Callable
在java中,创建线程一般有两种方式,一种是继承Thread类,一种是实现Runnable接口。然而,这两种方式的缺点是在线程任务执行结束后,无法获取执行结果。我们一般只能采用共享变量或共享存储以及线程通信的方式实现获得任务结果的目的;
不过,在java中,也提供了使用Callable和Future来实现获取任务结果的操作。Callable用来执行任务,产生结果,而Future用来获得结果;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}
Callable和Runnable的区别:
1.Callable能接受一个泛型,然后在call方法中返回一个这个类型的值,而Runnable的run方法没有返回值;
2.Callable的call方法可以抛出异常,而Runnable的run方法不会抛出异常;
Future模式
Future莫斯的核心在于:去除了函数的等待时间,并使得原来需要等待的时间段可以用于处理其他业务逻辑;
Future模式:对于多线程,如果线程A要等待线程B的结果,那么线程A没有必要等待线程B,知道线程B有结果,可以先拿到一个未来的Future,等线程B有结果时再取真实的结果;
package com.wn.callable;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class MyCallable implements Callable {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("callable接口中重写的call方法,可以有返回值并且抛出异常!!!");
return "callable";
}
//方案一
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyCallable myCallable = new MyCallable();
//利用FutureTask执行callable并且接受结构
FutureTask<String> stringFutureTask = new FutureTask<String>(myCallable);
//利用线程执行task任务
new Thread(stringFutureTask).start();
//接受结果,get方法会发生阻塞情况
System.out.println(stringFutureTask.get());
System.out.println("mycallable执行完毕!");
}
}
package com.wn.callable;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class MyCallable implements Callable {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("callable接口中重写的call方法,可以有返回值并且抛出异常!!!");
return "callable";
}
//方案二:submit(Callable task)
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyCallable myCallable = new MyCallable();
//创建一个线程
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//创建线程执行任务,接受任务结果
Future submit = executorService.submit(myCallable);
//接受返回值,get方法会阻塞当前线程
System.out.println(submit.get());
System.out.println("利用线程池执行mycallable,完毕!!!");
//停止
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
Future常用方法
V get():获取异步执行的结果,如果没有结果可用,此方法会阻塞知道异步计算完成;
V get(Long timeout,TimeUnit unit):获取异步执行结果,如果没哟结果可用,此方法会阻塞,但是会有时间限制,如果阻塞时间超过设定的timeout时间,该方法将抛出异常;
boolean isDone():如果任务执行结束,无论是正常结束或是中途取消还是发生异常,都返回true;
boolean isCanceller():如果任务完成前被取消,则返回true;
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterrupRunning):如果任务还没有开始,执行cancel方法将返回false;如果任务已经启动,执行cancel方法将以中断执行此任务线程的方式来试图停止任务,如果停止成功,返回true;
当任务已经启动,执行cancel(false)方法将不会对正在执行的任务线程产生影响(让线程正常执行到完成),此时返回false;
当任务已经启动,执行cancel方法将返回false,MayInterruptRunning参数表示是否中断执行中的线程;
实际上Future提供了三种功能:
1.能够中断执行中的任务;
2.判断任务是否执行完成;
3.获取任务执行完成后的结果;
get()方法的阻塞性
package com.wn.callable;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class FutureGet {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executor=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//创建一个Callable,三秒返回String类型
Callable callable = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("callable方法执行!");
return "callable";
}
};
System.out.println("提交任务之前:"+getStringDate());
Future future = executor.submit(callable);
System.out.println("提供任务之后,获取结果之前:"+getStringDate());
System.out.println("获取返回值:"+future.get());
System.out.println("获取到结果之后:"+getStringDate());
}
public static String getStringDate(){
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
String dataString = format.format(date);
return dataString;
}
}

通过上面的输出可以看到,在调动submit提交任务之后,主线程本来是继续运行到future.get()的时候就阻塞了,一直等到任务执行完毕,拿到了返回的返回值,主线程才会继续运行;
阻塞性是因为调用了get()方法时,任务没有执行完毕,所以会一直等到任务完成,形成了阻塞;
任务是在调用submit方法时就开始执行了,如果在调用get方法时,任务已经执行完毕,那么就不会造成阻塞;
下面调用方法前先休眠四秒,这时能马上得到返回值:
System.out.println("提交任务之前:"+getStringDate());
Future future = executor.submit(callable);
System.out.println("提供任务之后,获取结果之前:"+getStringDate());
Thread.sleep(4000);
System.out.println("休眠四秒:"+getStringDate());
System.out.println("获取返回值:"+future.get());
System.out.println("获取到结果之后:"+getStringDate());

可以看到,因为休眠了四秒,任务已经执行完毕,所以get方法立马就得到了结果;
submit(Runnable task)
因为Runnable是没有返回值,所以如果submit一个Runnable的话,get得到的值肯定为null;
public class SubmitRunnable {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
Future future = executor.submit(runnable);
System.out.println("获得返回值:"+future.get());
}
}

submit(Runnable task,T result)
虽然传入Runnable不能直接返回内容,但是可以通过submit(Runnable task,T result)传入一个载体,通过这个载体获取返回值;
创建一个类Data:
package com.wn.callable;
public class Data {
String name;
String sex;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
}
在Runnable的构造方法中传入:
package com.wn.callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
public class MyThreadData implements Runnable {
Data data;
public MyThreadData(Data data) {
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
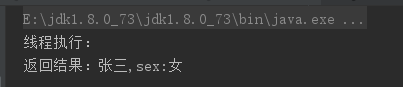
System.out.println("线程执行:");
data.setName("张三");
data.setSex("女");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] arg) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Data data = new Data();
Future<Data> submit = executor.submit(new MyThreadData(data), data);
System.out.println("返回结果:"+submit.get().getName()+",sex:"+submit.get().getSex());
}
}
get(long var1,TimeUnit var3)
前面用的get方法获取返回值,因为方法阻塞,有时需要等很久的时间,所以可以设置超时时间;
package com.wn.callable;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class GetTime {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
ExecutorService executor= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
//创建一个Callable,三秒返回String类型
Callable callable = new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("callable方法执行!");
return "callable";
}
};
System.out.println("提交任务之前:"+getStringDate());
Future future = executor.submit(callable);
System.out.println("提供任务之后,获取结果之前:"+getStringDate());
System.out.println("获取返回值:"+future.get(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS));
System.out.println("获取到结果之后:"+getStringDate());
}
public static String getStringDate(){
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss");
String dataString = format.format(date);
return dataString;
}
}
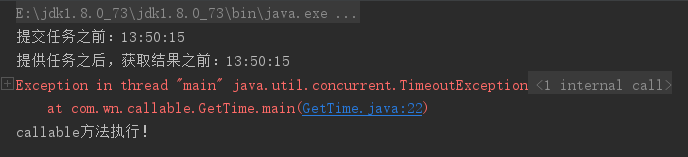
如果在二秒内没有获取,就抛出异常,主线程继续运行,不会在继续阻塞;