论文地址:《Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation》
论文包含两个关键:(1)使用CNN处理候选框,以便定位个分割目标。(2)当训练集较小时,有监督的预训练和特点区域的微调。
介绍
目标检测系统总概:(1)输入一张图 。(2)提取候选区域(2k左右)。(3)使用CNN计算每个候选区域的特征。(4)使用class-specific linear SVMs来分类。
使用R-CNN作目标检测
R-CNN由三个模块构成:(1)第一个模块产生候选区域。(2)第二个模块是一个大型的CNN网络,用来从候选区域提取固定长度的特征向量。(3)第三个模块是一组class-specific linear SVMs。
模型设计
候选区域
这里作者用到了“选择性搜索”(selective search),主要思路是根据图像的颜色、纹理、尺寸和空间交叠等参数来把图像分成许多子块,这种方法比穷举法效率更高。具体可以看这里:选择性搜索(selective search) ,Selective Search for Object Detection (C++ / Python)。
下面简单的使用代码实现selective search的算法:
#!/usr/bin/env python ''' Usage: ./ssearch.py input_image (f|q) f=fast, q=quality Use "l" to display less rects, 'm' to display more rects, "q" to quit. ''' import sys import cv2 if __name__ == '__main__': # If image path and f/q is not passed as command # line arguments, quit and display help message # speed-up using multithreads cv2.setUseOptimized(True); cv2.setNumThreads(4); # read image im = cv2.imread("D:\tensorflow\image.jpg") # resize image newHeight = 200 newWidth = int(im.shape[1]*200/im.shape[0]) im = cv2.resize(im, (newWidth, newHeight)) # create Selective Search Segmentation Object using default parameters ss = cv2.ximgproc.segmentation.createSelectiveSearchSegmentation() # set input image on which we will run segmentation ss.setBaseImage(im) # Switch to fast but low recall Selective Search method ss.switchToSelectiveSearchFast() # Switch to high recall but slow Selective Search method #ss.switchToSelectiveSearchQuality() # if argument is neither f nor q print help message # run selective search segmentation on input image rects = ss.process() print('Total Number of Region Proposals: {}'.format(len(rects))) # number of region proposals to show numShowRects = 100 # increment to increase/decrease total number # of reason proposals to be shown increment = 50 while True: # create a copy of original image imOut = im.copy() # itereate over all the region proposals for i, rect in enumerate(rects): # draw rectangle for region proposal till numShowRects if (i < numShowRects): x, y, w, h = rect cv2.rectangle(imOut, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA) else: break # show output cv2.imshow("Output", imOut) # record key press k = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF # m is pressed if k == 109: # increase total number of rectangles to show by increment numShowRects += increment # l is pressed elif k == 108 and numShowRects > increment: # decrease total number of rectangles to show by increment numShowRects -= increment # q is pressed elif k == 113: break # close image show window cv2.destroyAllWindows()
结果如下图:

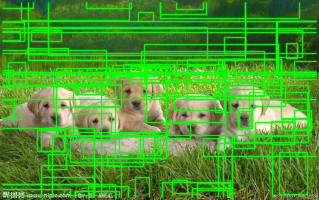
特征提取
使用Caffe实现的CNN来对每个候选区域进行特征提取,每个区域提取4096维的特征向量。使用包含5个卷积层和2个全连接层的CNN对减去均值的、大小为227*227的RGB图像通过前向传播来计算特征。为了使训练数据与CNN(要求输入数据为固定的227*227)匹配,需要对输入图像进行变形。
注:CNN见以下论文:《A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and G. Hinton. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In NIPS, 2012.》
非极大值抑制
使用selective search的快速模式来提取图像的2000多个候选区域,然后对每个候选区域进行变形,通过前向传播在对应的层得到特征。接着,对每一个类,使用针对该类训练过的SVM计算提取到的特征在该类上的分数。这样便得到了一张图的所有区域的Score,接着作者使用一种称为“非极大值抑制”的方法(每个类都是独立处理的)排除一些区域。如下的图像,关于“car”类会得到很多的方框,分类器根据分值从大到小排序:A,B,C,D,E,F。从最大概率的框A开始,判断B-F与之的重合区域,如果大于一个阈值,则丢弃概框。接着,最框B开始(如果B没有被丢弃的话),重复前面的操作。

训练
有监督的预训练
作者先把CNN在一个辅助数据集“ILSVRC 2012”上做了一个预训练(图像进行了分类标注,但没有边框标注),这应该是迁移学习的思想吧。
微调:fine-tuning
为了使CNN可以适用于目标检测任务,假设要检测的物体类别有N类,那么我们就需要把上面预训练阶段的CNN模型的最后一层给替换掉,替换成N+1个输出的神经元(加1,表示还有一个背景),然后这一层直接采用参数随机初始化的方法,其它网络层的参数不变;接着就可以开始继续SGD训练了。开始的时候,SGD学习率选择0.001,在每次训练的时候,我们batch size大小选择 128,其中32个是正样本、96个是负样本。
这里提到一个概念:定位精度评价公式(IOU),该公式定义了两个bounding box的重叠度,作者将IOU>0.5的bounding box判定为正,其余判定为负。
目标分类器
通过实验,得到最佳IOU重叠阈值为0.3。分类器输出的区域的IOU大于0.3的判定为正样本,否则判定为负样本。
作者在这里引入了“Hard negative mining”方法,首先是negative,即负样本,其次是hard,说明是困难样本,也就是说在对负样本分类时候,loss比较大(label与prediction相差较大)的那些样本,也可以说是容易将负样本看成正样本的那些样本,例如ROI里没有物体,全是背景,这时候分类器很容易正确分类成背景,这个就叫easy negative;如果ROI里有二分之一个物体,标签仍是负样本,这时候分类器就容易把他看成正样本,这时候就是had negative。hard negative mining就是多找一些hard negative加入负样本集,进行训练,这样会比easy negative组成的负样本集效果更好。主要体现在虚警率更低一些(也就是false positive少)。