JBPM之Environment分析
只要们稍微深入的学习一下JBPM,我们就会发现代码的每个角落都有environment的影子,可见environment的地位之重要,今天我们学习一下environment的作用和使用方法,以及其中的一些运行机制!
Environment的作用
线程安全对象,为每个线程维护一系列的资源
我们一般像这样使用Environment获取资源对象
static ThreadLocal<EnvironmentImpl> currentEnvironment = new ThreadLocal<EnvironmentImpl>();
//从当前的环境中获取对应的对象
public static <T> T getFromCurrent(Class<T> type) {
return getFromCurrent(type, true);
}
//根据类型名称查找相应对象
public static <T> T getFromCurrent(Class<T> type, boolean required) {
EnvironmentImpl environment = getCurrent();
if (environment==null) {
if (required) {
throw new JbpmException("no environment to get "+type.getName());
}
return null;
}
T object = environment.get(type);
if (object==null) {
if (required) {
throw new JbpmException("no "+type.getName()+" in current environment");
}
return null;
}
return object;
}
public static EnvironmentImpl getCurrent() {
return currentEnvironment.get();
}
之所以说environment是现成安全,是因为使用了ThreadLocal,其相关的知识请参考我以前的文章。
作为资源对象的承载容器,承载了不同生命周期和作用范围的变量等资源
BasicEnvironment中定义了承载各种Context的集合和Context方法
public Context getContext(String contextName) {
return contexts.get(contextName);
}
public void setContext(Context context) {
contexts.put(context.getName(), context);
}
public Context removeContext(Context context) {
return removeContext(context.getName());
}
public Context removeContext(String contextName) {
return contexts.remove(contextName);
}
public Context getEnvironmentFactoryContext() {
return getContext(Context.CONTEXTNAME_PROCESS_ENGINE);
}
public Context getEnvironmentContext() {
return getContext(Context.CONTEXTNAME_TRANSACTION);
}
各种Context如下图

可以通过特定的顺序在环境中查找需要的资源
BasicEnvironment中定义了各种按顺序查找对象的方法
public Object get(String name) {
return get(name, null);
}
public Object get(String name, String[] searchOrder) {
return get(name, searchOrder, true);
}
public Object get(String name, boolean nullIfNotFound) {
return get(name, null, nullIfNotFound);
}
public Object get(String name, String[] searchOrder, boolean nullIfNotFound) {
if (searchOrder == null) {
searchOrder = getDefaultSearchOrder();
}
for (String contextName : searchOrder) {
Context context = contexts.get(contextName);
if (context.has(name)) {
return context.get(name);
}
}
if (nullIfNotFound) {
return null;
} else {
throw new JbpmException("Null value found for " + name + " but null is not allowed");
}
}
public <T> T get(Class<T> type) {
return get(type, (String[]) null);
}
//在所有的context中查找与给定类型相同的实例,返回第一个找到的
public <T> T get(Class<T> type, String[] searchOrder) {
if (searchOrder==null) {
searchOrder = getDefaultSearchOrder();
}
for (String contextName : searchOrder) {
Context context = contexts.get(contextName);
T object = context.get(type);
if (object != null) return object;
}
return null;
}
/**
* searches an object based on type in the default search order.
* if this environment contains the given context, the search skips
* contexts registered after it.
*/
public <T> T get(Class<T> type, Context requester) {
String[] searchOrder = getDefaultSearchOrder();
int searchPosition = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < searchOrder.length; i++) {
if (contexts.get(searchOrder[i]) == requester) {
searchPosition = i + 1;
break;
}
}
for (int i = searchPosition; i < searchOrder.length; i++) {
Context context = contexts.get(searchOrder[i]);
T object = context.get(type);
if (object != null) return object;
}
return null;
}
可以使jbpm兼容企业版和标准版
注释说是可以实现的,但是自己并没有找到实现机制,希望明了的网友不吝赐教告知!
相关的Environment的uml类图

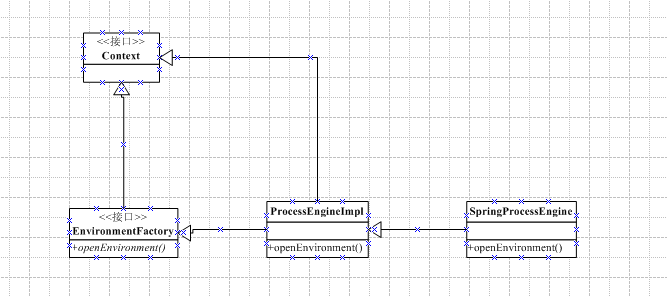
相关的EnvironmentFactory UML类图
环境生成机制

执行流程如上图所示,下面详细讲解
JBPM中环境的生成是由EnvironmentInterceptor拦截器调用EnvironmentFactory生成的。
1.在配置文件中做相应的配置
在配置文件中设置流程引擎初始化是初始化相关的拦截器
Jbpm.wire.bindings.xml
/>
在jbpm.tx.*.cfg.xml文件中定义拦截器策略,这里以展示一下hibernate的配置
<skip-interceptor />
<retry-interceptor />
<environment-interceptor />
<standard-transaction-interceptor />
</command-service>
<command-service name="newTxRequiredCommandService">
<retry-interceptor />
<environment-interceptor policy="requiresNew" />
<standard-transaction-interceptor />
</command-service>
2.解析配置文件并生成相关的descriptor
binding类用于解析xml定义,并最终生成descriptor(了解binding、descriptor请参考我相关的文章)
public CommandServiceBinding() {
super("command-service");
}
protected CommandServiceBinding(String tagName) {
super(tagName);
}
//解析command-service定义的拦截器策略
public Object parse(Element element, Parse parse, Parser parser) {
CommandServiceDescriptor commandServiceDescriptor = new CommandServiceDescriptor();
CommandService commandService = getCommandService(element, parse, parser);
commandServiceDescriptor.setCommandService(commandService);
//解析拦截器策略
List<Element> interceptorElements = XmlUtil.elements(element);
for (Element interceptorElement : interceptorElements) {
Descriptor interceptorDescriptor = (Descriptor) parser.parseElement(interceptorElement, parse, WireParser.CATEGORY_INTERCEPTOR);
commandServiceDescriptor.addInterceptorDescriptor(interceptorDescriptor);
}
return commandServiceDescriptor;
}
protected CommandService getCommandService(Element element, Parse parse, Parser parser) {
Boolean async = XmlUtil.attributeBoolean(element, "async", parse);
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(async)) {
AsyncCommandService asyncCommandService = new AsyncCommandService();
Boolean propagateUserId = XmlUtil.attributeBoolean(element, "propagate-auth", parse);
if (propagateUserId!=null) {
asyncCommandService.setPropagateUserId(propagateUserId);
}
return asyncCommandService;
}
return new DefaultCommandService();
}
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
CommandService commandService;
List<Descriptor> interceptorDescriptors;
//根据配置的拦截器策略初始化拦截器
public Object construct(WireContext wireContext) {
CommandService interceptedCommandService = commandService;
if (interceptorDescriptors!=null) {
//commandService配置的拦截器
for (int i=interceptorDescriptors.size()-1 ; i>=0; i--) {
Descriptor descriptor = interceptorDescriptors.get(i);
Interceptor interceptor = (Interceptor) descriptor.construct(wireContext);
interceptor.setNext(interceptedCommandService);
interceptedCommandService = interceptor;
}
}
return interceptedCommandService;
}
public Class< ? > getType(WireDefinition wireDefinition) {
return (name==null ? CommandService.class : null);
}
public void addInterceptorDescriptor(Descriptor descriptor) {
if (interceptorDescriptors==null) {
interceptorDescriptors = new ArrayList<Descriptor>();
}
interceptorDescriptors.add(descriptor);
}
public void setCommandService(CommandService commandService) {
this.commandService = commandService;
}
}
public EnvironmentInterceptorBinding() {
super("environment-interceptor");
}
//解析commandService中定义的environment-interceptor拦截器
public Object parse(Element element, Parse parse, Parser parser) {
EnvironmentInterceptorDescriptor environmentInterceptorDescriptor = new EnvironmentInterceptorDescriptor();
ConfigurationImpl configuration = parse.contextStackFind(ConfigurationImpl.class);
environmentInterceptorDescriptor.setConfiguration(configuration);
//每次执行拦截器都生成新的环境
if ( element.hasAttribute("policy")
&& ("requiresNew".equals(element.getAttribute("policy")))
) {
environmentInterceptorDescriptor.setPolicy(Policy.REQUIRES_NEW);
}
return environmentInterceptorDescriptor;
}
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected ConfigurationImpl configuration;
protected Policy policy;
//根据配置生成EnvironmentInterceptor拦截器
public Object construct(WireContext wireContext) {
//获取初始化的流程引擎实例作为环境工厂
EnvironmentFactory environmentFactory = (EnvironmentFactory) configuration.getProducedProcessEngine();
EnvironmentInterceptor environmentInterceptor = new EnvironmentInterceptor();
environmentInterceptor.setEnvironmentFactory(environmentFactory);
if (policy!=null) {
environmentInterceptor.setPolicy(policy);
}
return environmentInterceptor;
}
public void setPolicy(Policy policy) {
this.policy = policy;
}
public void setConfiguration(ConfigurationImpl configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
}
3.流程引擎初始化检查数据库,调用拦截器策略并初始化环境
类ConfigurationImpl 中流程引擎初始化的代码
if (!isConfigured) {
setResource(DEFAULT_CONFIG_RESOURCENAME);
}
if (jndiName!=null) {
try {
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
ProcessEngineImpl existing = (ProcessEngineImpl) initialContext.lookup(jndiName);
if (existing!=null) {
log.debug("found existing process engine under "+jndiName);
return existing;
}
} catch (NamingException e) {
log.debug("jndi name "+jndiName+" is not bound");
}
}
if (isSpringEnabled) {
return SpringProcessEngine.create(this);
}
return instantiateProcessEngine();
}
/**
* This method is called at the end of the buildProcessEngine() operation.
* Subclasses should override this method for custom ProcessEngine instantiation.
*/
protected ProcessEngine instantiateProcessEngine() {
return new ProcessEngineImpl(this);
}
ProcessEngineImpl
public ProcessEngineImpl(ConfigurationImpl configuration) {
initializeProcessEngine(configuration);
checkDb(configuration);
}
protected void initializeProcessEngine(ConfigurationImpl configuration) {
configuration.setProducedProcessEngine(this);
this.processEngineWireContext = configuration.getProcessEngineWireContext();
this.transactionWireDefinition = configuration.getTransactionWireDefinition();
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("created ProcessEngine "+System.identityHashCode(this));
if ( (processEngineWireContext!=null)
&& (processEngineWireContext.getWireDefinition()!=null)
&& (processEngineWireContext.getWireDefinition().getDescriptorTypes()!=null)
) {
log.trace(" process-engine-context "+System.identityHashCode(processEngineWireContext));
for (Class<?> descriptorType: processEngineWireContext.getWireDefinition().getDescriptorTypes()) {
log.trace(" "+descriptorType.getName());
}
}
if ( (transactionWireDefinition!=null)
&& (transactionWireDefinition.getDescriptorTypes()!=null)
) {
log.trace(" transaction-context:");
for (Class<?> descriptorType: transactionWireDefinition.getDescriptorTypes()) {
log.trace(" "+descriptorType.getName());
}
}
}
processEngineWireContext.create();
//根据配置的拦截器策略(相应的descriptor)生成相应的commandservice
userCommandService = (CommandService) processEngineWireContext.get(CommandService.NAME_TX_REQUIRED_COMMAND_SERVICE);
String jndiName = configuration.getJndiName();
if (jndiName!=null) {
try {
log.debug("publishing jBPM ProcessEngine in jndi at "+jndiName);
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
initialContext.bind(jndiName, this);
} catch (NamingException e) {
throw new JbpmException("JNDI binding problem", e);
}
}
}
protected void checkDb(ConfigurationImpl configuration) {
if (configuration.isCheckDb()) {
//按照配置的拦截器策略顺序执行,当运行到EnvironmentInterceptor时,根据配置选择是否生成新的环境
userCommandService.execute(new CheckDbCmd());
}
}