其他路径:
CSDN: https://blog.csdn.net/wodehao0808
微信公众号:程序喵星人
更多资源和视频教程,QQ:1902686547
2. 面向对象编程
面向对象编程也叫做OOP编程。
简单来说面向对象编程就是结构化编程,对程序中的变量结构划分,让编程更清晰。
2.1 类和对象
2.1.1 类
类实际上是创建对象的模板,每个对象都包含数据集合,并提供了处理和访问数据的方法。
类定义了类的每个对象(称为实例)可以包含什么数据和功能。
类中的数据和函数称为类的成员。
数据成员
函数成员
数据成员:
数据成员是包含类的数据--字段,常量和事件的成员。
函数成员:
函数成员提供了操作类中数据的某些功能。(方法,属性,构造方法和终结器(析构方法),运算符,和索引器)。
字段的声明
访问修饰符 类型 字段名称;
方法的声明
访问修饰符 返回值类型 方法名称(参数)
{
//方法体
}
2.1.2 对象
类创建的变量叫做对象。
实例化一个对象:
ClassName myClass = new ClassName();
其中ClassName是我们定义的类的名字,myClass是我们声明的变量(对象)的名字,后面的new是一个关键字,使用new 加上类型名()表示对该对象进行构造,如果不进行构造的话,这个对象是无法使用的。
2.1.3 Example: 类和对象
2.1.3.1 Customer.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Lesson_2_1
{
// 定义一个新的类型(类):Customer
class Customer
{
// 字段,数据成员
public string name;
public string address;
public int age;
public string buyTime;
// 方法,函数成员
public void Show()
{
Console.WriteLine("名字:" + name);
Console.WriteLine("年龄:" + age);
Console.WriteLine("地址:" + address);
Console.WriteLine("购买时间:" + buyTime);
}
}
}
2.1.3.2 Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// 类和对象
namespace Lesson_2_1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 如果要使用一个类的话,要先引入它所在的命名空间;
// 因为Customer位于当前的命名空间下,所以不需要引入,就可以直接使用Customer类;
Customer ctm; // 使用 Customer 模板,声明了一个变量(对象)
ctm = new Customer(); // 对象初始化
ctm.name = "张三";
Console.WriteLine("ctm对象的name = " + ctm.name);
ctm.Show(); // 调用对象的方法
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
2.2 类的定义和声明
定义一个车辆(Vehicle)类,具有Run、Stop等方法,具有Speed(速度)、MaxSpeed(最大速度)、Weight(重量)等域(也叫做字段)。
定义一个向量(Vector3)类,里面有x,y,z三个字段,有取得长度的方法,有设置属性(Set)的方法。
2.2.1 Example: 类的定义和声明
2.2.1.1 Vehicle.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Lesson_2_2
{
class Vehicle
{
public float speed;
public float maxSpeed;
public float weight;
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("这辆车正在以 {0}m/s 的速度行驶", speed);
}
public void Stop()
{
speed = 0; // 车子停下来
Console.WriteLine("这辆车已经停止了,当前速度是:" + speed);
}
}
}
2.2.1.2 Vector3.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Lesson_2_2
{
class Vector3
{
public float x, y, z;
public float GetLength()
{
return (float)Math.Sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z);
}
}
}
2.2.1.3 Vector3_2.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Lesson_2_2
{
class Vector3_2
{
// 一般情况下,都是将字段设为 private 权限
// private: 可以在类内部访问,但不可以在外部通过对象直接访问
private float _fX, _fY, _fZ;
// 通过提供公有方法去改变私有字段的值
public void SetX(float p_fX)
{
_fX = p_fX;
}
public void SetY(float p_fY)
{
_fY = p_fY;
}
public void SetZ(float p_fZ)
{
_fZ = p_fZ;
}
public float GetLength()
{
return (float)Math.Sqrt(_fX * _fX + _fY * _fY + _fZ * _fZ);
}
}
}
2.2.1.4 Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// 类的定义和声明
namespace Lesson_2_2
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 车辆
Vehicle vh = new Vehicle();
vh.speed = 60;
vh.Run();
vh.Stop();
// 向量Vector3
Vector3 vec = new Vector3();
vec.x = 1;
vec.y = 1;
vec.z = 1;
Console.WriteLine("向量Vector3的长度 = " + vec.GetLength());
// 向量Vector3_2
Vector3_2 vec2 = new Vector3_2();
// vec2._fX = 1; // private字段,不能在类外部通过对象直接访问
// vec2._fY = 1;
// vec2._fZ = 1;
vec2.SetX(1);
vec2.SetY(1);
vec2.SetZ(1);
Console.WriteLine("向量Vector3_2的长度 = " + vec2.GetLength());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
2.3 构造函数
构造函数就是用于初始化数据的函数。
声明基本的构造函数的语法就是声明一个和所在类同名的方法,但是该方法没有返回类型。
public class MyClass
{
public MyClass() // 构造函数
{
这个构造函数的函数体
}
}
当我们使用new关键字创建类的时候,就会调用构造方法。
我们一般会使用构造方法进行初始化数据的一些操作。
构造函数可以进行重载,跟普通函数重载是一样的规则。
注意:
当我们不写,任何构造函数的时候,编译器会提供给我们一个默认的 无参的构造函数,但是如果我们定义了一个或者多个构造函数,编译器就不会再提供默认的构造函数。
2.3.1 Example:构造函数
2.3.1.1 Vector3.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Lesson_2_3
{
class Vector3
{
private float _fX, _fY, _fZ;
// 当我们声明一个构造函数后,编译器不会再为我们提供一个默认的构造函数了
public Vector3()
{
Console.WriteLine("这是一个无参的构造函数");
}
// 构造函数重载
public Vector3(float p_fX, float p_fY, float p_fZ)
{
Console.WriteLine("这是一个有参的构造函数");
this._fX = p_fX; // 也可以 _fX = p_fX;
this._fY = p_fY; // 也可以 _fY = p_fY;
this._fZ = p_fZ; // 也可以 _fZ = p_fZ;
// this 就是调用该方法的对象
}
public float GetLength()
{
// this 就是调用该方法的对象
return (float)Math.Sqrt(this._fX * this._fX + this._fY * this._fY + this._fZ * this._fZ);
}
public void SetX(float p_fX)
{
this._fX = p_fX;
}
public void SetY(float p_fY)
{
this._fY = p_fY;
}
public void SetZ(float p_fZ)
{
this._fZ = p_fZ;
}
}
}
2.3.1.2 Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// 构造函数
namespace Lesson_2_3
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 使用无参构造函数
Vector3 vec = new Vector3();
vec.SetX(1);
vec.SetY(1);
vec.SetZ(1);
Console.WriteLine("无参构造函数,向量长度 = " + vec.GetLength());
// 有参构造函数
Vector3 vec2 = new Vector3(1, 1, 1); // 可以发现,使用有参构造函数,可以对字段进行初始化;构造函数的主要作用,也是用于初始化数据;
Console.WriteLine("有参构造函数,向量长度 = " + vec2.GetLength());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
2.4 属性的定义
2.4.1 属性的定义
属性的定义结构:
public int MyIntProp{
get{
// get code
}
set{
//set code
}
}
1,定义属性需要名字和类型
2,属性包含两个块 get块和set块
3,访问属性和访问字段一样。当取得属性的值的时候,就会调用属性中的get块,所以get块,需要一个返回值,返回值的类型就是属性的类型;当我们去给属性设置值的时候,就会调用属性中的set块,我们可以在set块中通过value访问到我们设置的值。
2.4.2 只读或只写属性
private string name;
public string name{
get{
return name;
}
}
属性可以只提供一个set块或者get块。
只读:只提供 get 块。
只写:只提供 set 块。
2.4.3 属性的访问修饰符
public string name{
get{
return name;
}
// private 修改了属性的访问权限
private set{
name = value;
}
}
2.4.4 自动实现的属性
public int Age{get;set;}
编译器会自动创建private int age字段。
2.4.5 Example:属性的定义
2.4.5.1 Vector3.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Lesson_2_4
{
class Vector3
{
// C#一般把字段定义为private,然后通过属性访问和修改字段值
private float _fX, _fY, _fZ;
// 属性
public float X // 属性和函数,一般都是使用大写字母开头
{
get { return _fX; } // get块中的返回值类型,需要跟属性类型保持一致
set { _fX = value; } // set块中,默认变量value,访问我们设置的值
}
public float Y
{
get { return _fY; }
set { _fY = value; }
}
public float Z
{
get { return _fZ; }
set { _fZ = value > 0 ? value : 0; } // 增加修改保护,例如银行余额不能负数等
}
public Vector3()
{
}
public Vector3(float p_fX, float p_fY, float p_fZ)
{
X = p_fX; // 使用属性的set块,修改对应字段的值
Y = p_fY;
Z = p_fZ;
}
public float GetLength()
{
return (float)Math.Sqrt(X * X + Y * Y + Z * Z); // 使用属性的get块,获得对应的值
}
// 只读属性
private int _iNum = 10;
public int Num
{
get { return _iNum; }
// 没有set块,表示这个属性是只读的
}
// 只写属性
private int _iCount;
public int Count
{
set { _iCount = value; Console.WriteLine("Count写入的值是:" + value); }
// 没有get块,表示这个属性是只写的
}
// 属性的访问修饰符
private string _strName;
public string Name
{
get { return _strName; }
private set { _strName = value; } // private 修饰符,表示set块是只能在类内部调用,外部无效
}
public void SetName(string p_strName)
{
Name = p_strName; // 类内部,可以使用属性Name的set块
}
// 自动实现的属性
public string School { get; set; } // 编译器,会自动为 属性School 生成相对应的字段 private string school;
}
}
2.4.5.2 Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// 属性
namespace Lesson_2_4
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Vector3 vec = new Vector3(1, 1, 1);
Console.WriteLine("vec的x是:" + vec.X);
Console.WriteLine("vec的y是:" + vec.Y);
Console.WriteLine("vec的z是:" + vec.Z);
Console.WriteLine("vec的长度是:" + vec.GetLength());
// 只读
// vec.Num = 10; // 无法通过属性设置值,因为属性是只读的,没有set块
Console.WriteLine("vec的只读属性:" + vec.Num);
// 只写
// int i = vec.Count; // 无法通过属性读取属性值,因为属性是只写的,没有get块
vec.Count = 100;
// 属性的访问权限
// vec.Name = "张三"; // 无法通过属性设置值,因为属性的 set块 的权限是private,外部无法直接访问
vec.SetName("张三"); // 通过额外的函数,在函数中(类内部)去访问该属性的 set块(private权限)
Console.WriteLine("vec的name是:" + vec.Name);
// 自动实现的属性
vec.School = "中学";
Console.WriteLine("vec的shcool是:" + vec.School);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
2.5 匿名类型
我们创建变量(对象的时候),必须指定类型,其实我们也可以不去指定类型,这个就是匿名类型,我们可以使用var声明一个匿名类型。
使用var声明的匿名类型,当初始化的时候,这个变量的类型就被确定下来,并且以后不可以修改。
var var1 = 34;
2.5.1 Example:匿名类型
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// 匿名类型
namespace Lesson_2_5
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 使用 var 声明匿名类型
var v1 = 12; // 根据初始化的值,推导出v1的类型;类型确定后,就不能更改
//v1 = "张三"; // v1的类型,已经推导确定了,不能再更改
var pi = 3.14;
var name = "张三";
Console.WriteLine("请输入:");
var s = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("v1 = " + v1);
Console.WriteLine("pi = " + pi);
Console.WriteLine("name = " + name);
Console.WriteLine("s = " + s);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
2.6 堆和栈
堆和栈 : 程序运行时的内存区域。
我们把内存分为 堆空间 和 栈空间。
栈空间 比较小,但是读取速度快。
堆空间 比较大,但是读取速度慢。
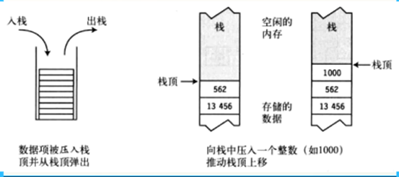
2.6.1 栈
栈的特征:
数据只能从栈的顶端插入和删除。
把数据放入栈顶称为入栈(push)。
从栈顶删除数据称为出栈(pop)。
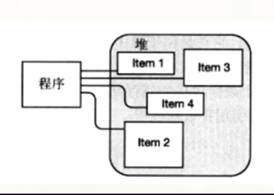
2.6.2 堆
堆是一块内存区域,与栈不同,堆里的内存能够以任意顺序存入和移除。
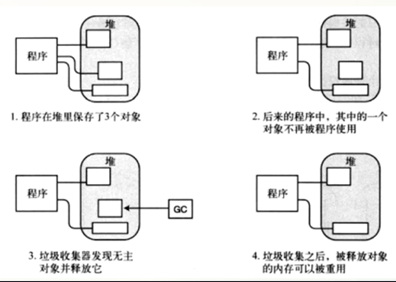
2.6.3 GC垃圾回收
GC Garbage Collector垃圾回收器。
CLR的GC就是内存管理机制,我们写程序不需要关心内存的使用,因为这些都是CLR帮我们做了。
2.6.4 值类型和引用类型
类型被分为两种:值类型(整数,bool struct char 小数等) 和 引用类型(string 数组 自定义的类,内置的类等)。
值类型只需要一段单独的内存,用于存储实际的数据,(单独定义的时候放在栈中)。
引用类型需要两段内存:
第一段存储实际的数据,它总是位于堆中。
第二段是一个引用,指向数据在堆中的存放位置。

当我们使用引用类型赋值的时候,其实是赋值给引用类型的引用(即在堆中的地址)。
如果数组是一个值类型的数组,那么数组中直接存储值。如果是一个引用类型的数组(数组中存储的是引用类型),那么数组中存储的是引用(内存地址)。
2.6.4.1 Example:值类型和引用类型
2.6.4.1.1 Vector3.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Lesson_2_6
{
class Vector3
{
public float x, y, z;
}
}
2.6.4.1.2 Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// 值类型和引用类型
namespace Lesson_2_6
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Test1();
Test2();
Test3();
Test4();
Test5();
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void Test1()
{
int i = 34; // 值类型,在栈中存储值:34
int j = 34; // 值类型,在栈中存储值:34
int temp = 34; // 值类型,在栈中存储值:34
char c = 'a'; // 值类型,在栈中存储值:a
bool b = true; // 值类型,在栈中存储值:true110
}
static void Test2()
{
int i = 34; // 值类型,在栈中存储值:34
int j = 234; // 值类型,在栈中存储值:34
string name = "my"; // 引用类型,在堆中存储值:my;在栈中存储(即name的值):my在堆中的地址。
}
static void Test3()
{
string name = "my";
string name2 = "you";
name = name2; // name保存:you在堆中的地址
name = "baidu"; // name保存:baidu在堆中的地址
Console.WriteLine("name = {0}, name2 = {1}", name, name2);
}
static void Test4()
{
Vector3 v = new Vector3(); // v指向堆1
v.x = 100;
v.y = 100;
v.z = 100;
Vector3 v2 = new Vector3(); // v2指向堆2
v2.x = 200;
v2.y = 200;
v2.z = 200;
v2 = v; // v2指向堆1
v2.x = 300; // 将堆1中的变量x的值改为300
Console.WriteLine("v.x = " + v.x); // v也是指向堆1的,所以,输出的值是 300
}
static void Test5()
{
// 如果数组是一个值类型的数组,那么数组中直接存储值;
// 如果数组是一个引用类型的数组(数组中存储的是引用类型),MAME数组中存储的是引用(即内存地址)
Vector3[] vArray = new Vector3[] { new Vector3(), new Vector3(), new Vector3() };
Vector3 v1 = vArray[0]; // v1指向堆1
vArray[0].x = 100; // 修改堆1中的x的值
v1.x = 200; // 修改堆1中的x的值
Console.WriteLine("vArray[0].x = " + vArray[0].x); // vArray[0]是指向堆1的,所以输出值是200
}
}
}