在介绍Spring IoC和MVC的加载前,用这篇小文章简单地记录下,最简单的web应用的加载过程。
一、从最简单的web应用出发
使用Eclipse直接创建一个Dynamic Web Project即可,工程如下test-web,然后右键→Run as→Run on Server,然后访问:http://localhost:8080/test-web/
可以看到,返回的是404错误,表示找不到请求的资源。
其实这个web应用是可运行而且没问题的。问题在于它没有Servlet可以接收并处理请求,在这里也没有定义首页和错误页的默认选项,因此应用直接返回了404找不到资源错误。如果把首页配置上去,默认的访问可以直接使用首页,我们增加web.xml和欢迎页index.jsp,如下
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" 5 id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> 6 <display-name>test-web</display-name> 7 <welcome-file-list> 8 <welcome-file>/WEB-INF/jsp/index.jsp</welcome-file> 9 </welcome-file-list> 10 </web-app>
index.jsp
1 <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" 2 pageEncoding="utf-8"%> 3 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> 4 <html> 5 <head> 6 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> 7 <title>Insert title here</title> 8 </head> 9 <body>Hello 10 </body> 11 </html>
重新启动应用,然后访问http://localhost:8080/test-web/,结果如下。
可见,确实得到了正确的响应。
二、Web应用的简单加载过程
那Web是怎样加载的呢?如下图:
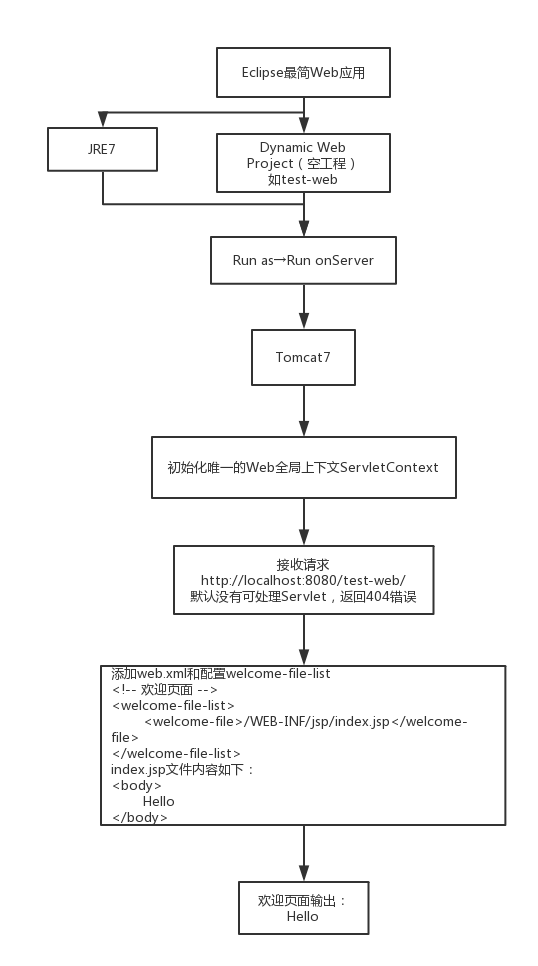
简单地说,web应用加载后,会先初始化整个web应用的唯一的ServletContext,即Servlet应用上下文(说白了就只有这一步)。这个上下文是必须要有的,而且每个web应用只有一个。ServletContext定义了运行在Servlet的应用程序环境的一些行为和观点,可以使用ServletContext实现对象来取得所请求资源的URL、设置与存储属性、应用程序初始参数,甚至动态设置Servlet实例。web.xml中配置的首页、错误页等,都会被web应用解析并按照最后的请求适配处理。
ServletContext属性的配置可以在web.xml的<context-param />中配置:
1 <context-param> 2 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 3 <param-value> 4 classpath*:applicationContext*.xml 5 </param-value> 6 </context-param>
总结一句话就是:web应用在部署时,web容器为web应用初始化了唯一的ServletContext,之后其他的可扩展选项按照配置进行初始化,然后就开始接收请求进行处理。
以上便是一个最简web应用的加载。
三、Web应用的常规加载过程
实际上,一个web.xml里面有很多的配置,而其中,接触最多的就是Listener、Filter、Servlet。在这里。我们并没有定义Listener、Filter、Servlet(实际处理请求的类),这是可行的,因为这些都是可扩展的选择。下面简单地介绍下这几个扩展选项:
1、Listener:
Web容器管理Servlet/JSP相关的对象生命周期,若对HttpServletRequest对象、HttpSession对象、ServletContext对象在生成、销毁或相关属性设置发生变化的时机点有兴趣,需要进行一些处理,如进行资源的加载、数据库的初始化等,可以使用Listener。主要有2大类的监听器Listener:
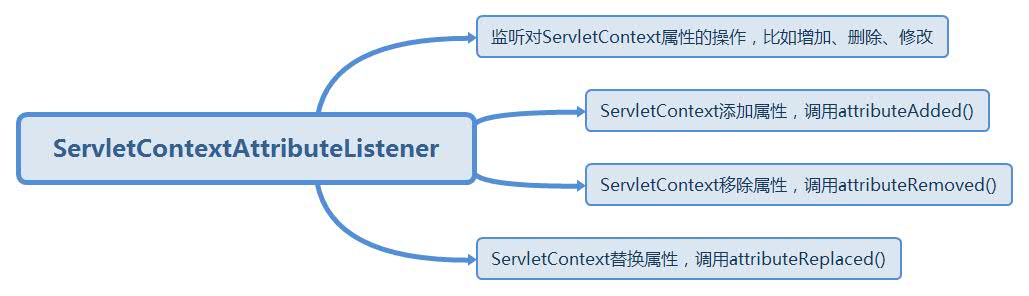
- ServletContext事件监听器:ServletContextListener、ServletContextAttributeListener
- HttpSession事件监听器:HttpSessionListener、HttpSessionAttributeListener、HttpSessionBindingListener、HttpSessionActivationListener
下面主要讲解ServletContext相关的2个监听器,其作用如下:
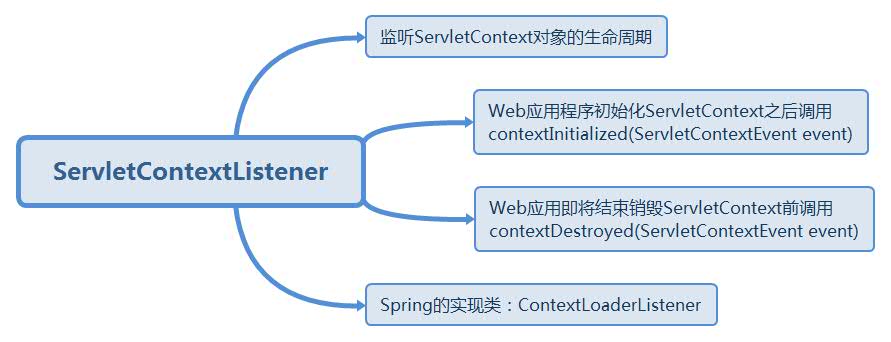
Spring IoC容器的配置就是ServletContextListener的实现类ContextLoaderListener,它在ServletContext加载之后就开始进行IoC容器的初始化和bean的加载解析。配置如下:
1 <!-- 默认的spring配置文件是在WEB-INF下的applicationContext.xml --> 2 <listener> 3 <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> 4 </listener> 5 <context-param> 6 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 7 <param-value> 8 classpath*:applicationContext*.xml 9 </param-value> 10 </context-param>
2、Filter
在容器调用Servlet的service()方法前,Servlet并不会知道有请求的到来,而在Servlet的service()方法运行后,容器真正对浏览器进行HTTP相应之前,浏览器也不会知道Servlet真正的响应是什么。过滤器Filter正如其名称所示,是介于Servlet之前,可拦截过滤浏览器对Servlet的请求,也可以改变Servlet对浏览器的响应。Filter的解析是按照其在web.xml中的声明顺序来的。
常见到的就是强制字符转码的CharacterEncodingFilter:
1 <filter> 2 <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> 3 <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> 4 <init-param> 5 <param-name>encoding</param-name> 6 <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> 7 </init-param> 8 </filter> 9 <filter-mapping> 10 <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> 11 <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> 12 </filter-mapping>
3、Servlet
这是处理实际请求的类,整个web应用存在的意义,是因为存在可以处理实际请求的Servlet,因此,一般Web应用中都需要配置Servlet。而Spring Web MVC中配置的类就是DispatcherServlet,如下:
1 <!-- springMVC的核心控制器 --> 2 <servlet> 3 <servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name> 4 <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> 5 <init-param> 6 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 7 <param-value>classpath*:springMVC-servlet.xml</param-value> 8 </init-param> 9 <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 10 </servlet> 11 <servlet-mapping> 12 <servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name> 13 <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> 14 </servlet-mapping>
从以上定义可以看出(实际上也可以进行调试debug):这些加载顺序 context-param ==> Listener ==> Filter ==> Servlet。
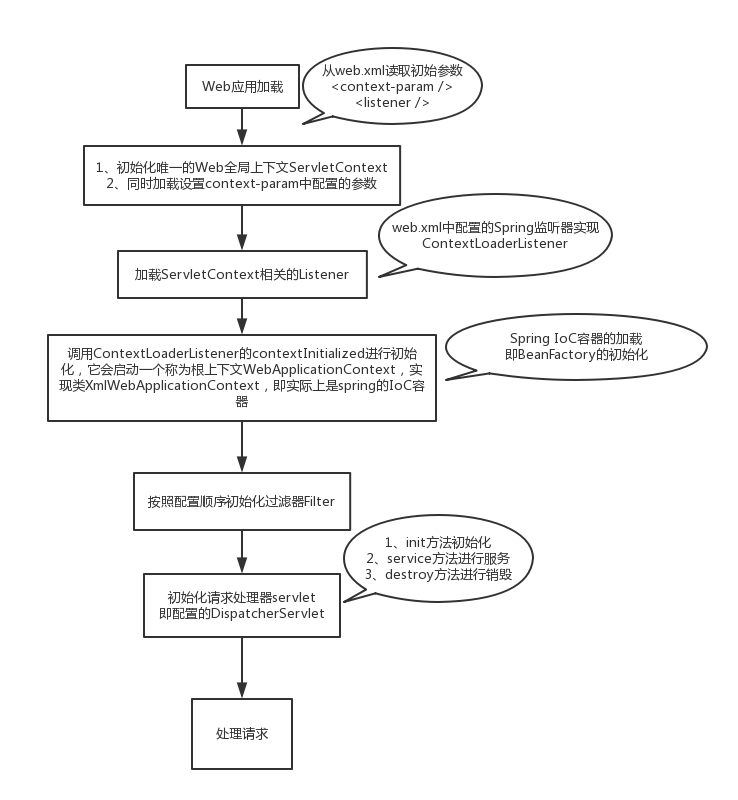
大体的加载流程表示如下:
- 读取web.xml的配置参数,如context-param、listener配置等
- web容器为web应用初始化一个唯一的全局上下文ServletContext,并把上述的参数配置即context-param,维护到ServletContext中。
- ServletContext初始化完成后,初始化配置的Listener,这里是Spring的ContextLoaderListener(实现了ServletContextListener,ServletContext初始化完成后会调用其contextInitialized方法),初始化Spring的IoC容器,即ApplicationContext,同时把自己设置给ServletContext,并设置WebApplicationContext.ROOTWEBAPPLICATIONCONTEXTATTRIBUTE。
- 按照顺序加载配置Filter
- 加载配置的Servlet。这里是DispatcherServlet,它会初始化自己的ApplicationContext(主要是controller),同时把IoC容器的ApplicationContext,即WebApplicationContext.ROOTWEBAPPLICATIONCONTEXTATTRIBUTE设置为自己的父容器,并注册在ServletContext。
整体的web.xml配置
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" 5 id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> 6 7 <!-- 默认的spring配置文件是在WEB-INF下的applicationContext.xml --> 8 <listener> 9 <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> 10 </listener> 11 <context-param> 12 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 13 <param-value> 14 classpath*:applicationContext*.xml 15 </param-value> 16 </context-param> 17 18 <!-- 强制进行转码 --> 19 <filter> 20 <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> 21 <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> 22 <init-param> 23 <param-name>encoding</param-name> 24 <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> 25 </init-param> 26 </filter> 27 <filter-mapping> 28 <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> 29 <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> 30 </filter-mapping> 31 32 <!-- springMVC的核心控制器 --> 33 <servlet> 34 <servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name> 35 <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> 36 <init-param> 37 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 38 <param-value>classpath*:springMVC-servlet.xml</param-value> 39 </init-param> 40 <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 41 </servlet> 42 <servlet-mapping> 43 <servlet-name>springMVC</servlet-name> 44 <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> 45 </servlet-mapping> 46 47 <!-- session配置 --> 48 <session-config> 49 <session-timeout>30</session-timeout> 50 </session-config> 51 52 <!-- 欢迎页面 --> 53 <welcome-file-list> 54 <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> 55 <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> 56 </welcome-file-list> 57 58 <!-- 错误页面 --> 59 <error-page> 60 <error-code>403</error-code> 61 <location>/WEB-INF/jsp/403.jsp</location> 62 </error-page> 63 <error-page> 64 <error-code>404</error-code> 65 <location>/WEB-INF/jsp/404.jsp</location> 66 </error-page> 67 <error-page> 68 <error-code>500</error-code> 69 <location>/WEB-INF/jsp/500.jsp</location> 70 </error-page> 71 <error-page> 72 <exception-type>java.lang.Throwable</exception-type> 73 <location>/WEB-INF/jsp/error.jsp</location> 74 </error-page> 75 </web-app>
备注:web.xml的其他配置、IoC的记载、DispatcherServlet的解析等后续将进行逐一介绍。