定义Restful的视图:
1. 从`flask_restful`中导入`Api`,来创建一个`api`对象。
2.如果使用Flask-Restful,则定义视图函数的时候,要继承自flask-restful.Resource类,然后再根据当前请求的method来定义相应的方法。
3. 使用`api.add_resource`来添加视图与`url`。
比如期望客户端是使用get方法发送过来的请求,那么就定义一个get方法。类似于MethodView。示例代码如下:
案例1:
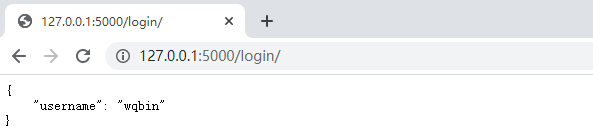
from flask_restful import Api, Resource app = Flask(__name__) api = Api(app) class Login(Resource): def get(self): return {"username": "wqbin"} api.add_resource(Login, '/login/', endpoint='login_func') with app.test_request_context(): print(url_for('login_func'))
案例2:
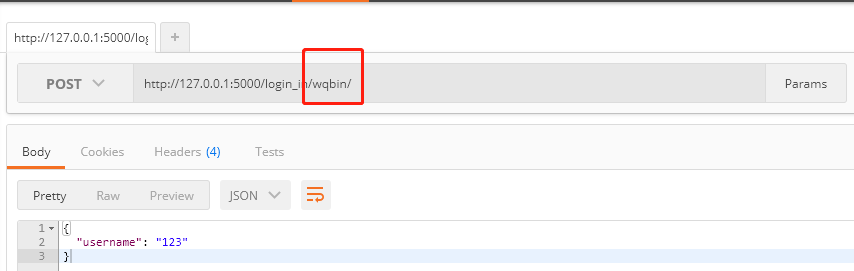
class Login_in(Resource): def post(self,username): return {"username": '123'} api.add_resource(Login_in, '/login_in/<username>/',endpoint="login_in_func") # with app.test_request_context(): print(url_for('login_in_func',username='wqbin'))
注意事项:
1.endpoint 是用来给url_for反转url的时候指定的。如果不写endpoint,那么将会使用视图的名字的小写来作为endpoint。
2.add_resource的第二个参数是访问这个视图函数的ur1,这个ur1可以跟之前的route一样,可以传递参数。并且还有一点不同的是,这个方法可以传递多个ur1来指定这个视图函数。
参数解析:
Flask-Restful插件提供了类似wTForas来验证提交的数据是否合法的包,叫做reqparse。以下是基本用法:
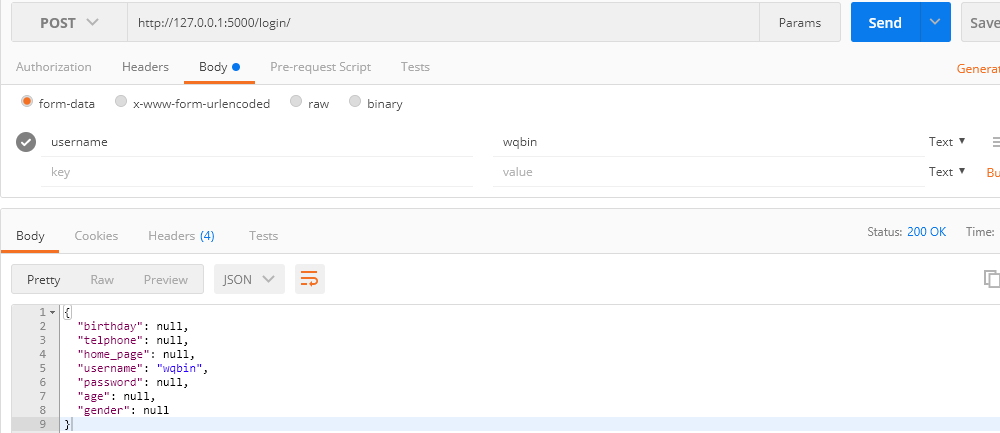
class LoginView(Resource): def post(self): # username # password from datetime import date parser = reqparse.RequestParser() parser.add_argument('birthday', type=inputs.date, help='生日字段验证错误!') parser.add_argument('telphone',type=inputs.regex(r'1[3578]d{9}')) parser.add_argument('home_page',type=inputs.url,help='个人中心链接验证错误!') parser.add_argument('username',type=str,help='用户名验证错误!',required=True) parser.add_argument('password',type=str,help='密码验证错误!') parser.add_argument('age',type=int,help='年龄验证错误!') parser.add_argument('gender',type=str,choices=['male','female','secret']) args = parser.parse_args() print(args) return args api.add_resource(LoginView, '/login/')
add_argument可以指定这个字段的名字,这个字段的数据类型等。以下将对这个方法的一些参数做详细讲解:
1.default:黑默认值,如果这个参数没有值,那么将使用这个参数指定的值。
2.required:是否必须。默认为False,如果设置为True,那么这个参数就必须提交上来。
3.type:这个参数的数据类型,如果指定,那么将使用指定的数据类型来强制转换提交上来的值。
4.choices:选项。提交上来的值只有满足这个选项中的值才符合验证通过,否则验证不通过。
5.help:错误信息。如果验证失败后,将会使用这个参数指定的值作为错误信息。
6.trim:是否要取出前后的空格。
其中的type,可以使用python 自带的一些数据类型,也可以使用f1ask-restful.inputs下的一些特定的数据类型来强制转换。比如一些常用的:
1.url:会判断这个参数的值是否是一个url,如果不是,那么就会抛出异常。
2.regex:正则表达式。
3.date:将这个字符串转换为datetime.date数据类型。如果转换不成功,则会抛出一个异常。
输出字段:
对于一个视图函数,可以指定某些字段用于返回。一般可以使用ORM模型或者自定义的模型的会自动的获取模型中的相应的字段,生成json数据,然后再返回给客户端。
这其中需要导入flask_restful.marshal_with 装饰器。并且需要写一个字典,来指示需要返回的字段,以及该字段的数据类型。
示例代码如下:
from flask_restful import Resource, fields, marshal_with, Api api = Api(app) class Article(object): def __init__(self,title,content): self.title = title self.content = content article = Article(title='blog',content='flask_restful.marshal_with content') # class ArticleView(Resource): resource_fields = { 'title': fields.String, 'content': fields.String, 'page': fields.Integer } # restful规范中,要求,定义好了返回的参数 # 即使这个参数没有值,也应该返回,返回一个None回去 @marshal_with(resource_fields) def get(self): return article api.add_resource(ArticleView,'/article/',endpoint='article')
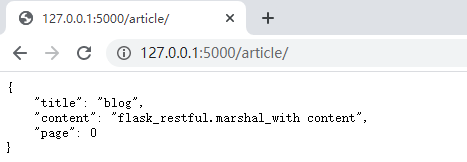
在get方法中,返回user的时候,flask-restful会自动的读取artical模型上的title以及content还有page属性。组装成一个json格式的字符串返回给客户端。
重命名属性:
面向公众的字段名称往往是不同于内部的属性名。使用attribute可以配置这种映射。比如现在想要返回user.school中的值,但是在返回给外面的时候,想以education 返回回去,那么可以这样写:
resource_fields={ 'education':fields.String(attribute='school')}
默认值:
在返回一些字段的时候,有时候可能没有值,那么这时候可以在指定fields的时候给定一个默认值,示例代码如下:
resource_fields = {'read_count': fields.Integer(default=80)}
复杂结构:
有时候想要在返回的数据格式中,形成比较复杂的结构。
那么可以使用一些特殊的字段来实现。
比如要在一个字段中放置一个列表则使用fields.List,是一个字典则使用fields.Nested。
以下将讲解下复杂结构的用法:
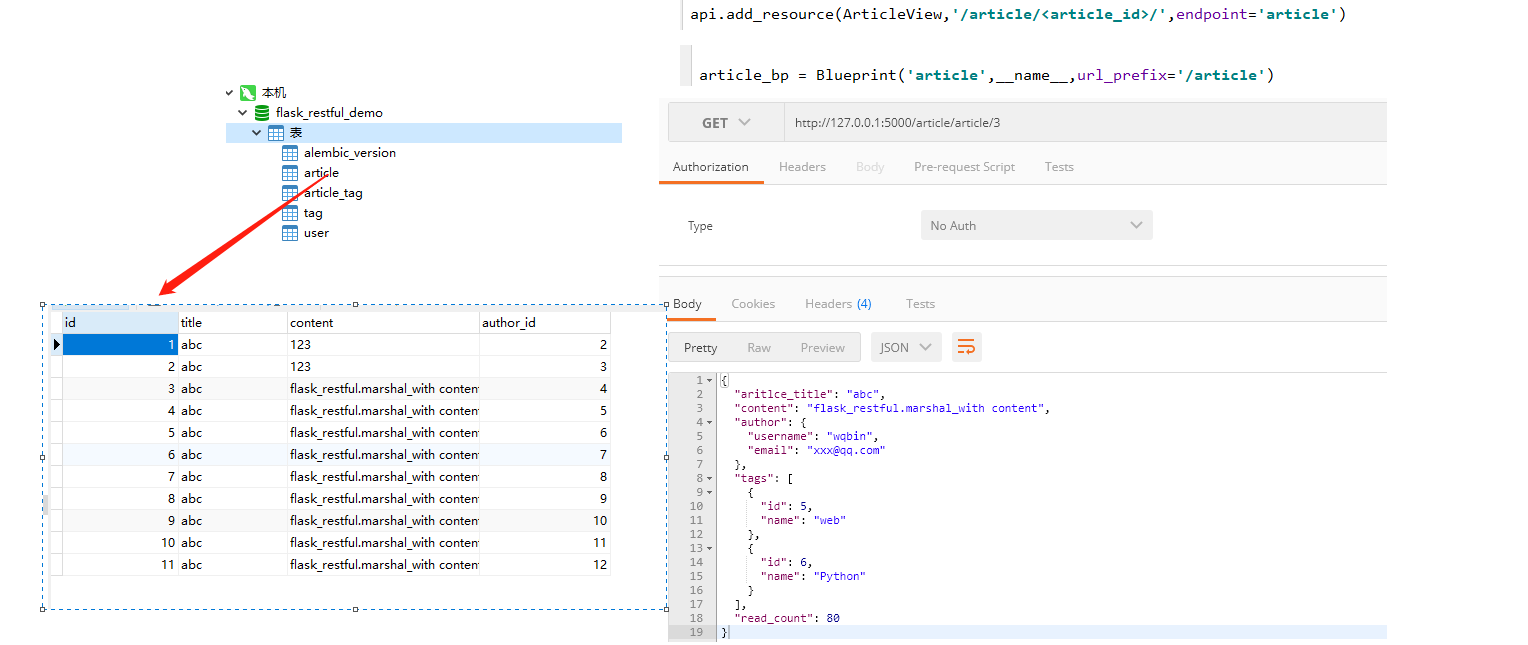
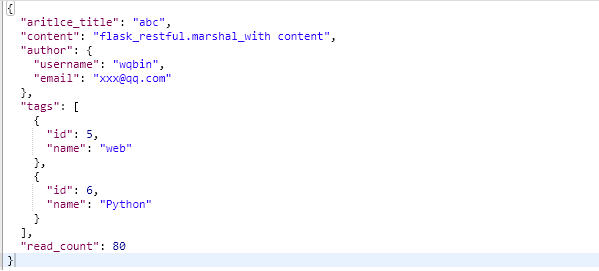
class ArticleView(Resource): resource_fields = { 'aritlce_title':fields.String(attribute='title'), 'content':fields.String, 'author': fields.Nested({ 'username': fields.String, 'email': fields.String }), 'tags': fields.List(fields.Nested({ 'id': fields.Integer, 'name': fields.String })), 'read_count': fields.Integer(default=80) } @marshal_with(resource_fields) def get(self,article_id): article = Article.query.get(article_id) return article
Flask-restful蓝图注意事项:
1. 在蓝图中,如果使用`flask-restful`,那么在创建`Api`对象的时候,就不要再使用`app`了,而是使用蓝图。
2. 如果在`flask-restful`的视图中想要返回`html`代码模版的渲染而不是原始代码,
那么就应该使用`api.representation`这个装饰器来定义一个输出函数,在这个函数中会对`html`代码进行一个封装再返回。
示例代码如下:
@api.representation('text/html') def output_html(data,code,headers): print(data) # 在representation装饰的函数中,必须返回一个Response对象 resp = make_response(data) return resp class ListView(Resource): def get(self): return render_template('index.html') api.add_resource(ListView,'/list/',endpoint='list')

综合项目

from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy db = SQLAlchemy()

from exts import db # 第一个:用户 # 第二个:文章 # 第三个:标签 class User(db.Model): __tablename__ = 'user' id = db.Column(db.Integer,primary_key=True) username = db.Column(db.String(50)) email = db.Column(db.String(50)) article_tag_table = db.Table('article_tag', db.Column('article_id',db.Integer,db.ForeignKey("article.id"),primary_key=True), db.Column('tag_id',db.Integer,db.ForeignKey("tag.id"),primary_key=True) ) class Article(db.Model): __tablename__ = 'article' id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True) title = db.Column(db.String(100)) content = db.Column(db.Text) author_id = db.Column(db.Integer,db.ForeignKey('user.id')) author = db.relationship("User",backref='articles') tags = db.relationship("Tag",secondary=article_tag_table,backref='tags') class Tag(db.Model): __tablename__ = 'tag' id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True) name = db.Column(db.String(50))

from flask import Blueprint,render_template,make_response from flask_restful import Api,Resource,fields,marshal_with from models import Article article_bp = Blueprint('article',__name__,url_prefix='/article') api = Api(article_bp) @api.representation('text/html') def output_html(data,code,headers): print(data) # 在representation装饰的函数中,必须返回一个Response对象 resp = make_response(data) return resp class ArticleView(Resource): resource_fields = { 'aritlce_title':fields.String(attribute='title'), 'content':fields.String, 'author': fields.Nested({ 'username': fields.String, 'email': fields.String }), 'tags': fields.List(fields.Nested({ 'id': fields.Integer, 'name': fields.String })), 'read_count': fields.Integer(default=80) } @marshal_with(resource_fields) def get(self,article_id): article = Article.query.get(article_id) return article # /article/article/1/ api.add_resource(ArticleView,'/<article_id>/',endpoint='article') class ListView(Resource): def get(self): return render_template('index.html') api.add_resource(ListView,'/list/',endpoint='list')

#自定义 import config from exts import db from models import User,Article,Tag from articleviews import article_bp,ArticleView #flask from flask import Flask from flask_restful import Resource, fields, marshal_with, Api app = Flask(__name__) app.config.from_object(config) db.init_app(app) app.register_blueprint(article_bp) #1. flask-restful结合蓝图使用 #2. 使用flask-restful渲染模版 api = Api(app) article = Article(title='blog',content='flask_restful.marshal_with content') api.add_resource(ArticleView,'/article/',endpoint='article') @app.route('/') def hello_world(): user = User(username='wqbin',email='1445207429@qq.com') article = Article(title='abc',content='flask_restful.marshal_with content') article.author = user tag1 = Tag(name='web') tag2 = Tag(name='Python') article.tags.append(tag1) article.tags.append(tag2) db.session.add(article) db.session.commit() return 'Hello World!' if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True)

from flask_script import Manager from app import app from flask_migrate import MigrateCommand,Migrate from exts import db import models manager = Manager(app) Migrate(app,db) manager.add_command('db',MigrateCommand) if __name__ == '__main__': manager.run()