一、创建一个字符串
1.String(char a[]):用一个字符数组a创建一个string类型
char a[]= {'h','e','l','l','o'};
String s=new String (a);
System.out.println(s);
2.
char a[]= {'h','e','l','l','o'};
String s=new String (a,1,4);
第一个数字表示从哪个字符开始截取,第二个数字表示截取字符的长度。
字符数组下标从零开始。
3.字符串常量的引用赋值给字符串变量
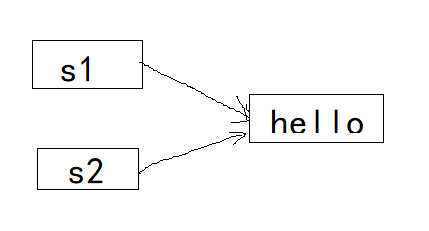
String s1,s2;
s1="hello";
s2="hello";
此时s1,s2引用有相同的字符串常量,因此具有相同的实体。
二、连接字符串“+”
三、获取字符串信息
1.长度length()方法
2.indexOf(String s):要搜索的字符串的首次出现的位置
lastIndexOf():最后一次出现的位置
3.charAt(int index):
四、字符串操作
1.截取 substring()
System.out.println(s1.substring(1,2));
2.去除第一个和最后一个空格
trim()
3.字符串替换
System.out.println(s1.replace('l','a'));
有几个要替换的字符换几个
4.判断字符串的开始与结尾
判断是否该字符串以指定的内容开始或结束,返回布尔类型
参数必须为字符串
System.out.println(s2.startsWith("l"));
System.out.println(s1.endsWith("l"));
5.==:判断的是字符串的地址是否相同
String s1,s2;
s1="hello";
s2="hello";
System.out.println(s1==s2);
//true
String s1=new String("hello");
String s2=new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1==s2);
//false
equals()
String s1,s2;
s1="hello";
s2="hello";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
//true
String s1=new String("hello");
String s2=new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
//true
equalsIgnoreCase()
忽略大小写
6.按字典序比较两个字符串
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));
如果不相等,前面的字典序在前,返回负数;在后返回正数
相等,返回0.
7.字符大小写转换
System.out.println(s1.toLowerCase());
System.out.println(s2.toUpperCase());
8.字符串分割
split()
split把字符串分割后,返回的类型是数组String[]类型。你得用数组接收
String [] a1=s1.split(" ");
for(String a : a1)
System.out.println(a);
8.格式化字符串
format()
String str=String.format("%d", 400/2);
9.正则表达式
10.字符串生成器