在上一篇文章中我们介绍了JDK1.8的新特性有以下几项。
4.默认方法
5.Stream
6.Optional类
7.Nashorm javascript引擎
8.新的日期时间API
9.Base64
之前学习了前面两项Lambda表达式,方法引用,这一篇学习函数式接口。
所谓的函数式接口它只能定义一个抽象方法,其他方法可以用default或者static关键对方法进行限定。
下面先来通过实例来验证一下。
自定义一个函数式接口,然后定义一个叫testA的抽象方法,再定义一个叫testB的抽象方法。
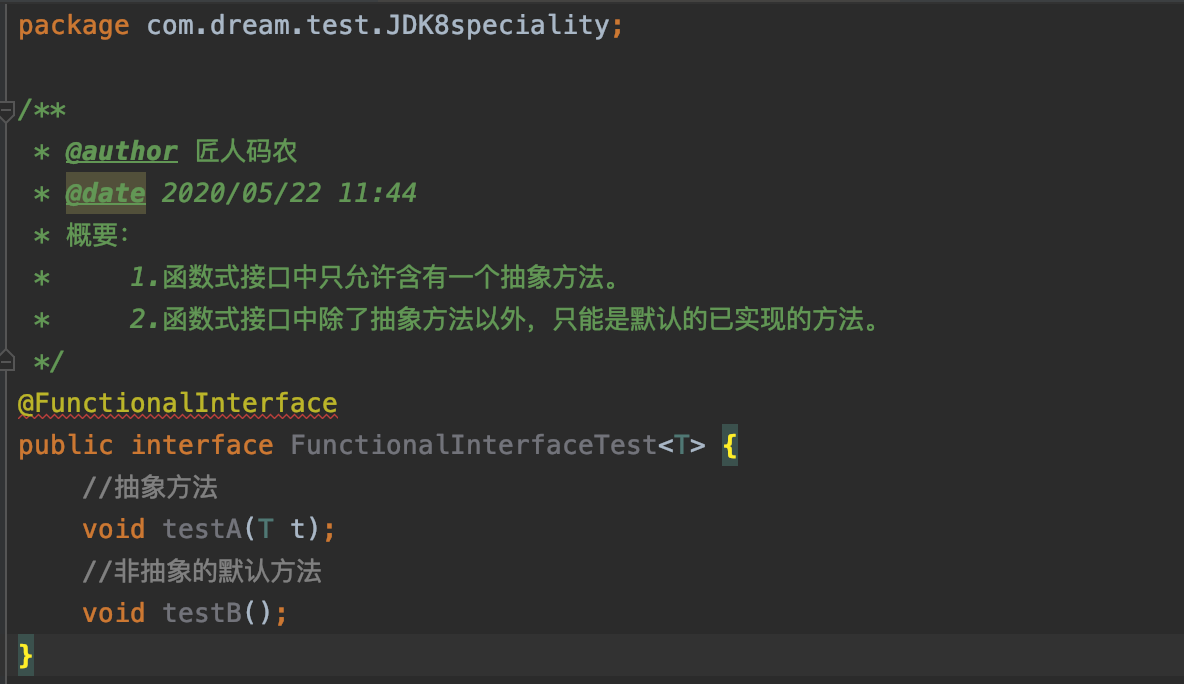
此时@FunctionalInterface注解会提示如下错误。(在接口中发现有复数个没有被覆盖的抽象方法)
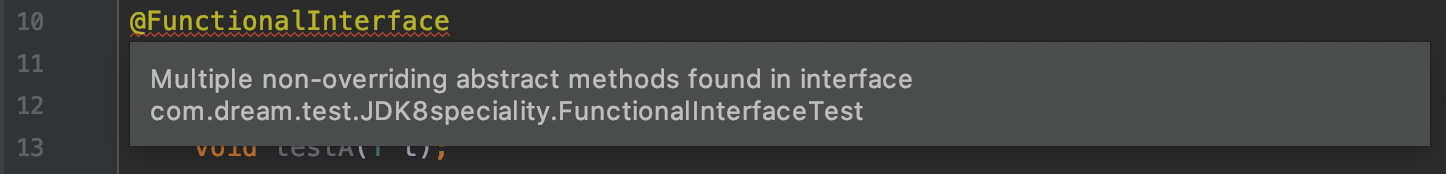
那我接下来把testB改为非抽象方法试试。
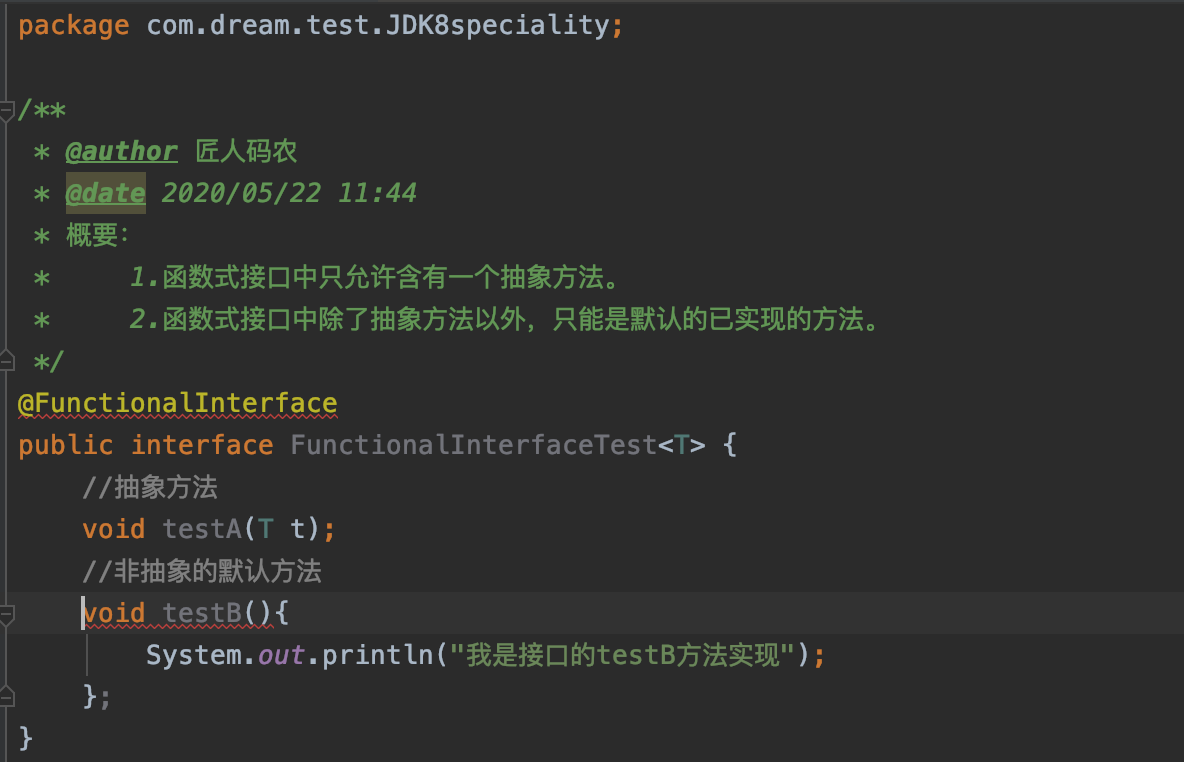
发现改完之后又多了一处错误。我们继续看看新出的错误。

接下来我们把方法加上default关键字
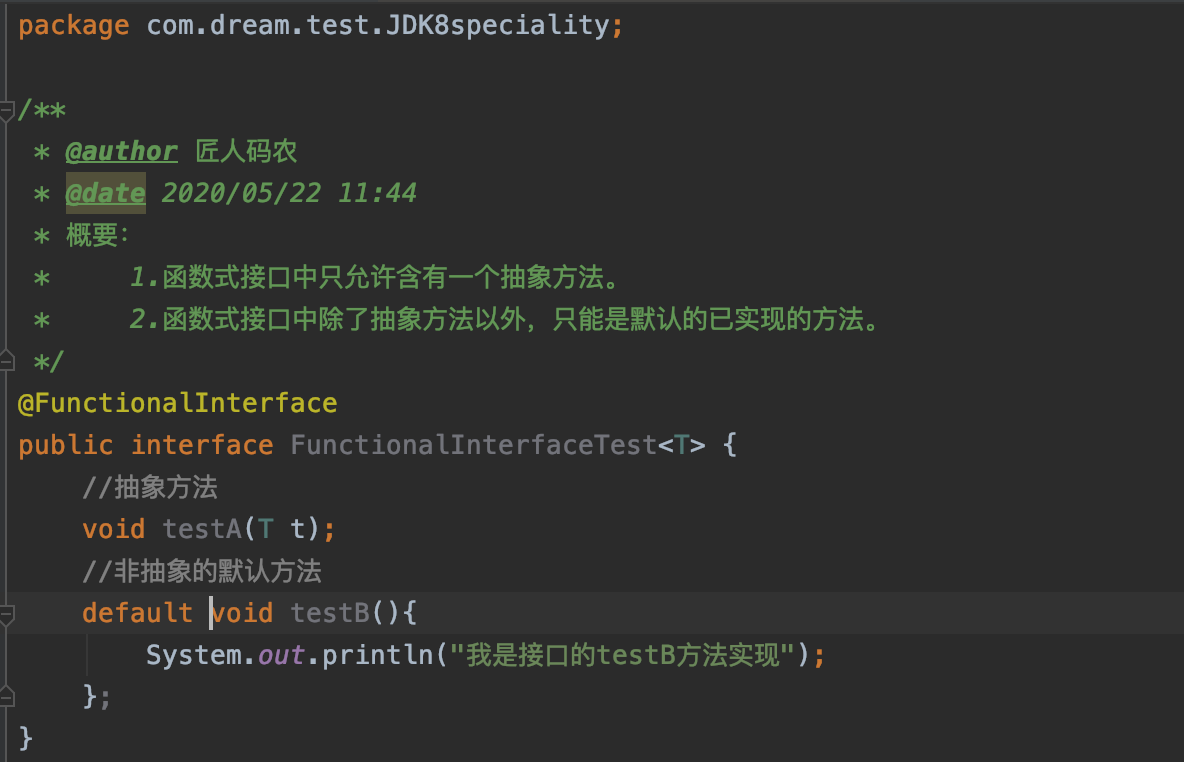
这时候就没有错误信息啦。说明函数式接口中可以除了含有抽象方法外可以有默认的非静态方法。
下面我把default改成static试一试看看可不可以有静态方法。
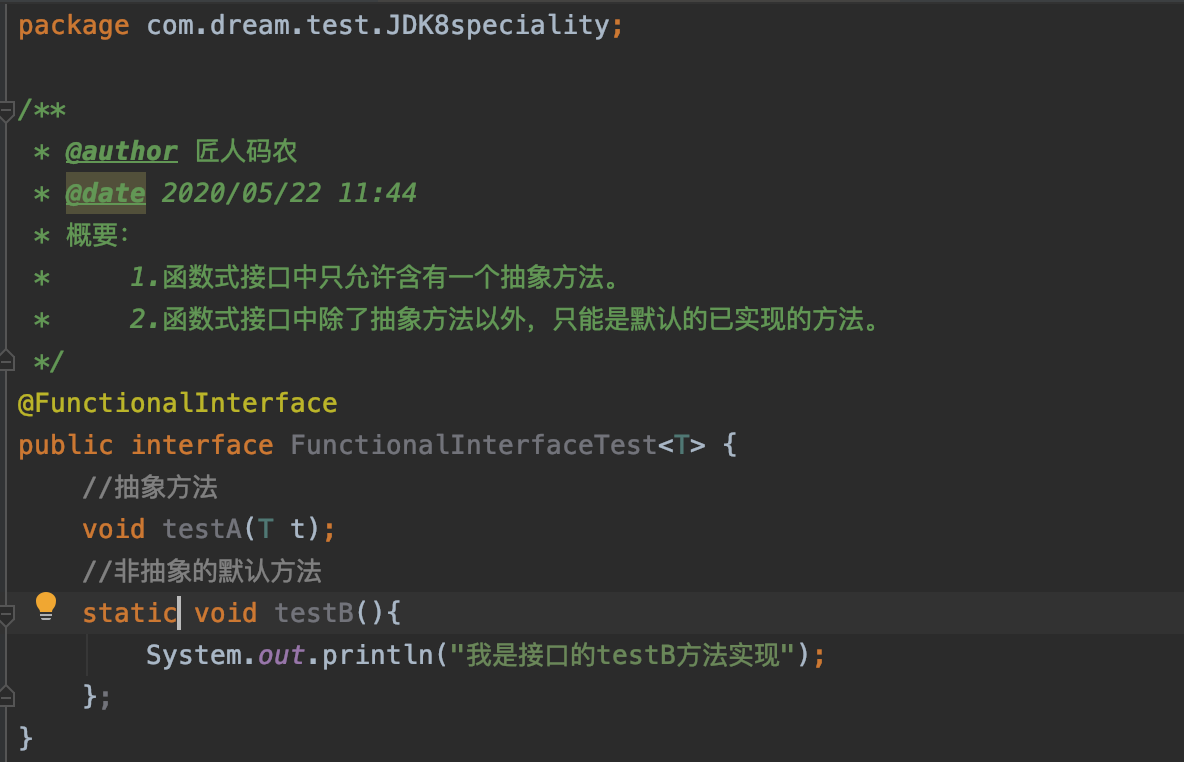
此时发现也没有问题。那就说明函数式接口中还可以有静态方法。
因为Object类是所有类的父类,所有接口中能被重写的方法都可以在接口中定义。比如
toString,equals方法。
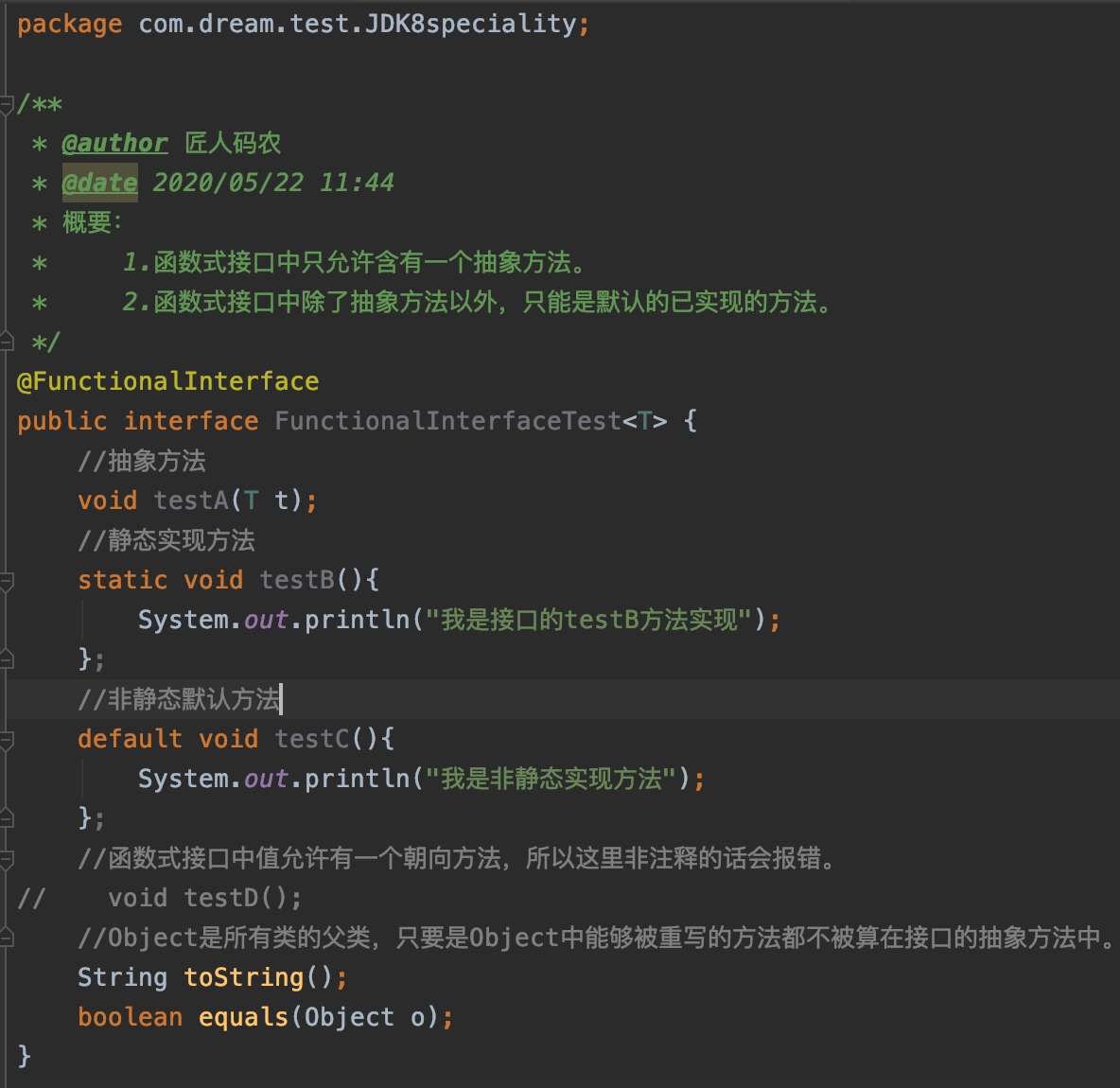
了解完函数式接口,接下来说一下API内置的四大函数式接口。
主要就以下
1. Consumer -- 消费性接口
2. Supplier -- 供给型接口
3. Function -- 函数型接口
4. Predicate -- 断言型接口
下面我们依次来看一下API源代码,以及通过写实例来理解一下每种类型接口使用方法以及特点。
1. Consumer(有传入,没有传出的时候使用)
官方源代码如下,为了起来方便简洁把开头的注释去掉了,只保留了方法的注释。
1 package java.util.function; 2 3 import java.util.Objects; 4 5 @FunctionalInterface 6 public interface Consumer<T> { 7 8 /** 9 * Performs this operation on the given argument. 10 * 11 * @param t the input argument 12 */ 13 void accept(T t); 14 15 /** 16 * Returns a composed {@code Consumer} that performs, in sequence, this 17 * operation followed by the {@code after} operation. If performing either 18 * operation throws an exception, it is relayed to the caller of the 19 * composed operation. If performing this operation throws an exception, 20 * the {@code after} operation will not be performed. 21 * 22 * @param after the operation to perform after this operation 23 * @return a composed {@code Consumer} that performs in sequence this 24 * operation followed by the {@code after} operation 25 * @throws NullPointerException if {@code after} is null 26 */ 27 default Consumer<T> andThen(Consumer<? super T> after) { 28 Objects.requireNonNull(after); 29 return (T t) -> { accept(t); after.accept(t); }; 30 } 31 }
直接看accept抽象方法,接收一个泛型T类型的t,返回值类型是void,我们把它叫做消费型接口。特点就是有去无回。
下面我们直接看实例
1 public class InfixFunctionTest { 2 //1.消费型接口 3 @Test 4 public void test1(){ 5 //把传入的字符串打印 6 Consumer<String> con = x -> System.out.println(x);//定义函数式的实现 7 con.accept("Hello Consumer!");//接收参数 8 } 9 10 }
执行结果
com.dream.test.JDK8speciality.InfixFunctionTest,test1 Hello Consumer! Process finished with exit code 0
我们只需要在Lambda表达式的参数列表中传入一个x,然后实现是:得到一个无返回类型的打印语句。
2. Supplier(没有传入,有传出的时候使用)
官方源码
1 package java.util.function; 2 3 /** 4 * Represents a supplier of results. 5 * 6 * <p>There is no requirement that a new or distinct result be returned each 7 * time the supplier is invoked. 8 * 9 * <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a> 10 * whose functional method is {@link #get()}. 11 * 12 * @param <T> the type of results supplied by this supplier 13 * 14 * @since 1.8 15 */ 16 @FunctionalInterface 17 public interface Supplier<T> { 18 19 /** 20 * Gets a result. 21 * 22 * @return a result 23 */ 24 T get(); 25 }
get方法没有传入参数,返回一个T,称为供给型接口。特点就是只求回报不求付出。
实例
1 public class InfixFunctionTest { 2 3 //2.供给型接口 4 @Test 5 public void test2(){ 6 Supplier<String> su = () -> new String(); 7 String str = su.get(); 8 System.out.println("供给型接口的值:" + str); 9 } 10 11 }
执行结果
com.dream.test.JDK8speciality.InfixFunctionTest,test2
供给型接口的值:
Process finished with exit code 0
我们在Lambda表达式传入参数用()代表没有参数传入,然后返回一个String类型的对象。
3.Function(有传入参数,传出的时候使用)
官方源码
1 package java.util.function; 2 3 import java.util.Objects; 4 5 /** 6 * Represents a function that accepts one argument and produces a result. 7 * 8 * <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a> 9 * whose functional method is {@link #apply(Object)}. 10 * 11 * @param <T> the type of the input to the function 12 * @param <R> the type of the result of the function 13 * 14 * @since 1.8 15 */ 16 @FunctionalInterface 17 public interface Function<T, R> { 18 19 /** 20 * Applies this function to the given argument. 21 * 22 * @param t the function argument 23 * @return the function result 24 */ 25 R apply(T t); 26 27 /** 28 * Returns a composed function that first applies the {@code before} 29 * function to its input, and then applies this function to the result. 30 * If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to 31 * the caller of the composed function. 32 * 33 * @param <V> the type of input to the {@code before} function, and to the 34 * composed function 35 * @param before the function to apply before this function is applied 36 * @return a composed function that first applies the {@code before} 37 * function and then applies this function 38 * @throws NullPointerException if before is null 39 * 40 * @see #andThen(Function) 41 */ 42 default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) { 43 Objects.requireNonNull(before); 44 return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v)); 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * Returns a composed function that first applies this function to 49 * its input, and then applies the {@code after} function to the result. 50 * If evaluation of either function throws an exception, it is relayed to 51 * the caller of the composed function. 52 * 53 * @param <V> the type of output of the {@code after} function, and of the 54 * composed function 55 * @param after the function to apply after this function is applied 56 * @return a composed function that first applies this function and then 57 * applies the {@code after} function 58 * @throws NullPointerException if after is null 59 * 60 * @see #compose(Function) 61 */ 62 default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) { 63 Objects.requireNonNull(after); 64 return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t)); 65 } 66 67 /** 68 * Returns a function that always returns its input argument. 69 * 70 * @param <T> the type of the input and output objects to the function 71 * @return a function that always returns its input argument 72 */ 73 static <T> Function<T, T> identity() { 74 return t -> t; 75 } 76 }
Function接口提供了一个抽象方法,两个默认方法和一个静态方法。这里我只对最常用的抽象方法做出解释。
apply方法接收一个T类型的t,返回一个R类型的值。我们称之为函数型接口。特点就是你来我往。(俗话说的好,来而不往非礼也!哈哈哈!)
实例
1 public class InfixFunctionTest { 2 3 //3.函数型接口 4 @Test 5 public void test3(){ 6 Function<String,Camera> fun = (x) -> new Camera(x);//Function抽象函数的实现。 7 Camera camera = fun.apply("Sony-A7R3");//接收传入的参数 8 System.out.println("cameraName: " + camera.getCameraName() + " price:" + camera.getPrice()); 9 } 10 11 }
Camera类
1 //相机类 2 class Camera{ 3 //相机名字 4 private String cameraName; 5 //相机价格 6 private Integer price; 7 8 //无参数构造器 9 public Camera(){ 10 11 } 12 13 //有参数构造器 14 public Camera(String cameraName){ 15 this.cameraName = cameraName; 16 } 17 18 //有参数构造器 19 public Camera(String cameraName,Integer price){ 20 this.cameraName = cameraName; 21 this.price = price; 22 } 23 24 public String getCameraName() { 25 return cameraName; 26 } 27 28 public void setCameraName(String cameraName) { 29 this.cameraName = cameraName; 30 } 31 32 public Integer getPrice() { 33 return price; 34 } 35 36 public void setPrice(Integer price) { 37 this.price = price; 38 } 39 }
执行结果
com.dream.test.JDK8speciality.InfixFunctionTest,test3 cameraName: Sony-A7R3 price:null Process finished with exit code 0
Lam表达式中传入一个参数x,然后x作为构造器的参数,返回一个Camera对象。
4.Predicate(传入一个参数,返回一个布尔类型的结果)
官网源码
1 package java.util.function; 2 3 import java.util.Objects; 4 5 /** 6 * Represents a predicate (boolean-valued function) of one argument. 7 * 8 * <p>This is a <a href="package-summary.html">functional interface</a> 9 * whose functional method is {@link #test(Object)}. 10 * 11 * @param <T> the type of the input to the predicate 12 * 13 * @since 1.8 14 */ 15 @FunctionalInterface 16 public interface Predicate<T> { 17 18 /** 19 * Evaluates this predicate on the given argument. 20 * 21 * @param t the input argument 22 * @return {@code true} if the input argument matches the predicate, 23 * otherwise {@code false} 24 */ 25 boolean test(T t); 26 27 /** 28 * Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical 29 * AND of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed 30 * predicate, if this predicate is {@code false}, then the {@code other} 31 * predicate is not evaluated. 32 * 33 * <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed 34 * to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the 35 * {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated. 36 * 37 * @param other a predicate that will be logically-ANDed with this 38 * predicate 39 * @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical 40 * AND of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate 41 * @throws NullPointerException if other is null 42 */ 43 default Predicate<T> and(Predicate<? super T> other) { 44 Objects.requireNonNull(other); 45 return (t) -> test(t) && other.test(t); 46 } 47 48 /** 49 * Returns a predicate that represents the logical negation of this 50 * predicate. 51 * 52 * @return a predicate that represents the logical negation of this 53 * predicate 54 */ 55 default Predicate<T> negate() { 56 return (t) -> !test(t); 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * Returns a composed predicate that represents a short-circuiting logical 61 * OR of this predicate and another. When evaluating the composed 62 * predicate, if this predicate is {@code true}, then the {@code other} 63 * predicate is not evaluated. 64 * 65 * <p>Any exceptions thrown during evaluation of either predicate are relayed 66 * to the caller; if evaluation of this predicate throws an exception, the 67 * {@code other} predicate will not be evaluated. 68 * 69 * @param other a predicate that will be logically-ORed with this 70 * predicate 71 * @return a composed predicate that represents the short-circuiting logical 72 * OR of this predicate and the {@code other} predicate 73 * @throws NullPointerException if other is null 74 */ 75 default Predicate<T> or(Predicate<? super T> other) { 76 Objects.requireNonNull(other); 77 return (t) -> test(t) || other.test(t); 78 } 79 80 /** 81 * Returns a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according 82 * to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)}. 83 * 84 * @param <T> the type of arguments to the predicate 85 * @param targetRef the object reference with which to compare for equality, 86 * which may be {@code null} 87 * @return a predicate that tests if two arguments are equal according 88 * to {@link Objects#equals(Object, Object)} 89 */ 90 static <T> Predicate<T> isEqual(Object targetRef) { 91 return (null == targetRef) 92 ? Objects::isNull 93 : object -> targetRef.equals(object); 94 } 95 }
Predicate接口提供了一个抽象方法,三个默认方法和一个静态方法。这里是对抽象方法进行举例说明。
由于返回一个布尔类型的值,我们称之为断言型。特点就是发出请求,等待指示(做还是不做,哈哈)。
1 public class InfixFunctionTest { 2 3 //4.断言式接口 4 @Test 5 public void test4(){ 6 Predicate<String> pre = x -> x == null; 7 Boolean b =pre.test(null); 8 System.out.println("断言式测试结果:" + b); 9 } 10 11 }
执行结果
com.dream.test.JDK8speciality.InfixFunctionTest,test4 断言式测试结果:true Process finished with exit code 0
Lambda表达式传入一个参数x,判断x是不是null。
以上实例中都省略了头部的打包和导入包信息,包信息如下。
1 package com.dream.test.JDK8speciality; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 5 import java.util.function.Consumer; 6 import java.util.function.Function; 7 import java.util.function.Predicate; 8 import java.util.function.Supplier;
java.util.function包下除了上面这几个基本函数式接口外,还有好多。其他的都是这几个基本的衍生。这几个搞懂了,其他的就都不难理解了。有兴趣的可以自己进行研究。
以上就是对函数式的学习。如果各位大神发现有不对或者不好的地方,欢迎指正。非常感谢!
上一篇文章