1. 删除列层次化索引
用pandas利用df.groupby.agg() 做聚合运算时遇到一个问题:产生了列方向上的两级索引,且需要删除一级索引。具体代码如下:
# 每个uesr每天消费金额统计:和、均值、最大值、最小值、消费次数、消费种类、 action_info = student_action.groupby(['outid','date']).agg({'opfare':['sum','mean','max','min'], 'acccode':['count','unique'],}).reset_index()
action_info 表结果如下:

删除列的层次化索引操作如下:
# 列的层次化索引的删除 levels = action_info.columns.levels labels = action_info.columns.labels print(levels,labels) action_info.columns = levels[1][labels[1]]
2. agg()与apply()的区别
以 student_action表为例:
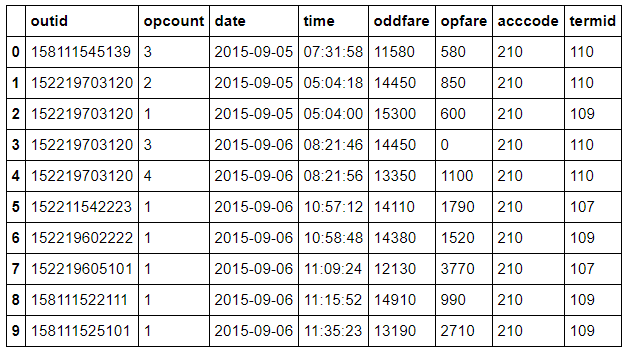
apply()方法:
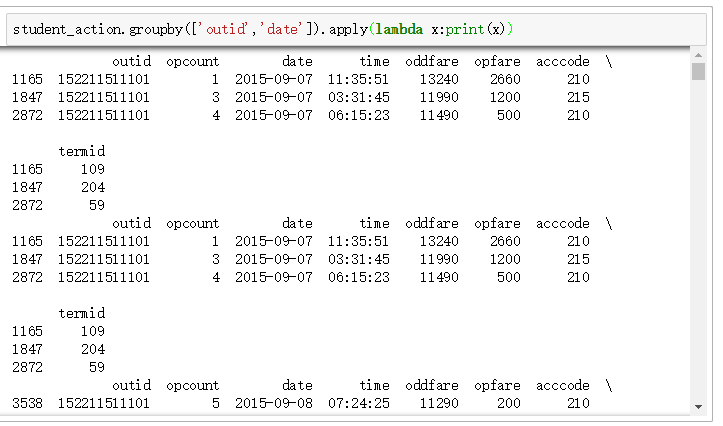
agg()方法:
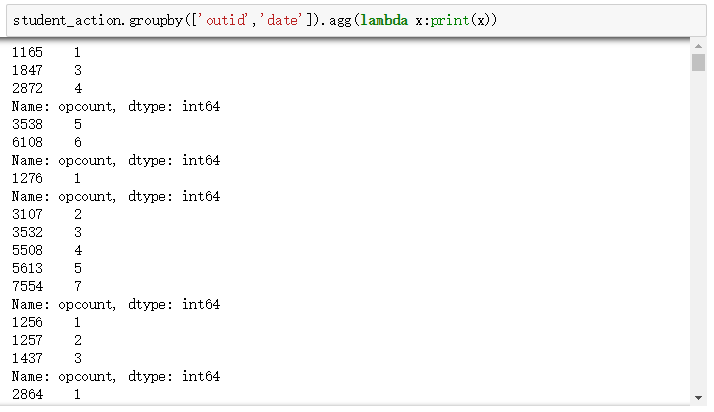
可以看到,apply()可以展示所有维度的数据,而agg()仅可以展示一个维度的数据。
事实上,如果值是一维数组,在利用完特定的函数之后,能做到简化的话,agg就能调用,反之,如果比如自定义的函数是排序,或者是一些些更复杂统计的函数,当然是agg所不能解决的,这时候用apply就可以解决。因为他更一般化,不存在什么简化,什么一维数组,什么标量值。且apply会将当前分组后的数据一起传入,可以返回多维数据。
例子:根据 student_action表,统计每个学生每天最高使用次数的终端、最低使用次数的终端以及最高使用次数终端的使用次数、最低使用次数终端的使用次数。
针对这个例子,有两种方法:
方法一:low到爆 永不使用!!
1. 构造每个用户每天的终端列表,需要one-hot termid
2. 构造groupby.agg()所使用的方法
2.1 列表模糊查找,找到包含'termid_'的字段名
termid_features = [x for i,x in enumerate(student_termid_onehot.columns.tolist()) if x.find('termid_')!=-1]
2.2 构造指定长度,指定元素的列表
sum_methods= ['sum'for x in range(0, len(termid_features))]
2.3 agg_methods=dict(zip(termid_features,sum_methods))
3. 每个学生每天的终端使用次数明细表
find_termid_df = student_termid_onehot.groupby(['outid','date']).agg(agg_methods).reset_index()
4. 找到student_termid_onehot中包含 'termid_'字段元素的最大值对应的字段名
4.1 构造列表保存
4.2 遍历每行数据,构造dict,并过滤value =0.0 的 k-v
4.3 找到每个dict的value值最大的key
max(filtered_statics_dict, key=filtered_statics_dict.get)
方法二:优雅直观
def transmethod(df): """ 每个用户每天消费记录最大值、最高使用次数的终端、最低使用次数的终端 以及最高使用次数终端的使用次数、最低使用次数终端的使用次数。 df type: outid opcount date time oddfare opfare acccode 3538 152211511101 5 2015-09-08 07:24:25 11290 200 210 6108 152211511101 6 2015-09-08 12:09:01 10440 850 210 termid 3538 13 6108 39 """ # 每日最大消费额 maxop = df['opfare'].max() statics_dict={} for i in set(df['acccode'].tolist()): statics_dict[i] = df['acccode'].tolist().count(i) highest_termid = max(statics_dict, key=statics_dict.get) lowhest_termid = min(statics_dict, key=statics_dict.get) highest_termid_freq = statics_dict[highest_termid] lowhest_termid_freq = statics_dict[lowhest_termid] return maxop,highest_termid,highest_termid_freq,lowhest_termid,lowhest_termid_freq
groupby.apply() 组合使用:
pd.DataFrame(student_action.groupby(['outid','date']).apply(lambda x:transmethod(x)))
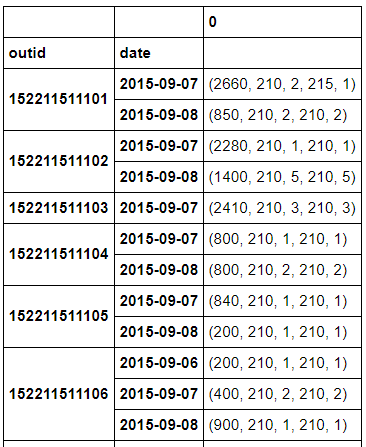
可以发现,apply()方法要比agg()方法灵活的多的多!
3. 总结
- 列层次索引的删除
- 列表的模糊查找方式
- 查找dict的value值最大的key 的方式
- 当做简单的聚合操作(max,min,unique等),可以使用agg(),在做复杂的聚合操作时,一定使用apply()