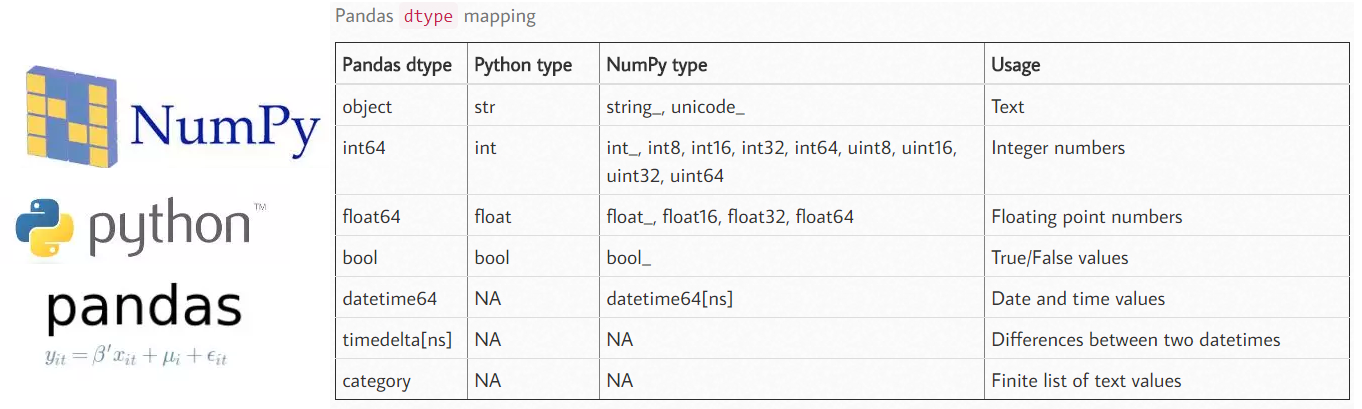
当利用pandas进行数据处理的时候,经常会遇到数据类型的问题,当拿到数据的时候,首先需要确定拿到的是正确类型的数据,一般通过数据类型的转化,这篇文章就介绍pandas里面的数据类型(data types也就是常用的dtyps),以及pandas与numpy之间的数据对应关系。
dataframe中的 object 类型来自于 Numpy, 他描述了每一个元素 在 ndarray 中的类型 (也就是Object类型)。而每一个元素在 ndarray 中 必须用同样大小的字节长度。 比如 int64 float64, 他们的长度都是固定的 8 字节。
但是对于string 来说,string 的长度是不固定的, 所以pandas 储存string时 使用 narray, 每一个object 是一个指针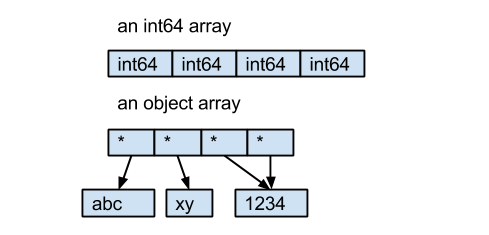
我们以官网案例作为解析,这样可以省去很多时间。
import pandas as pd import numpy as np df = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/chris1610/pbpython/blob/master/data/sales_data_types.csv?raw=True")
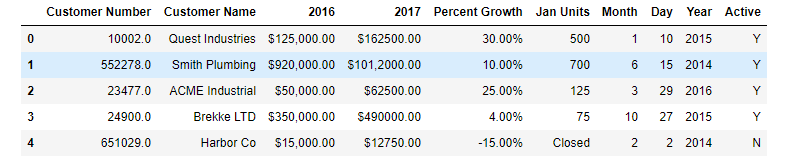
然后我们查看每个字段的数据类型:
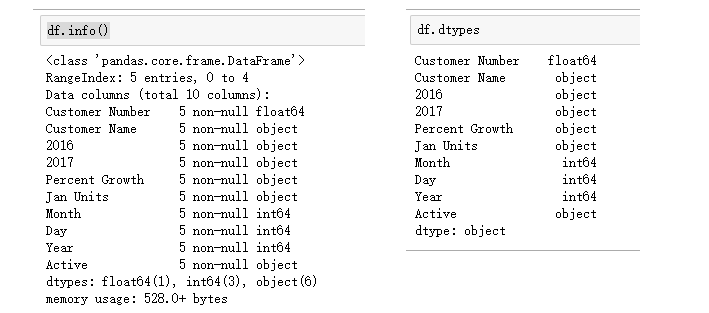
数据类型问题如下:
-
Customer number 应该是int64,不应该是float64
-
2016和2017两个字段是object字符串,但我们应该将其转换为float64或者int64
-
Percent Growth 应该是数字,但是这里是object字符串
-
Year、Month、Day 三个字段应该合并为一个datetime类型的日期数据
-
Active应该是bool型数据
数据类型转换的方法
转换数据类型的思路
-
使用astype()方法强制转化dtype
-
自定义一个数据转换函数函数
-
使用pandas内置的tonumeric()和todatetime()
-
导入数据时转换数据类型
1、使用astype()方法
处理pandas数据类型最简单的办法是astype()
df['Customer Number'].astype('int')

def astype(self, dtype, copy=True, errors='raise', **kwargs): ############################################################## dtype : data type, or dict of column name -> data type Use a numpy.dtype or Python type to cast entire pandas object to the same type. Alternatively, use {col: dtype, ...}, where col is a column label and dtype is a numpy.dtype or Python type to cast one or more of the DataFrame's columns to column-specific types. errors : {'raise', 'ignore'}, default 'raise'. Control raising of exceptions on invalid data for provided dtype. - ``raise`` : allow exceptions to be raised - ``ignore`` : suppress exceptions. On error return original object raise_on_error : DEPRECATED use ``errors`` instead kwargs : keyword arguments to pass on to the constructor ##############################################################
方法:
df["Customer Number"] = df['Customer Number'].astype('int') df=df.astype({"Customer Number":'int64'}) df.dtypes

那么如何将2016、2017、PercentGrowth、JanUnits列 从 字符串 转化为 数字,很明显传统的astype的方法是不行的。
需要自定义类型转换方法。
2、自定义转换函数
自定义:
以 2016和2017列为例,在强制从字符串转为数字之前,我们需要先将 "$"、"."、"," 剔除掉,然后再转换。
def convert_currency(val): """ Convert the string number value to a float - Remove $ - Remove commas - Convert to float type """ new_val = val.replace(',','').replace('$', '') return float(new_val) df['2016']=df['2016'].apply(convert_currency) df.dtypes

也可以使用lamda表达式
例如下面的
df['Percent Growth']=df['Percent Growth'].apply(lambda x: x.replace('%', '')).astype('float') / 100 df.dtypes

np.where()方法:
np.where(condition, do1, do2)
如果condition满足条件,执行do1,否则执行do2
import numpy as np df["Active"] = np.where(df["Active"] == "Y", True, False) df
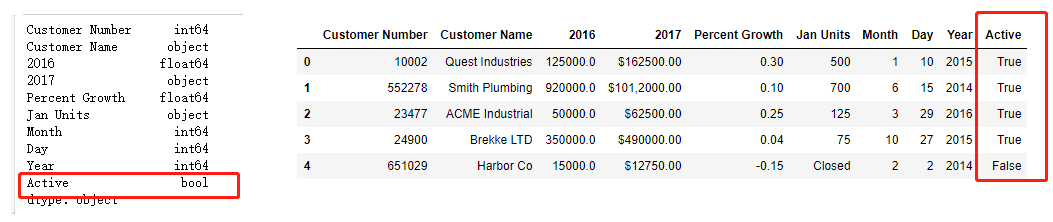
3、pandas内置的处理函数
pandas还有
pd.to_numeric(arg,errors='raise')
pd.to_datetime(arg,errors='raise')
函数帮助我们转为数据类型。
errors参数有:
-
raise, errors默认为raise
-
ignore 忽略错误,并把转化前的值直接返回
-
coerce 将错误数据标注为NaN
因为数据不一定是干净的,对于错误数据我们有三种处理措施。
pd.to_numeric(df['Jan Units'], errors='coerce')

pd.to_numeric(df['Jan Units'], errors='ignore')

to_datetime
convert the separate month, day and year columns into a datetime . The pandas pd.to_datetime() function is quite configurable but also pretty smart by default.
he function combines the columns into a new series of the appropriate datateime64 dtype.
df["Start_Date"] = pd.to_datetime(df[['Month', 'Day', 'Year']])
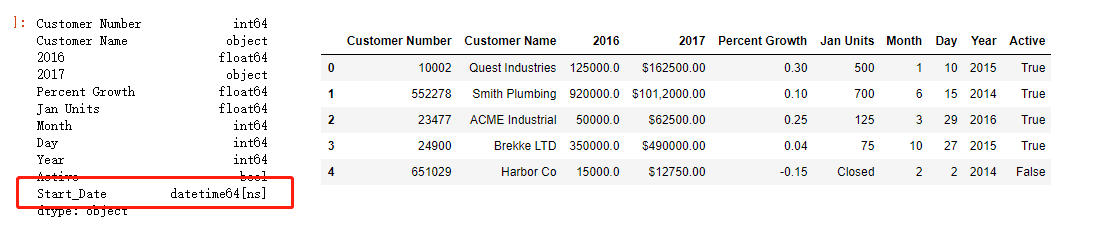
四、导入数据时转换数据类型
除了上面的三种方法,实际上我们也可以在导入数据的时候就处理好。
def convert_currency(val): """ Convert the string number value to a float - Remove $ - Remove commas - Convert to float type """ new_val = val.replace(',','').replace('$', '') return float(new_val) df_2 = pd.read_csv("https://github.com/chris1610/pbpython/blob/master/data/sales_data_types.csv?raw=True", dtype={'Customer Number': 'int'}, converters={'2016': convert_currency, '2017': convert_currency, 'Percent Growth': lambda x: float(x.replace('%', '')) / 100, 'Jan Units': lambda x: pd.to_numeric(x, errors='coerce'), 'Active': lambda x: np.where(x == "Y", True, False) })
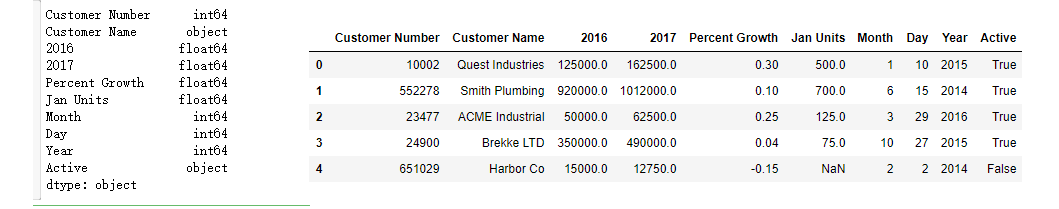
这章内容参考博客见文档