版” 和 “注解xml合并版”。
前期准备
开发环境
- 开发工具:IDEA
- JDK:1.8
- 技术:SpringBoot、Maven、Mybatis
创建项目
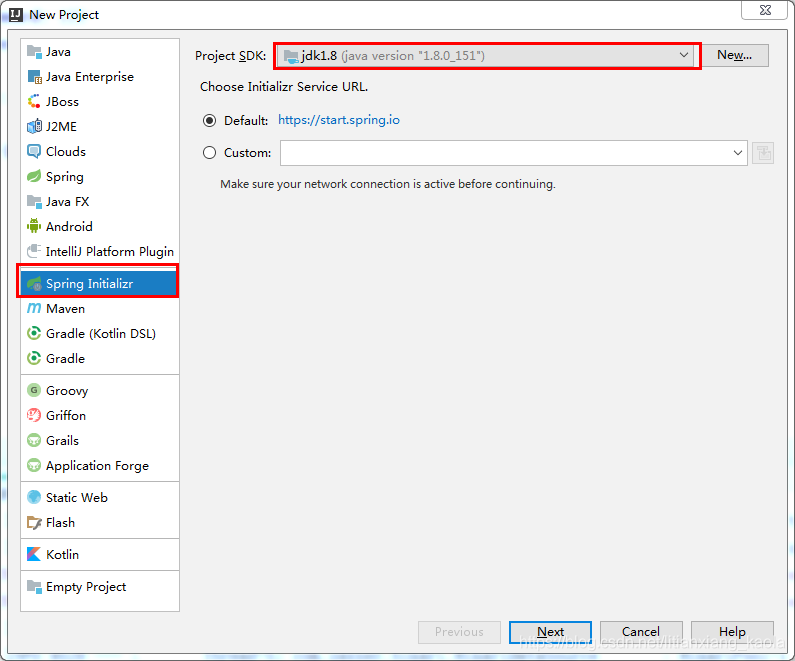
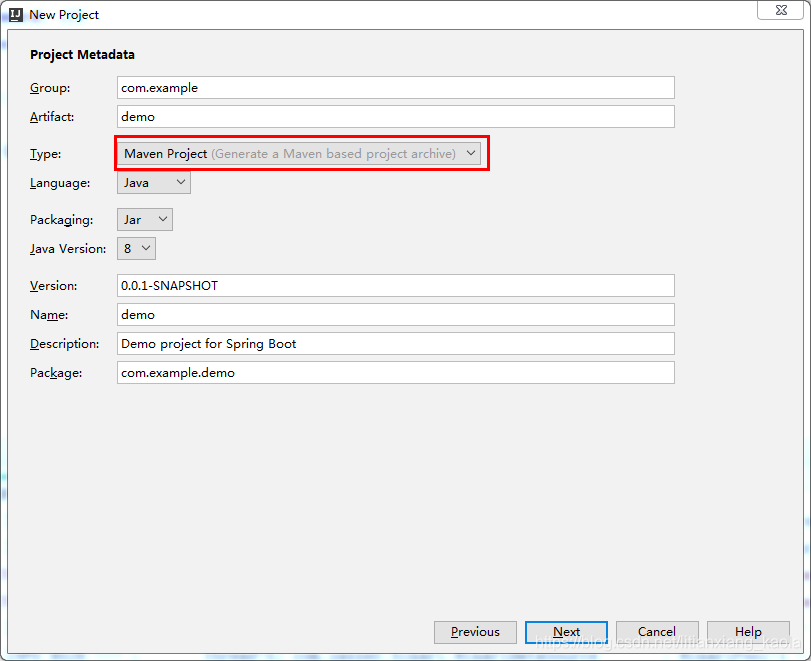
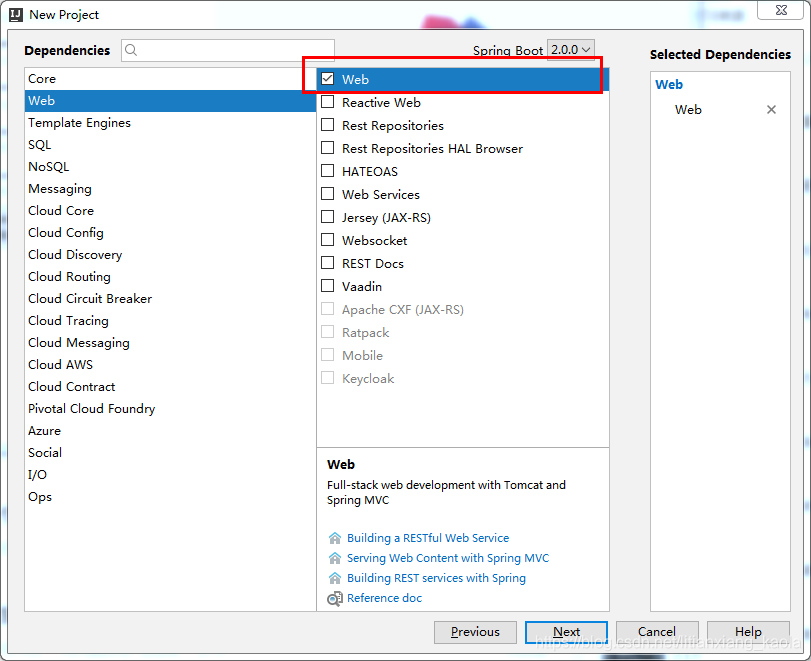
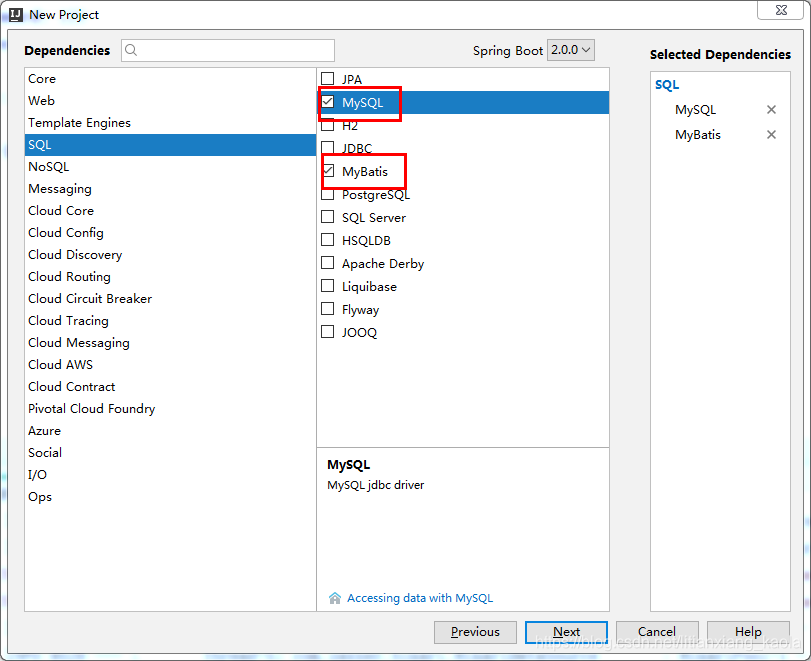

项目结构
Maven依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>demo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.3.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
全注解版
SpringBoot配置文件
这里使用yml格式的配置文件,将application.properties改名为application.yml。
#配置数据源 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dianping?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 username: root password: 123 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
SpringBoot会自动加载application.yml相关配置,数据源就会自动注入到sqlSessionFactory中,sqlSessionFactory会自动注入到Mapper中。
实体类
public class Happiness { private Long id; private String city; private Integer num; //getters、setters、toString }
映射类
@Mapper public interface HappinessDao { @Select("SELECT * FROM happiness WHERE city = #{city}") Happiness findHappinessByCity(@Param("city") String city); @Insert("INSERT INTO happiness(city, num) VALUES(#{city}, #{num})") int insertHappiness(@Param("city") String city, @Param("num") Integer num); }
Service类
事务管理只需要在方法上加个注解:@Transactional
@Service public class HappinessService { @Autowired private HappinessDao happinessDao; public Happiness selectService(String city){ return happinessDao.findHappinessByCity(city); } @Transactional public void insertService(){ happinessDao.insertHappiness("西安", 9421); int a = 1 / 0; //模拟故障 happinessDao.insertHappiness("长安", 1294); } }
Controller类
@RestController @RequestMapping("/demo") public class HappinessController { @Autowired private HappinessService happinessService; @RequestMapping("/query") public Happiness testQuery(){ return happinessService.selectService("北京"); } @RequestMapping("/insert") public Happiness testInsert(){ happinessService.insertService(); return happinessService.selectService("西安"); } }
测试
http://localhost:8080/demo/query
http://localhost:8080/demo/insert
注解xml合并版
项目结构
SpringBoot配置文件
#配置数据源
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dianping
username: root
password: 123
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#指定mybatis映射文件的地址
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
映射类
@Mapper public interface HappinessDao { Happiness findHappinessByCity(String city); int insertHappiness(HashMap<String, Object> map); }
映射文件
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.dao.HappinessDao"> <select id="findHappinessByCity" parameterType="String" resultType="com.example.demo.domain.Happiness"> SELECT * FROM happiness WHERE city = #{city} </select> <insert id="insertHappiness" parameterType="HashMap" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> INSERT INTO happiness(city, num) VALUES(#{city}, #{num}) </insert> </mapper>
Service类
事务管理只需要在方法上加个注解:@Transactional
@Service public class HappinessService { @Autowired private HappinessDao happinessDao; public Happiness selectService(String city){ return happinessDao.findHappinessByCity(city); } @Transactional public void insertService(){ HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("city", "西安"); map.put("num", 9421); happinessDao.insertHappiness(map); int a = 1 / 0; //模拟故障 happinessDao.insertHappiness(map); } }
Controller类
@RestController @RequestMapping("/demo") public class HappinessController { @Autowired private HappinessService happinessService; @RequestMapping("/query") public Happiness testQuery(){ return happinessService.selectService("北京"); } @RequestMapping("/insert") public Happiness testInsert(){ happinessService.insertService(); return happinessService.selectService("西安"); } }
SpringBoot整合Mybatis打印sql语句
如果使用的是application.properties文件,加入如下配置
logging.level.com.example.demo.mapper=debug
logging.level,后面的路径指的是mybatis对应的方法接口所在的包。并不是mapper.xml所在的包。
如果使用的是application.yml文件,加入如下配置:
logging:
level:
com.example.demo.mapper: debug
在mybatis中@MapperScan和@Mapper的区别
在使用Mybatis时需要把映射类*.mapper注册到Bean工厂中,这时候我们有两种方式可以注入,一种是在每个*.mapper类上加上@Mapper注解,另一种就是在Application启动类上加@MapperScan注解来扫描类
(1)方式一:使用@Mapper注解
为了让DemoMapper能够让别的类进行引用,我们可以在DemMapper类上添加@Mapper注解:

直接在Mapper类上面添加注解@Mapper,这种方式要求每一个mapper类都需要添加此注解,比较麻烦。
(2)方式二:使用@MapperScan注解
通过使用@MapperScan可以指定要扫描的Mapper类的包的路径,比如:

使用@MapperScan注解多个包
