(1)组件扫描
1)什么是组件扫描?
Spring容器启动之后,会扫描base-package指定的包及其子包下面的所有的类,如果这些类前面添加了特定的注解(比如,添加了@Component),则容器会将该类实例化(即纳入容器进行管理)。
2)如何使用组件扫描?
step1.在类前面添加相应的注解:
@Component 通用注解
@Service 用于业务层
@Repository 用于持久层(数据访问层)
@Controller 用于控制层
step2.在配置文件当中,配置组件扫描:
Spring容器启动之后,会扫描base-package指定的包及其子包下面的所有的类,如果这些类前面添加了特定的注解(比如,添加了@Component),则容器会将该类实例化(即纳入容器进行管理)。
<context:component-scan base-package="annotation"/>
(2)使用注解指定作用域
@Component("stu1") // 声明为通用组件
@Scope("singleton") // 作用域
public class Student {
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student的无参构造器");
}
}
(3)使用注解指定初始化方法和销毁方法
@PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println("Student的init方法"); } @PreDestroy public void destroy(){ System.out.println("Student的destroy方法"); }
(4)使用注解指定延迟加载
@Lazy(true) public class Student { public Student() { System.out.println("Student的无参构造器"); } }
(5)依赖注入相关的注解
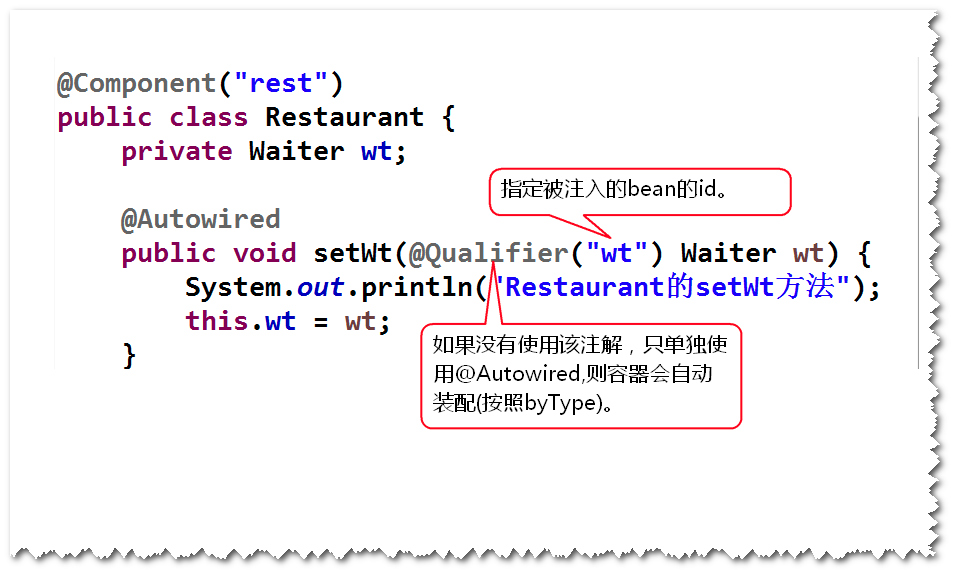
1) @Autowired和@Qualifier
a.这两个注解支持set方法注入和构造器注入。
b.在set方法注入时,@Autowired可以加到set方法前或者属性前,
@Qualifier用来指定被注入的bean的id。
注:如果不使用@Qualifier,则容器会按照类型来查找对应的bean来注入。

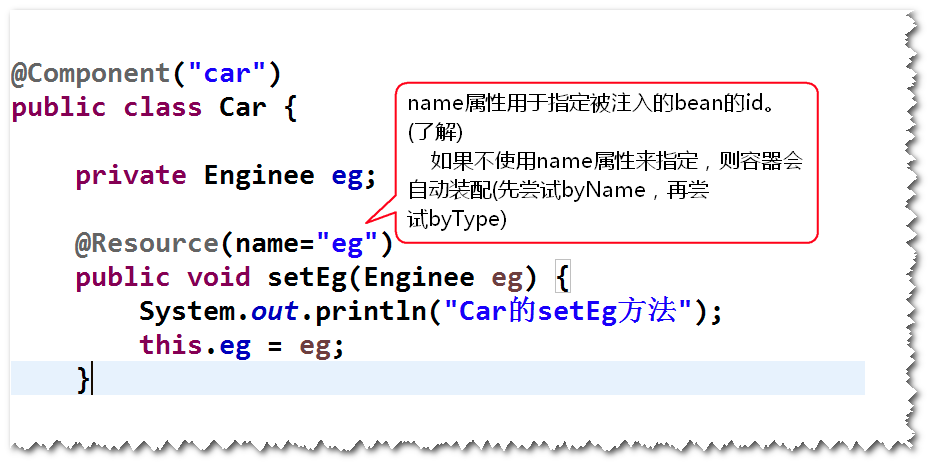
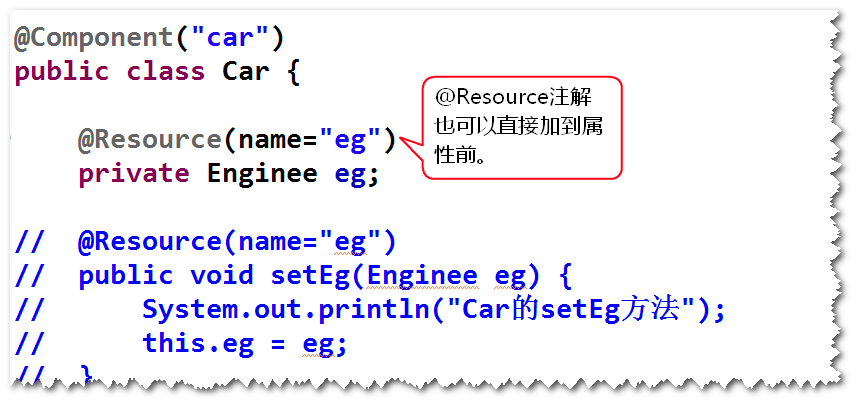
2) @Resource
该注解只支持set方法注入
(6)注入基本类型的值
@Component("teacher")
public class Teacher {
@Value("小花")
private String name;
@Value("50")
private int age;
@Value("#{config.pagesize}")
private int pageSize;
}