Java深入学习16:NIO详解2-Selector
一、概念介绍
1- Selector(选择器)介绍
选择器(Selector) 是 SelectableChannle 对象的多路复用器,Selector 可以同时监控多个 SelectableChannel 的 IO 状况,也就是说,利用 Selector 可使一个单独的线程管理多个 Channel。Selector 是非阻塞 IO 的核心。
使用Selector的好处在于: 使用更少的线程来就可以来处理通道了, 相比使用多个线程,避免了线程上下文切换带来的开销。
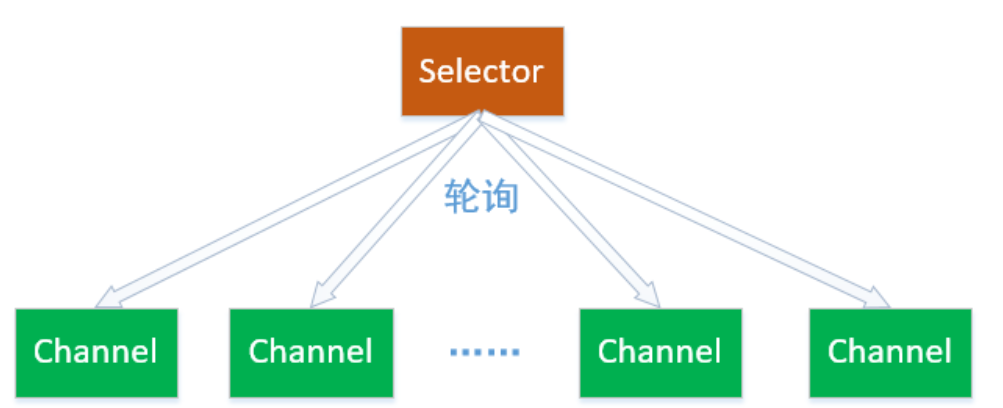
2- 阻塞与非阻塞
传统的 IO 流都是阻塞式的。也就是说,当一个线程调用 read() 或 write() 时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在此期间不能执行其他任务。因此,在完成网络通信进行 IO 操作时,由于线程会阻塞,所以服务器端必须为每个客户端都提供一个独立的线程进行处理,当服务器端需要处理大量客户端时,性能急剧下降。
Java NIO 是非阻塞模式的。当线程从某通道进行读写数据时,若没有数据可用时,该线程可以进行其他任务。线程通常将非阻塞 IO 的空闲时间用于在其他通道上执行 IO 操作,所以单独的线程可以管理多个输入和输出通道。因此,NIO 可以让服务器端使用一个或有限几个线程来同
时处理连接到服务器端的所有客户端。
二、代码示例(对方法做了简单的解释)
1- Socket方案1:客户端传数据,客户端接收
package nio.blockingnio; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.SocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; /* * 一、使用 NIO 完成网络通信的三个核心: * * 1. 通道(Channel):负责连接 * * java.nio.channels.Channel 接口: * |--SelectableChannel * |--SocketChannel * |--ServerSocketChannel * |--DatagramChannel * * |--Pipe.SinkChannel * |--Pipe.SourceChannel * * 2. 缓冲区(Buffer):负责数据的存取 * * 3. 选择器(Selector):是 SelectableChannel 的多路复用器。用于监控 SelectableChannel 的 IO 状况 * */ public class BlockingNIOTest { @Test public void client() throws IOException { //1-获取Socket通道和文件通道 // SocketChannel.open(): Opens a socket channel and connects it to a remote address. //InetSocketAddress: This class implements an IP Socket Address (IP address + port number) SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8001)); FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ); //2-分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(10240); //3-读取本地文件,并发送到服务器 while(inChannel.read(buf) != -1){ buf.flip(); socketChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } //4-关闭通道 inChannel.close(); socketChannel.close(); } @Test public void server() throws IOException { //1-获取ServerSocke通道并绑定链接 // ServerSocketChannel.open(): Opens a server-socket channel. // ServerSocketChannel.bind(): Binds the channel's socket to a local address and configures the socket to listen for connections. ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8001)); //2-获取本地文件写入通道 FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("5.jpg"),StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE); //3-获取客户端连接通道 //ServerSocketChannel.accept(): Accepts a connection made to this channel's socket. SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); //4-分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(10240); //5-接收客户端的数据,并保存到本地 while(socketChannel.read(buf) != -1){ buf.flip(); outChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } //6-关闭通道 socketChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); serverSocketChannel.close(); } }
2- Socket方案2:客户端传数据,客户端接收数据后,并返回数据给客户端(使用socketChannel.shutdownOutput()关闭客户端数据传输)
import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.nio.file.Paths; import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; public class BlockingNIOTest2 { @Test public void client() throws IOException { //1- 获取SocketChannel通道,并写入数据,发送到服务器 SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8001)); FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10240); while(inChannel.read(buffer) != -1){ buffer.flip(); socketChannel.write(buffer); buffer.clear(); } //2-关闭SocketChannel写数据的链接,但是不关闭通道本身。 //SocketChannel.shutdownOutput(): Shutdown the connection for writing without closing the channel. socketChannel.shutdownOutput(); //3-接收服务端的反馈 int len = 0; while((len = socketChannel.read(buffer)) != -1){ buffer.flip(); System.out.println("client output: " + new String(buffer.array(), 0, len)); buffer.clear(); } //4-关闭通道 inChannel.close();; socketChannel.close(); } @Test public void server() throws IOException { ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open().bind(new InetSocketAddress(8001)); FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("6.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.READ); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10240); SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); while(socketChannel.read(buffer) != -1){ buffer.flip(); outChannel.write(buffer); buffer.clear(); } //传输数据 buffer.put("helleo tyj".getBytes()); buffer.flip(); socketChannel.write(buffer); buffer.clear(); socketChannel.close();; outChannel.close(); serverSocketChannel.close(); } }
3-Socket方案3:客户端传数据,客户端接收;使用选择器Selector
import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.Buffer; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.*; import java.time.LocalDateTime; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Scanner; public class NonBlockingNIOTest { @Test public void client() throws IOException { SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8001)); socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); String str = ""; while(scanner.hasNext()){ str = scanner.next(); byteBuffer.put((LocalDateTime.now().toString()+" client: " + str).getBytes()); byteBuffer.flip(); socketChannel.write(byteBuffer); byteBuffer.clear(); } scanner.close(); } @Test public void server() throws IOException { //1-获取通道 ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //2-切换成非阻塞模式 //ServerSocketChannel.configureBlocking(): Adjusts this channel's blocking mode. serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //3-绑定连接 serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8001)); //4-获取选择器 //Selector.open(): Opens a selector. Selector selector = Selector.open(); //5-将通道注册到选择器上,并指定"监听接收事件" //ServerSocketChannel.register(): Registers this channel with the given selector, returning a selection key. serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //6-轮询的方式获取选择器上已经“准备就绪”的事件 //selector.select(): Selects a set of keys whose corresponding channels are ready for I/O operations. while(selector.select() > 0){ //7-获取当前选择器上所有注册的“选择键(已经就绪的监听事件)” //selector.selectedKeys(): Returns this selector's selected-key set. Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while(keyIterator.hasNext()){ //8-获取"准备就绪"的事件 SelectionKey selectionKey = keyIterator.next(); //9-判断具体是什么事件就绪 // selectionKey.isAcceptable(): Tests whether this key's channel is ready to accept a new socket connection. if(selectionKey.isAcceptable()){ //10-如果是“接收就绪”,获取客户端连接 SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); //11-切换成非阻塞模式 socketChannel.configureBlocking(false); //12-将该通道注册到选择器上 socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ); }else if(selectionKey.isReadable()){ //13-获取当前选择器上“读就绪”状态的通道 //selectionKey.channel(): Returns the channel for which this key was created. This method will continue to return the channel even after the key is cancelled. SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel(); //14-获取通道,读取数据 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); int len = 0; while((len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer)) != -1){ byteBuffer.flip(); System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array(),0,len)); byteBuffer.clear(); } } //15-取消选择建SelectionKey keyIterator.remove(); } } } }
END