一:springmvc运行过程:
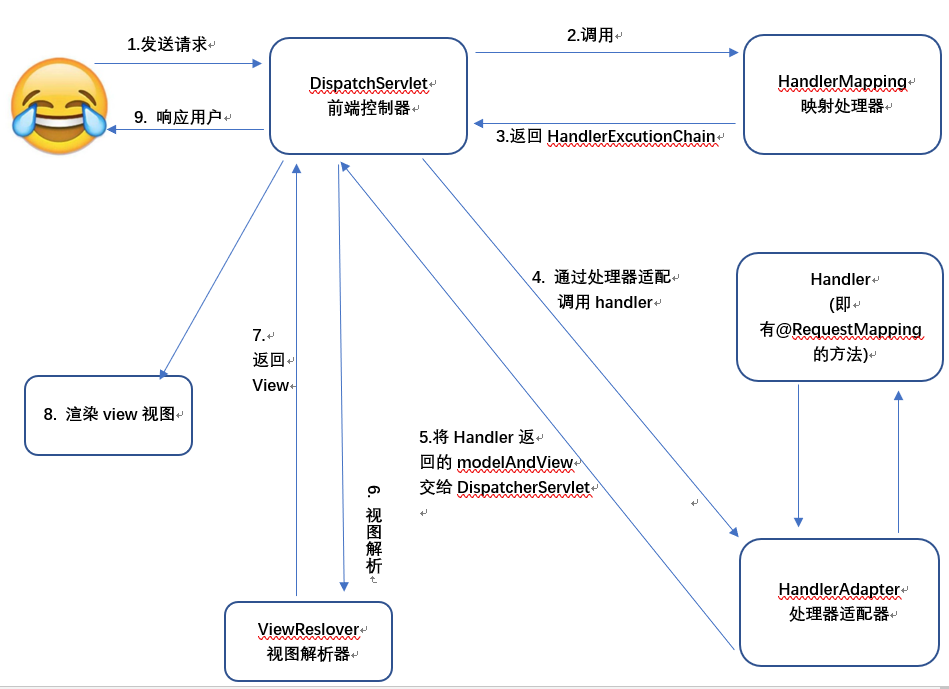
1. dispatcherServlet 通过 HandlerMapping 找到controller
2. controller经过后台逻辑处理得到结果集modelandview
3. 视图解析器解析model,渲染view展示页面。
二:springmvc容器是什么:
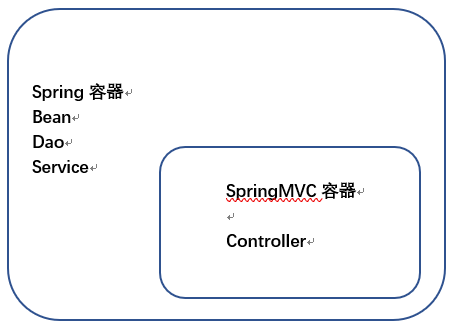
很多人喜欢把spring和springmvc混为一谈, 其实它们是完全不同的两个概念。spring主要是创建对像管理依赖的; 而springmvc是一种mvc分层思想将功能模块化,处理用户请求的。而且spring和springmvc是有父子容器关系存在的。子容器可以获取父容器中的对象(可以理解成面向对象中的继承),例如controller通过@Autowired注入spring中的对象, 而如果把controller交给spring来管理,就会出现404异常,因为spring初始化只管理bean,并不会把url和method关联起来。
三:springmvc案例解析:
3.1 自定义springmvc注解@MyController和@MyRequestMapping

3.2 实现过程
public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet { // springmvc 容器对象 key:类名id ,value bean对象 private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> springmvcBeans = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(); // springmvc 容器对象 keya:请求地址 ,vlue 类对象 private ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> urlBeans = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(); // springmvc 容器对象 key:请求地址 ,value 方法名称 private ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> handlermapping = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, String>(); /** * 容器启动时 */ @Override public void init() throws ServletException { // 1. 扫描当前包(及子包)下面的所有类 List<Class<?>> classes = ClassUtil.getClasses("org.wulei.controller"); try { // 将这些类放到mvc容器 this.findClassMVCAnnotation(classes); } catch (Exception e) { } // 将url和方法绑定起来 this.headlerMapping(); } /* 初始化有controller注解的bean,放入mvc容器。*/ public void findClassMVCAnnotation(List<Class<?>> classes) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException { for (Class<?> classInfo : classes) { // 2. 判断类上是否有加上controller注解 MytController myController = classInfo.getDeclaredAnnotation(MytController.class); if (myController != null) { // 默认bean名称是类名小写 String beanName = ClassUtil.toLowerCaseFirstOne(classInfo.getSimpleName()); // 3. 实例化对象 , 放入mvc容器 Object object = ClassUtil.newInstance(classInfo); springmvcBeans.put(beanName, object); } } } /* 通过handlerMapping将url和method关联起来 */ public void headlerMapping() { // 4. 遍历mvc的bean容器所有的类 for(Map.Entry<String, Object> mvcBean : springmvcBeans.entrySet()) { Object object = mvcBean.getValue(); Class<? extends Object> classInfo = object.getClass(); // 5. 判断类上面是否有url映射(即:@RequestMapping注解) MyRequestMapping requestMapping = classInfo.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class); // 6. 获取类上的url地址 String baseUrl = ""; if(requestMapping != null) { baseUrl = requestMapping.value(); } // 7. 获取方法上的url映射路径 Method[] methods = classInfo.getDeclaredMethods(); if(methods.length>0) { for(Method method : methods) { MyRequestMapping methodRequestMapping = method.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class); if(methodRequestMapping != null) { // 8. 将 classUrl 和 methodUrl 拼接起来,得到完整url路径。 String methodUrl = baseUrl+methodRequestMapping.value(); // 9. 将url和method绑定起来,存入容器。 urlBeans.put(methodUrl, object); handlermapping.put(methodUrl, method.getName()); /** * 到上面容器就就初始化完成,可以对外提供服务了。 * 现在可以每个方法断点调试看运行过程。 */ } } } } } /** * 处理用户请求 */ @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { // 1. 获取请求url地址 String url = req.getRequestURI(); if(StringUtils.isEmpty(url)) return; // 2. 通过url获取容器中的controller对象 Object object = urlBeans.get(url); if(object == null) { resp.getWriter().println("ERROR: not found 404 url"); return; } // 3. 使用url获取方法. String methodName = handlermapping.get(url); if(StringUtils.isEmpty(methodName)) resp.getWriter().println("ERROR: not found method"); // 4. java反射获取被调用的方法 String resultPage = null; try { Method method = object.getClass().getMethod(methodName); resultPage = (String) method.invoke(object); resp.getWriter().println(resultPage); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 5.调用视图转换器渲染给页面展示 this.myResourceViewResolver(resultPage, req, resp); } /** * 视图解析器 */ private void myResourceViewResolver(String pageName, HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException { // 根路径 String prefix = "/"; String suffix = ".jsp"; req.getRequestDispatcher(prefix + pageName + suffix).forward(req, res); } @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { doPost(req, resp); } }
3.3 测试 (正确的url会跳转到相应页面,错误的url会找不到路径)

四:源码解析
4.1 springmvc初始化阶段
4.1.1 我们在用springmvc的时候, 首先会配置 dispatcherServlet,它会拦截符合规则的url请求。
<servlet> <servlet-name>WEB</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!-- 指定springmvc扫描文件 --> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:config/spring-*.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!-- 优先级 --> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <!-- 拦截规则 --> <servlet-name>WEB</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
4.1.2 可以看出 dispatcherServlet 最终还是继承于httpservlet, 说明它也会满足servlet的工作原理。
Servlet 生命周期:
Servlet 加载—>实例化—>服务—>销毁。
init():在Servlet的生命周期中,仅执行一次init()方法。负责初始化Servlet对象。
service():负责响应客户的请求。每次请求都会调用相应的doGet/doPost功能。
destroy():仅执行一次,在服务器端停止且卸载Servlet时执行该方法,负责释放占用的资源。

4.1.3 HttpServletBean 重写了 httpservlet 的 init()方法, 通过initServletBean() 方法来初始化bean, 具体实现在子类FrameworkServlet中。
/** * Map config parameters onto bean properties of this servlet, and * invoke subclass initialization. * @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required * properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails. */ @Override public final void init() throws ServletException { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'"); } // 初始化DespatcherService的配置参数 try { PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); throw ex; } // 让子类来初始化bean initServletBean(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully"); } }
4.1.4 FrameworkServlet重写了initServletBean(),并在这个方法中调用了initWebApplicationContext()方法
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { // 获取 ContextLoaderListener 初始化 WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // 将 Spring 的容器设为 SpringMVC 容器的父容器 cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null) { wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null) { wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // dispatcherServlet 重写这个方法 onRefresh(wac); } if (this.publishContext) { // 发布这个容器到 ServletContext 中 String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } return wac; }
4.1.5 dispatcherServlet 重写onRefresh(),调用initHandlerMappings将url和method关联起来
/** * Initialize the HandlerMappings used by this class. * <p>If no HandlerMapping beans are defined in the BeanFactory for this namespace, * we default to BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping. */ private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) { this.handlerMappings = null; if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) { // 获取HandlerMapping实例 Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values()); // 排序 OrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later. } } // Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering // a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found. if (this.handlerMappings == null) { this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default"); } } }
4.2 springmvc运行阶段
4.2.1 上面已经说过每次请求都会执行servlet的service()方法,FrameworkServlet重写了这个方法。
/** * Override the parent class implementation in order to intercept PATCH * requests. */ @Override protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // 获取请求方式例如 get / post String method = request.getMethod(); if (method.equalsIgnoreCase(RequestMethod.PATCH.name())) { processRequest(request, response); } else { super.service(request, response); } }
4.2.2 然后会根据请求方式去httpsrevlet中调用具体的方法。
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String method = req.getMethod(); // get请求 if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) { long lastModified = getLastModified(req); if (lastModified == -1) { // servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason // to go through further expensive logic doGet(req, resp); } else { long ifModifiedSince; try { ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE); } catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) { // Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set ifModifiedSince = -1; } if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) { maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); doGet(req, resp); } else { resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED); } } // head请求 } else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) { long lastModified = getLastModified(req); maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); doHead(req, resp); // post请求 } else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) { doPost(req, resp); // put请求 } else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) { doPut(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) { doDelete(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) { doOptions(req,resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) { doTrace(req,resp); } else { // 以上都不满足, 说明请求方式有问题。 String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); Object[] errArgs = new Object[1]; errArgs[0] = method; errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg); } }
4.2.3 FrameworkServlet重写了这些方法,并最终都是通过 processRequest( ) 方法来处理请求的。
@Override protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); } /** * Delegate POST requests to {@link #processRequest}. * @see #doService */ @Override protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); } /** * Delegate PUT requests to {@link #processRequest}. * @see #doService */ @Override protected final void doPut(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); }
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Throwable failureCause = null; // 获取当前请求的相关信息 LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); // 初始化 ContextHolders initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try { // 最终处理是dispatcherServlet 中的doService()方法调用 doDispatch()来处理的 doService(request, response); }
4.2.4 doDispatch() 方法的主要过程是通过 HandlerMapping 获取 Handler,再找到用于执行它的 HandlerAdapter,执行 Handler 后得到 ModelAndView
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // 获取处理请求的具体方法 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // 获取处理请求的适配器 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } // 检查请求路径 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // 得到modelandview mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(request, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } // 处理请求结果 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Error err) { triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } }
4.2.5 跳转页面
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; // 有异常就直接抛出异常 if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } // 所有条件都符合就跳转页面 if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } }