最短路径算法(Shortest Path Algorithm)
地图寻路最优路径
距离最短
红灯最少
速度最快
建模
使用有向有权图(graph)表示:岔口为顶点,岔口相连为边,单行线建立单向边,双行线建立双向边,岔口之间的距离为边的权重。
-
public class Graph { // 有向有权图的邻接表表示 private LinkedList<Edge> adj[]; // 邻接表 private int v; // 顶点个数 public Graph(int v) { this.v = v; this.adj = new LinkedList[v]; for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i) { this.adj[i] = new LinkedList<>(); } } public void addEdge(int s, int t, int w) { // 添加一条边 this.adj[s].add(new Edge(s, t, w)); } private class Edge { public int sid; // 边的起始顶点编号 public int tid; // 边的终止顶点编号 public int w; // 权重 public Edge(int sid, int tid, int w) { this.sid = sid; this.tid = tid; this.w = w; } } // 下面这个类是为了dijkstra实现用的 private class Vertex { public int id; // 顶点编号ID public int dist; // 从起始顶点到这个顶点的距离 public Vertex(int id, int dist) { this.id = id; this.dist = dist; } } }
经典单源最短路径算法(一个顶点到一个顶点): Dijkstra 算法
-
// 因为Java提供的优先级队列,没有暴露更新数据的接口,所以我们需要重新实现一个 private class PriorityQueue { // 根据vertex.dist构建小顶堆 private Vertex[] nodes; private int count; public PriorityQueue(int v) { this.nodes = new Vertex[v+1]; this.count = v; } public Vertex poll() { // TODO: 留给读者实现... } public void add(Vertex vertex) { // TODO: 留给读者实现...} // 更新结点的值,并且从下往上堆化,重新符合堆的定义。时间复杂度O(logn)。 public void update(Vertex vertex) { // TODO: 留给读者实现...} public boolean isEmpty() { // TODO: 留给读者实现...} } public void dijkstra(int s, int t) { // 从顶点s到顶点t的最短路径 int[] predecessor = new int[this.v]; // 用来还原最短路径 Vertex[] vertexes = new Vertex[this.v]; for (int i = 0; i < this.v; ++i) { vertexes[i] = new Vertex(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE); } PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(this.v);// 小顶堆 boolean[] inqueue = new boolean[this.v]; // 标记是否进入过队列 vertexes[s].dist = 0; queue.add(vertexes[s]); inqueue[s] = true; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Vertex minVertex= queue.poll(); // 取堆顶元素并删除 if (minVertex.id == t) break; // 最短路径产生了 for (int i = 0; i < adj[minVertex.id].size(); ++i) { Edge e = adj[minVertex.id].get(i); // 取出一条minVetex相连的边 Vertex nextVertex = vertexes[e.tid]; // minVertex-->nextVertex if (minVertex.dist + e.w < nextVertex.dist) { // 更新next的dist nextVertex.dist = minVertex.dist + e.w; predecessor[nextVertex.id] = minVertex.id; if (inqueue[nextVertex.id] == true) { queue.update(nextVertex); // 更新队列中的dist值 } else { queue.add(nextVertex); inqueue[nextVertex.id] = true; } } } } // 输出最短路径 System.out.print(s); print(s, t, predecessor); } private void print(int s, int t, int[] predecessor) { if (s == t) return; print(s, predecessor[t], predecessor); System.out.print("->" + t); }
- 算法解析
- 从优先级队列中取出 dist 最小的顶点 minVertex,然后考察这个顶点可达的所有顶点(代码中的 nextVertex)。
- 如果 minVertex 的 dist 值加上 minVertex 与 nextVertex 之间边的权重 w 小于 nextVertex 当前的 dist 值,也就是说,存在另一条更短的路径,经过 minVertex 到达 nextVertex。那我们就把 nextVertex 的 dist 更新为 minVertex 的 dist 值加上 w。
- 然后,把 nextVertex 加入到优先级队列中。
- 重复这个过程,直到找到终止顶点 t 或者队列为空。
- 两个额外的变量:predecessor 数组和 inqueue 数组
- predecessor 数组的作用是为了还原最短路径,它记录每个顶点的前驱顶点。通过递归的方式,将这个路径打印出来。
- inqueue 数组是为了避免将一个顶点多次添加到优先级队列中。更新了某个顶点的 dist 值之后,如果这个顶点已经在优先级队列中了,就不要再将它重复添加进去了。
- 图示
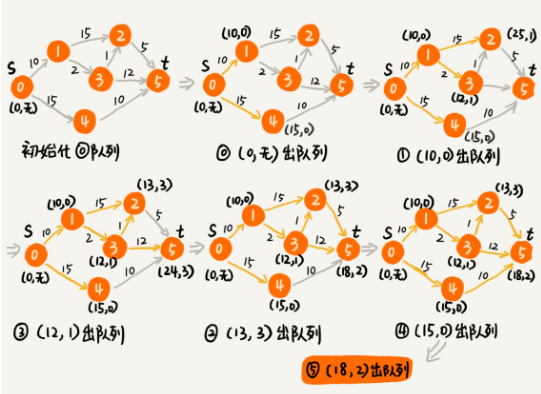
- 时间复杂度:O(V * E)
获取翻译结果高分TOP K
- 借助 Dijkstra 算法的核心思想,高效地解决:
- 每个单词的可选翻译是按照分数从大到小排列的,所以 a0b0c0 肯定是得分最高组合结果。
- 我们把 a0b0c0 及得分作为一个对象,放入到优先级队列中。
- 每次从优先级队列中取出一个得分最高的组合,并基于这个组合进行扩展。
- 扩展的策略是每个单词的翻译分别替换成下一个单词的翻译。比如 a0b0c0 扩展后,会得到三个组合,a1b0c0、a0b1c0、a0b0c1。把扩展之后的组合,加到优先级队列中。
- 重复这个过程,直到获取到 k 个翻译组合或者队列为空。

总结
Dijkstra 算法的核心思想:
确定当前最优结果,基于此结果不断扩展;
使用优先级队列,存储扩展结果;
每次1组堆顶元素出队,n组基于堆顶扩展的结果入队;
达到目标则终止操作,根据最后的出队结果打印路径就是最终结果。