一、SaltStack概述
Salt,,一种全新的基础设施管理方式,部署轻松,在几分钟内可运行起来,扩展性好,很容易管理上万台服务器,速度够快,服务器之间秒级通讯。
salt底层采用动态的连接总线, 使其可以用于编配, 远程执行, 配置管理等等.
多种配置管理工具对比:
Puppet(rubby开发,现在很少使用)
ansible(python开发,轻量级,没有agent,大规模环境下使用ssh会很慢,串行传输)
Saltstack(python开发,远程执行、配置管理、事件驱动基础设施、使用saltcloud可以管理私有云和公有云)
官方文档:https://docs.saltstack.com/en/getstarted/;
官方提供官方yum源:repo.slatstack.com–>可以使用cobbler自定义yum仓库进行同步
官方安装源:http://repo.saltstack.com/2016.11.html#rhel;
Saltstack组件:
SaltMaster
SaltMinion
Execution Modules
环境说明:
主机名 IP地址 说明 系统 linux-node1.example.com 192.168.56.11 模式:master Centos 7.4 x86_64 linux-node2.example.com 192.168.56.12 模式:minion Centos 7.4 x86_64
二、SaltStack安装
1.安装指定的yum源
[root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/salt-repo-2016.11-2.el7.noarch.rpm [root@linux-node2 ~]# yum install https://repo.saltstack.com/yum/redhat/salt-repo-2016.11-2.el7.noarch.rpm
2.安装salt-master和salt-minion
[root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install -y salt-master [root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install -y salt-minion [root@linux-node2 ~]# yum install -y salt-minion
3.修改minion配置并启动
[root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl start salt-master #启动salt-master [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion #配置salt-minion master: 192.168.56.11 #可以是主机名需要解析(指定服务端的IP地址),冒号有空格 id: 唯一标识符,可以不配,不配默认就是主机名 [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl start salt-minion #启动salt-minion [root@linux-node2 salt]# vim minion master: 192.168.56.11 #可以是主机名需要解析(指定服务端的IP地址),冒号有空格 id: 唯一标识符,可以不配,不配默认就是主机名 [root@linux-node2 salt]# systemctl start salt-minion minion配置中有一个id配置,默认是hostname,如果id配置和hostname不一致会导致无法进行通信,那么当hostname做了修改,或者错误的时候该怎么配置呢? ①关闭salt-minion ②salt-key -d id 在master上删除minion的id ③minion上删除pki目录 ④minion上删除minion_id文件 ⑤修改完成,启动minion #此处必须先停掉minion修改,并删除相应的文件,否则会默认地去查找原先的配置,已踩坑 #以下是刚装完查看minion_id变成了www.test123.com。进行修改成linux-node2.example.com [root@linux-node2 salt]# cat minion_id www.test123.com [root@linux-node2 salt]# systemctl stop salt-minion [root@linux-node2 salt]# rm -rf pki [root@linux-node2 salt]# rm -rf minion_id [root@linux-node2 salt]# systemctl start salt-minion [root@linux-node2 salt]# cat minion_id linux-node2.example.com
4.配置说明
[root@linux-node2 salt]# ll 总用量 124 -rw-r----- 1 root root 2624 9月 15 23:19 cloud drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 9月 16 00:41 cloud.conf.d drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 9月 16 00:41 cloud.deploy.d drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 9月 16 00:41 cloud.maps.d drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 9月 16 00:41 cloud.profiles.d drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 9月 16 00:41 cloud.providers.d -rw-r----- 1 root root 46034 9月 15 23:19 master drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 9月 16 00:41 master.d -rw-r----- 1 root root 35101 1月 16 10:29 minion drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 27 1月 16 11:47 minion.d -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23 1月 16 11:45 minion_id drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 19 1月 16 11:45 pki -rw-r----- 1 root root 26984 9月 15 23:19 proxy drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 9月 16 00:41 proxy.d -rw-r----- 1 root root 344 9月 15 23:19 roster 说明: (1)salt-minion首次启动会在/etc/salt/pki/minion目录下生成公钥和秘钥 [root@linux-node2 salt]# ll /etc/salt/pki/minion/ 总用量 12 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 450 1月 16 11:47 minion_master.pub -r-------- 1 root root 1674 1月 16 11:45 minion.pem -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 450 1月 16 11:45 minion.pub (2)并且在salt-master的/etc/salt/pki/master/minion_pre中存放了salt-minion的公钥。 [root@linux-node1 ~]# ll /etc/salt/pki/master/minions_pre/ linux-node1.example.com linux-node2.example.com
5.配置salt-master和slat-minion通信
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt-key Accepted Keys: 同意的 Denied Keys: 拒绝的 Unaccepted Keys: 等待同意的 linux-node1.example.com linux-node2.example.com Rejected Keys: 同意认证的方法: 分为三种: [root@linux-node1 salt]# salt-key -A [root@linux-node1 salt]# salt-key -a 指定id [root@linux-node1 salt]# salt-key -a 支持通配符 [root@linux-node1 master]# salt-key -a linux* The following keys are going to be accepted: Unaccepted Keys: linux-node1.example.com linux-node2.example.com Proceed? [n/Y] Y Key for minion linux-node1.example.com accepted. Key for minion linux-node2.example.com accepted. salt-key 命令参数介绍 -L 列出所有 -d 删除指定的支持通配符 -D 删除所有 -A 添加所有 -a 指定添加 同意之后生成的文件 pki/ ├── master │ ├── master.pem │ ├── master.pub │ ├── minions │ │ ├── linux-node1.example.com │ │ └── linux-node2.example.com │ ├── minions_autosign │ ├── minions_denied │ ├── minions_pre │ └── minions_rejected └── minion ├── minion_master.pub 同意之后master发送公钥 ├── minion.pem └── minion.pub
##############################################################
1.远程执行
第一条命令: [root@linux-node1 master]# salt '*' test.ping linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True 说明: salt:命令 *:匹配目标,使用通配符 test.ping:模块.方法 #此处的ping并非ICMP的ping命令,而是master向minion发送了一个包,minion收到了,返回一个True [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'uptime' linux-node1.example.com: 11:51:47 up 21 days, 5:57, 2 users, load average: 0.04, 0.03, 0.05 linux-node2.example.com: 11:51:47 up 12 days, 6:26, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.03, 0.05 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'w' linux-node1.example.com: 11:52:11 up 21 days, 5:58, 2 users, load average: 0.03, 0.02, 0.05 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT root pts/2 192.168.56.1 06Jan18 6:51 3.27s 3.27s -bash root pts/3 192.168.56.1 06Jan18 3.00s 6:17 0.46s /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/salt * cmd.run w linux-node2.example.com: 11:52:11 up 12 days, 6:26, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.03, 0.05 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT root pts/1 192.168.56.1 Mon10 21:59m 0.28s 0.28s -bash root pts/3 192.168.56.1 06Jan18 6:59 4.82s 0.02s -bash [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'df -h' linux-node2.example.com: Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/centos-root 18G 17G 1.1G 95% / devtmpfs 905M 0 905M 0% /dev tmpfs 916M 12K 916M 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 916M 41M 876M 5% /run tmpfs 916M 0 916M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 497M 171M 326M 35% /boot tmpfs 184M 0 184M 0% /run/user/0 /dev/loop0 4.1G 4.1G 0 100% /mnt linux-node1.example.com: Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/centos-root 18G 11G 7.2G 60% / devtmpfs 905M 0 905M 0% /dev tmpfs 916M 28K 916M 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 916M 57M 860M 7% /run tmpfs 916M 0 916M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/sda1 497M 171M 326M 35% /boot tmpfs 184M 0 184M 0% /run/user/0 [root@linux-node1 ~]# netstat -tulnp|grep minion minion不需要监听端口,说明minion需要主动去链接master,master监听端口为4505、4506 [root@linux-node1 ~]# netstat -tulnp|grep python tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:4505 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 37039/python tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:4506 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 37045/python #master和minion默认使用一个叫zeroMQ进行并行通信,zeroMQ属于底层(传输层)的消息队列, #相当于一个发布与订阅系统,比如你订了一个教室听课,那么所有订了此间课室的人都能听到老师的课程。 [root@linux-node1 ~]# lsof -ni:4505 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME salt-mast 37039 root 16u IPv4 3394584 0t0 TCP *:4505 (LISTEN) salt-mast 37039 root 18u IPv4 3412804 0t0 TCP 192.168.56.11:4505->192.168.56.12:43126 (ESTABLISHED) salt-mast 37039 root 19u IPv4 3412811 0t0 TCP 192.168.56.11:4505->192.168.56.11:38262 (ESTABLISHED) salt-mini 39623 root 27u IPv4 3412810 0t0 TCP 192.168.56.11:38262->192.168.56.11:4505 (ESTABLISHED)
查看4505端口,我们可以发现salt-minion使用一个随机端口通过4505端口与salt-master通信,master使用4505端口发送指定到salt-minion上进行执行。而4606端口是用于接收数据的返回,用于zeroMQ的请求与响应的系统。
可以通过date命令查看salt的并行通信,可以看到是同时返回 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'date' linux-node2.example.com: Tue Jan 16 12:01:52 CST 2018 linux-node1.example.com: Tue Jan 16 12:01:52 CST 2018
2.配置管理
(1)saltstack是使用YAML的格式作为管理文件的格式,下面的YAML的样例:
YAML样例: house: family: name: Doe parents: - John - Jane children: - Paul - Mark - Simone address: number: 34 street: Main Street city: Nowheretown zipcode: 12345
(2)YAML的规则:
①缩进表示层级关系,默认缩进是2个空格、4个空格、6个空格
②冒号后面有个空格,以冒号结尾可以有空格,可以无空格
③短横线代表一个列表,短横线后面有个空格
(3)定义yaml文件放的位置:salt内置一个fileserver,在master文件配置:file_roots
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master #定义yaml文件放的位置,base环境是必备的 file_roots: base: - /srv/salt/base dev: - /srv/salt/dev test: - /srv/salt/test prod: - /srv/salt/prod [root@linux-node1 ~]# mkdir -p /srv/salt/{base,dev,test,prod} [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master [root@linux-node1 ~]# cd /srv/salt/base/ [root@linux-node1 base]# mkdir web [root@linux-node1 web]# vim apache.sls #编写安装apache的YAML文件 apache-install: pkg.installed:---------->模块pkg,方法installed,会匹配操作系统进行选择安装的方法 - name: httpd--------->装的包的名称 apache-service:----------->id要唯一 service.running:-------->状态模块service,running为模块的方法 - name: httpd--------->管理服务的名称 - enable: True-------->设置开机自动启动 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node2.example.com' state.sls web.apache #如果apache.sls的位置是在prod目录下,需要在后面增加saltenv=prod #salt 'linux-node2.example.com' state.sls web.apache saltenv=prod 实现自动化安装,需要写一个top.sls top.sls是state系统的入口文件,它在大规模配置管理工作中负责制定哪些设备调用哪些states.sls文件。top.sls入口文件不是必须的,如果只需要简单地对某台机器进行配置管理工作,我们可以直接使用state.sls命令来指定states.sls文件即可。 [root@linux-node1 base]# pwd /srv/salt/base [root@linux-node1 base]# vim top.sls #必须在base环境下写 base: 'linux-node1.example.com': - web.apache 'linux-node2.example.com': - web.apache **************************** 如果只有一个任务在全部机子上执行,也可以: base: '*' - web.apache **************************** [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' state.highstate #去top.sls读取,*代表通知哪些主机 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' state.highstate test=True #在不想影响当前主机的运行情况,可以使用test=True 进行预测试
######################################################################
1、什么是Grains?
Grains是saltstack的组件,用于收集salt-minion在启动时候的信息,又称为静态信息。可以理解为Grains记录着每台Minion的一些常用属性,比如CPU、内存、磁盘、网络信息等。我们可以通过grains.items来查看某台Minion的所有Grains信息。
Grains是服务器的一系列粒子信息,也就是服务器的一系列物理,软件环境信息。在执行salt的sls时候可以根据Grains信息的不同对服务器进行匹配分组,例如可以根据系统是centos服务器跟系统是redhat环境的安装不同的软件包。
Grains功能:1.收集资产信息 2.信息查询
官方文档:https://docs.saltstack.com/en/getstarted/overview.html
2、Grains的功能使用
(1)Grains查询信息
[root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.items #查看所有grains的key和values [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get saltversion #查看salt的版本 linux-node2.example.com: 2016.11.8 linux-node1.example.com: 2016.11.8 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get ip4_interface #查看ip [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get ip4_interface:eth0
(2)Grains目标匹配
grains可以用于进行目标匹配,比如让所有的centos系统进行某个操作。使用salt -G
#(1)对os系统为centos系统执行一个uptime的命令: [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -G 'os:Centos' cmd.run 'uptime' #查看负载 linux-node2.example.com: 14:17:06 up 13 days, 8:51, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 linux-node1.example.com: 14:17:06 up 22 days, 8:23, 2 users, load average: 0.01, 0.02, 0.05 #(2)在init为systemd的系统上执行查看负载: [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -G 'init:systemd' cmd.run 'uptime' linux-node1.example.com: 14:21:00 up 22 days, 8:27, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 linux-node2.example.com: 14:21:00 up 13 days, 8:55, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
(3)Grains在top file中进行匹配
#在top.sls中定义对系统是CentOS的服务之星web.apached定义的状态信息 [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/salt/base/top.sls base: 'os:CentOS': - match: grain - web.apache [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' state.highstate linux-node2.example.com: ---------- ID: apache-install Function: pkg.installed Name: httpd Result: True Comment: All specified packages are already installed Started: 14:28:57.612549 Duration: 2490.712 ms Changes: ---------- ID: apache-service Function: service.running Name: httpd Result: True Comment: The service httpd is already running Started: 14:29:00.104396 Duration: 41.901 ms Changes: Summary for linux-node2.example.com ------------ Succeeded: 2 Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 2 Total run time: 2.533 s linux-node1.example.com: ---------- ID: apache-install Function: pkg.installed Name: httpd Result: True Comment: All specified packages are already installed Started: 14:29:12.061257 Duration: 11458.788 ms Changes: ---------- ID: apache-service Function: service.running Name: httpd Result: True Comment: The service httpd is already running Started: 14:29:23.520720 Duration: 46.868 ms Changes: Summary for linux-node1.example.com
(4)Grains自定义
Grains的四种存在形式:
①Core grains.
②在 /etc/salt/grains 自定义grains。
③在 /etc/salt/minion 自定义grains。
④在 _grains 目录自定义grain,同步到minions。
#生产环境使用自定义一个grains [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/grains test-grains: linux-node2 #冒号后面有空格 [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get test-grains linux-node1.example.com: linux-node2 linux-node2.example.com: [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/grains test-grains: linux-node2 hehe: haha [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' saltutil.sync_grains [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' grains.get hehe linux-node1.example.com: haha linux-node2.example.com:
3、什么是Pillar?
Pillar是Salt最重要的系统之一,它跟grains的结构一样,也是一个字典格式,数据通过key/value的格式进行存储。在Salt的设计中,Pillar使用独立的加密sessiion。可用于提供开发接口,用于在master端定义数据,然后再minion中使用,一般传输敏感的数据,例如ssh key,加密证书等。
pillar和states建立方式类似,由sls文件组成,有一个入口文件top.sls,通过这个文件关联其他sls文件,默认路径在/srv/pillar,可通过/etc/salt/master里面pillar_roots:指定位置。
pillar到底什么作用呢?那么下面介绍一个简单的例子,你就明白了。
用zabbix监控新上架的服务器(10台),需要将zabbix_agentd.conf分发到被监控主机,这个文件中hostname的ip每台都不同,我们不可能写10分配置文件吧!那么如何让hostname在分发的时候就根据被监控主机IP,修改成自己的呢?这时就用到渲染了,默认渲染器是jinja,支持for in循环判断,格式是{%…%}{% end* %},这样一来salt会先让jinja渲染,然后交给yaml处理。
4、Pillar的功能使用
(1)如何定义Pillar数据
a.master配置文件中定义pillar:
默认情况下,master配置文件中的所有数据都添加到Pillar中,且对所有minion可用。如果要禁用这一默认值,可以在master配置文件中添加如下数据,重启服务后生效:
#默认的pillar的items为空,需要修改/etc/salt/master [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' pillar.items linux-node1.example.com: ---------- linux-node2.example.com: ---------- [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master #pillar_opts: False 打开该项,修改成True pillar_opts: True [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' pillar.items
b.使用SLS文件定义Pillar
Pillar使用与State相似的SLS文件。Pillar文件放在master配置文件中pillar_roots定义的目录下。示例如下:
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master pillar_roots: base: - /srv/pillar/base prod: - /srv/pillar/prod #此段代码定义了base环境下的Pillar文件保存在/srv/pillar/base目录下。prod环境下的Pillar文件保存在/srv/pillar/prod下。 [root@linux-node1 ~]# mkdir -p /srv/pillar/{base,prod} [root@linux-node1 ~]# tree /srv/pillar/ /srv/pillar/ ├── base └── prod [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master #创建base环境下的pillar文件为apache [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/base/apache.sls {% if grains['os'] == 'CentOS' %} apache: httpd {% elif grains['os'] == 'Debian' %} apache: apache2 {% endif %} #与State相似,Pillar也有top file,也使用相同的匹配方式将数据应用到minion上。示例如下: [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/pillar/base/top.sls base: '*': - apache [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' pillar.items linux-node1.example.com: ---------- apache: httpd linux-node2.example.com: ---------- apache: httpd #在base环境下,引用pillar [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/salt/base/web/apache.sls apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: {{ pillar['apache'] }} apache-service: service.running: - name: {{ pillar['apache'] }} - enable: True [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' state.highstate linux-node2.example.com: ---------- ID: apache-install Function: pkg.installed Name: httpd Result: True Comment: All specified packages are already installed Started: 15:15:13.424547 Duration: 940.333 ms Changes: ---------- ID: apache-service Function: service.running Name: httpd Result: True Comment: The service httpd is already running Started: 15:15:14.366780 Duration: 55.706 ms Changes: Summary for linux-node2.example.com ------------ Succeeded: 2 Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 2 Total run time: 996.039 ms linux-node1.example.com: ---------- ID: apache-install Function: pkg.installed Name: httpd Result: True Comment: All specified packages are already installed Started: 15:15:14.648492 Duration: 8242.769 ms Changes: ---------- ID: apache-service Function: service.running Name: httpd Result: True Comment: The service httpd is already running Started: 15:15:22.891907 Duration: 42.651 ms Changes: Summary for linux-node1.example.com ------------ Succeeded: 2 Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 2 Total run time: 8.285 s
总结:
1.pillar和状态一样,有pillar_roots,在master中配置
2.到配置的地方/srv/pillar/base下写一个apache.sls
3.pillar必须在top file指定才能使用,在top.sls中指定所有的minion,都需要执行在base环境下的apache.sls
4.用之前查看是否能获取到pillar值:salt ‘*’ pillar.items
5.更改状态配置,把name改为一个pillar的引用,这是一个jinja的语法
5、Grains VS Pillar
名称 存储位置 类型 采集方式 场景 Grains minion 静态 minion启动时,可以刷新 1.获取信息 2.匹配 Pillar master 动态 指定,实时生效 1.匹配 2.敏感数据配置
#######################################################################
1.目标
2.执行模块
3.返回
salt ‘*’ cmd.run ‘uptime’ 命令 目标 执行模块 执行模块参数
1、SlatStack远程执行–目标
执行目标:https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/targeting/index.html#advanced-targeting-methods
- (1)和Minion ID相关的目标匹配方式
1、MinionID匹配 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node1.example.com' service.status sshd linux-node1.example.com: True 2、通配符* ? [1-2]等匹配 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux*' service.status sshd linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node?.example.com' service.status sshd linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt 'linux-node[1-2].example.com' service.status sshd linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True 3、列表匹配 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -L 'linux-node1.example.com,linux-node2.example.com' test.ping linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True 4、正则表达式匹配 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -E 'linux-(node1|node2)*' test.ping linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True
- (2)和Minion无关匹配
1、Grains匹配 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -G 'os:CentOS' test.ping linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True 2、子网、IP地址匹配 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -S '192.168.56.0/24' test.ping linux-node1.example.com: True linux-node2.example.com: True 3、Pillar匹配 #这里目标key:value,是在pillar系统中定义 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -I 'apache:httpd' test.ping linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True
- (3)混合匹配(少用)
- (4)Node Groups匹配
#在master配置文件进行定义node-groups [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master nodegroups: web-group: 'L@linux-node1.example.com,linux-node2.example.com' [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -N web-group test.ping linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True
- (5)批处理执行–Batch size
#先执行1台完成后再执行一台,按比例去执行 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' -b 1 test.ping Executing run on ['linux-node2.example.com'] jid: 20180117172632455823 linux-node2.example.com: True retcode: 0 Executing run on ['linux-node1.example.com'] jid: 20180117172632650981 linux-node1.example.com: True retcode: 0 #按比例匹配执行,好比在重启服务器时,为了不影响业务,可以先重启一部分,再重启后面一部分 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt -G 'os:CentOS' --batch-size 50% test.ping Executing run on ['linux-node2.example.com'] jid: 20180117172759207757 linux-node2.example.com: True retcode: 0 Executing run on ['linux-node1.example.com'] jid: 20180117172759402383 linux-node1.example.com: True retcode: 0
2、SlatStack远程执行–执行模块
执行模块:https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/modules/all/index.html#all-salt-modules
3、SlatStack远程执行–返回
返回模块:https://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/returners/index.html
Return组件可以理解为SaltStack系统对执行Minion返回后的数据进行存储或者返回给其他程序,它支持多种存储方式,如MySQL、Redis、ELK、zabbix,通过Return我们可以对SaltStack的每次操作进行记录,对以后的日志审计提供了数据来源。
Return是在Master端触发任务,然后Minion接受处理任务直接与Return存储服务器建立链接,然后把数据存储到服务器。
返回是minion直接将命令执行结果写入到MySQL,需要的依赖包:MySQL-python
- (1)SATL.RETURNERS.MYSQL(minion返回MySQL)
 View Code
View Code(1)所有minion需要安装MySQL-python [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'yum install -y MySQL-python' [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' pkg.install MySQL-python #使用pkg模块安装MySQL-python (2)安装mariadb数据库 [root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install -y mariadb-server [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl start mariadb (3)创建salt库,创建jid、salt_returns、salt_events表,授权 [root@linux-node1 ~]# mysql -uroot -p Enter password: MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE `salt` -> DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 -> DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_general_ci; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> USE `salt`; Database changed MariaDB [salt]> CREATE TABLE `jids` ( -> `jid` varchar(255) NOT NULL, -> `load` mediumtext NOT NULL, -> UNIQUE KEY `jid` (`jid`) -> ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [salt]> CREATE TABLE `salt_returns` ( -> `fun` varchar(50) NOT NULL, -> `jid` varchar(255) NOT NULL, -> `return` mediumtext NOT NULL, -> `id` varchar(255) NOT NULL, -> `success` varchar(10) NOT NULL, -> `full_ret` mediumtext NOT NULL, -> `alter_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, -> KEY `id` (`id`), -> KEY `jid` (`jid`), -> KEY `fun` (`fun`) -> ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec) MariaDB [salt]> CREATE TABLE `salt_events` ( -> `id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, -> `tag` varchar(255) NOT NULL, -> `data` mediumtext NOT NULL, -> `alter_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, -> `master_id` varchar(255) NOT NULL, -> PRIMARY KEY (`id`), -> KEY `tag` (`tag`) -> ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) MariaDB [salt]> show tables; +----------------+ | Tables_in_salt | +----------------+ | jids | | salt_events | | salt_returns | +----------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [salt]> grant all on salt.* to salt@'%' identified by 'salt'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) (4)修改salt-minion,配置MySQL链接 [root@linux-node2 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion ###### Returner settings ###### ############################################ mysql.host: '192.168.56.11' mysql.user: 'salt' mysql.pass: 'salt' mysql.db: 'salt' mysql.port: 3306 [root@linux-node2 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion ###### Returner settings ###### ############################################ mysql.host: '192.168.56.11' mysql.user: 'salt' mysql.pass: 'salt' mysql.db: 'salt' mysql.port: 3306 [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion (5)测试,并在数据库查看返回结果 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' test.ping --return mysql linux-node2.example.com: True linux-node1.example.com: True MariaDB [salt]> select * from salt_returns; +-----------+----------------------+--------+-------------------------+---------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+ | fun | jid | return | id | success | full_ret | alter_time | +-----------+----------------------+--------+-------------------------+---------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+ | test.ping | 20180118093222060862 | true | linux-node2.example.com | 1 | {"fun_args": [], "jid": "20180118093222060862", "return": true, "retcode": 0, "success": true, "fun": "test.ping", "id": "linux-node2.example.com"} | 2018-01-18 09:32:22 | | test.ping | 20180118093222060862 | true | linux-node1.example.com | 1 | {"fun_args": [], "jid": "20180118093222060862", "return": true, "retcode": 0, "success": true, "fun": "test.ping", "id": "linux-node1.example.com"} | 2018-01-18 09:32:24 | +-----------+----------------------+--------+-------------------------+---------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+---------------------+ 2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 使用salt的job_cache机制将命令写入mysql(常用方法)
- 执行的所有命令都会写入mysql,不用使用return,把cache写在mysql
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master master_job_cache: mysql mysql.host: '192.168.56.11' mysql.user: 'salt' mysql.pass: 'salt' mysql.db: 'salt' mysql.port: 3306 [root@linux-node1 ~]# systemctl restart salt-master [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'w' [root@linux-node1 ~]# mysql -uroot -p123456 -e "select * from salt.salt_returns;" #加上-v参数可以看到jid,并且通过jid可以查看运行的结果 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt '*' cmd.run 'uptime' -v Executing job with jid 20180118095000725560 ------------------------------------------- linux-node2.example.com: 09:50:00 up 14 days, 4:24, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05 linux-node1.example.com: 09:50:00 up 23 days, 3:56, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.06, 0.18 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20180118095000725560 linux-node1.example.com: 09:50:00 up 23 days, 3:56, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.06, 0.18 linux-node2.example.com: 09:50:00 up 14 days, 4:24, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
############################################################################
1、salt-ssh的使用
官方文档:https://docs.saltstack.com/en/2016.11/topics/ssh/index.html
(1)安装salt-ssh [root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install -y salt-ssh (2)配置salt-ssh [root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/roster linux-node1: host: 192.168.56.11 user: root passwd: 123123 linux-node2: host: 192.168.56.12 user: root passwd: 123123 (3)使用ssh远程执行 [root@linux-node1 ~]# salt-ssh '*' -r 'uptime' linux-node2: ---------- retcode: 0 stderr: stdout: root@192.168.56.12's password: 14:07:19 up 14 days, 8:41, 2 users, load average: 0.04, 0.08, 0.07 linux-node1: ---------- retcode: 0 stderr: stdout: root@192.168.56.11's password: 14:07:20 up 23 days, 8:13, 2 users, load average: 2.86, 0.81, 0.34
2、配置管理
(1)什么是状态?
States是Saltstack中的配置语言,在日常进行配置管理时需要编写大量的States文件。比如我们需要安装一个包,然后管理一个配置文件,最后保证某个服务正常运行。这里就需要我们编写一些states sls文件(描述状态配置的文件)去描述和实现我们的功能。编写的states sls文件都是YAML语法,states sls文件也支持使用Python语言编写。
所谓的状态就是希望系统运行某些命令之后的结果。描述状态使用YAML格式的文件。SLS:salt state
举例安装apache,如下:
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /srv/salt/base/web/apache.sls apache: pkg.installed: - name: httpd service.running: - name: httpd file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 解释说明: apache:id声明,在所有环境(base、prod)下全局唯一 pkg:状态模块 .:引用关系 installed:模块中的方法 ::代表层级关系 name:可以理解为参数,后面跟的是参数值 file.managed:文件管理模块,必须要有source指定文件的来源路径 source:文件的来源路径,salt://代表着环境的根路径,这的根路径为:/srv/salt/base/ user、group、mode:分别指定文件的所属者,所属组和权限 以上的文件还可以使用分id的写法: apache-install: pkg.installed: - name: httpd apache-service: service.running: - name: httpd apache-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 存在指定多个配置文件,还可以使用一下写法:(不适用name作为参数传递时,id就是name) /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf: file.managed: - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 /etc/httpd/conf/php.conf: file.managed: - source: salt://apache/files/php.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644
(2) LAMP的状态设计与实现部署
1、设计分析
1 名称 软件包 配置文件 服务 2 使用模块 pkg file service 3 LAMP httpd、php、mariadb、mariadb-server、php-mysql、php-pdo、php-cli /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf、/etc/php.ini httpd、mysqld
2、Aapche的状态配置
1 [root@linux-node1 prod]# pwd 2 /srv/salt/prod 3 [root@linux-node1 prod]# mkdir apache php mysql 4 [root@linux-node1 prod]# tree 5 . 6 ├── apache 7 ├── mysql 8 └── php 9 10 3 directories, 0 files 11 12 [root@linux-node1 prod]# cd apache/ 13 [root@linux-node1 apache]# vim apache.sls #编写apache的状态模块 14 apache-install: 15 pkg.installed: 16 - name: httpd 17 18 apache-config: 19 file.managed: 20 - name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf 21 - source: salt://apache/files/httpd.conf #salt://代表着环境的根路径 22 - user: root 23 - group: root 24 - mode: 644 25 26 apache-service: 27 service.running: 28 - name: httpd 29 - enable: True 30 [root@linux-node1 apache]# mkdir files #创建source目录 31 [root@linux-node1 apache]# cd files/ 32 [root@linux-node1 files]# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf . 33 [root@linux-node1 apache]# tree 34 . 35 ├── apache.sls 36 └── files 37 └── httpd.conf 38 39 1 directory, 2 files 40 [root@linux-node1 apache]# salt 'linux-node1' state.sls apache.apache saltenv=prod
3、php的状态配置
[root@linux-node1 prod]# cd php [root@linux-node1 php]# mkdir files [root@linux-node1 php]# vim init.sls php-install: pkg.installed: - pkgs: - php - php-pdo - php-mysql php-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/php.ini - source: salt://php/files/php.ini - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 [root@linux-node1 php]# cp /etc/php.ini files/ [root@linux-node1 php]# tree . ├── files │ └── php.ini └── init.sls 1 directory, 2 files
4、mysql的状态配置

[root@linux-node1 prod]# cd mysql/ [root@linux-node1 mysql]# vim init.sls mysql-install: pkg.installed: - pkgs: - mariadb - mariadb-server mysql-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/my.cnf - source: salt://mysql/files/my.cnf - user: root - gourp: root - mode: 644 mysql-service: service.running: - name: mariadb-server - enable: True [root@linux-node1 mysql]# mkdir files [root@linux-node1 mysql]# cp /etc/my.cnf files/ [root@linux-node1 prod]# tree . ├── apache │ ├── files │ │ └── httpd.conf │ └── init.sls ├── mysql │ ├── files │ │ └── my.cnf │ └── init.sls └── php ├── files │ └── php.ini └── init.sls [root@linux-node1 prod]# salt -S '192.168.56.11' state.sls php.init saltenv=prod linux-node1.example.com: ---------- ID: php-install Function: pkg.installed Result: True Comment: The following packages were installed/updated: php-mysql The following packages were already installed: php-pdo, php Started: 10:30:14.780998 Duration: 118711.436 ms Changes: ---------- php-mysql: ---------- new: 5.4.16-43.el7_4 old: ---------- ID: php-config Function: file.managed Name: /etc/php.ini Result: True Comment: File /etc/php.ini is in the correct state Started: 10:32:13.556562 Duration: 51.913 ms Changes: Summary for linux-node1.example.com ------------ Succeeded: 2 (changed=1) Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 2 Total run time: 118.763 s
5、写入top file,执行高级状态

[root@linux-node1 base]# pwd /srv/salt/base [root@linux-node1 base]# vim top.sls prod: 'linux-node1.example.com': - apache.init - php.init - mysql.init [root@linux-node1 base]# salt 'linux-node1*' state.highstate linux-node1.example.com: ---------- ID: apache-install Function: pkg.installed Name: httpd Result: True Comment: All specified packages are already installed Started: 10:39:04.214911 Duration: 762.144 ms Changes: ---------- ID: apache-config Function: file.managed Name: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf Result: True Comment: File /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf is in the correct state Started: 10:39:04.979376 Duration: 13.105 ms Changes: ---------- ID: apache-service Function: service.running Name: httpd Result: True Comment: The service httpd is already running Started: 10:39:04.992962 Duration: 36.109 ms Changes: ---------- ID: php-install Function: pkg.installed Result: True Comment: All specified packages are already installed Started: 10:39:05.029241 Duration: 0.65 ms Changes: ---------- ID: php-config Function: file.managed Name: /etc/php.ini Result: True Comment: File /etc/php.ini is in the correct state Started: 10:39:05.029987 Duration: 10.642 ms Changes: ---------- ID: mysql-install Function: pkg.installed Result: True Comment: All specified packages are already installed Started: 10:39:05.040793 Duration: 0.422 ms Changes: ---------- ID: mysql-config Function: file.managed Name: /etc/my.cnf Result: True Comment: File /etc/my.cnf is in the correct state Started: 10:39:05.041301 Duration: 7.869 ms Changes: ---------- ID: mysql-service Function: service.running Name: mariadb Result: True Comment: The service mariadb is already running Started: 10:39:05.049284 Duration: 28.054 ms Changes: Summary for linux-node1.example.com ------------ Succeeded: 8 Failed: 0 ------------ Total states run: 8 Total run time: 858.995 ms
#########################################################################
一、部署Redis主从
需求:
- 192.168.56.11是主,192.168.56.12是从
- redis监听自己的ip地址,而不是0.0.0.0
分析:
linux-node1 安装 配置 启动
linux-node2 安装 配置 启动 设置主从
[root@linux-node1 ~]# yum install redis -y [root@linux-node1 prod]# mkdir redis/files -p [root@linux-node1 redis]# cp /etc/redis.conf /srv/salt/prod/redis/files/ [root@linux-node1 redis]# tree . ├── files │ └── redis.conf └── init.sls 1 directory, 2 files [root@linux-node1 redis]# vim init.sls redis-install: pkg.installed: - name: redis redis-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/redis.conf - source: salt://redis/files/redis.conf - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 - template: jinja defaults: PORT: 6379 IPADDR: {{ grains['fqdn_ip4'][0] }} redis-service: service.running: - name: redis - enable: True - reload: True [root@linux-node1 redis]# salt '*' state.sls redis.init saltenv=prod #测试单一执行sls是否成功 [root@linux-node1 redis]# netstat -tulnp|grep redis-server tcp 0 0 192.168.56.11:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 10186/redis-server [root@linux-node2 ~]# netstat -tulnp |grep redis-server tcp 0 0 192.168.56.12:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17973/redis-server 主从配置: [root@linux-node1 redis]# vim master.sls include: - redis.init [root@linux-node1 redis]# vim slave.sls include: - redis.init slave_config: cmd.run: - name: redis-cli -h 192.168.56.12 slaveof 192.168.56.11 6379--->设置主从 - unless: redis-cli -h 192.168.56.12 info |grep role:slave-->判断node2是否为从,如果是就不执行设置主从 - require: - service: redis-service [root@linux-node1 redis]# vim /srv/salt/base/top.sls #配置top file prod: 'linux-node1.example.com': - lamp - redis.master 'linux-node2.example.com': - lamp - redis.slave [root@linux-node1 redis]# salt '*' state.highstate ...... ---------- ID: slave_config Function: cmd.run Name: redis-cli -h 192.168.56.12 slaveof 192.168.56.11 6379 Result: True Comment: Command "redis-cli -h 192.168.56.12 slaveof 192.168.56.11 6379" run Started: 12:08:46.428924 Duration: 31.328 ms Changes: ---------- pid: 18132 retcode: 0 stderr: stdout: OK Summary for linux-node2.example.com ------------- Succeeded: 14 (changed=1) Failed: 0 ------------- Total states run: 14 Total run time: 1.527 s ...... [root@linux-node1 redis]# tree . ├── files │ └── redis.conf ├── init.sls ├── master.sls └── slave.sls 1 directory, 4 files [root@linux-node1 redis]# cat slave.sls include: - redis.init slave_config: cmd.run: - name: redis-cli -h 192.168.56.12 slaveof 192.168.56.11 6379 - unless: redis-cli -h 192.168.56.12 info |grep role:slave - require: - service: redis-service
TIPS:生产环境中,务必使用test=True进行与测试,并且目标选择一个节点进行,避免错误,影响业务的运行。
二、SaltStack–Job管理
官方文档:https://docs.saltstack.com/en/2016.11/ref/modules/all/salt.modules.saltutil.html
在SaltStack里面执行任何一个操作都会在Master上产生一个jid号。Minion端会在cache目录下的proc目录创建一个以jid为名称的文件,这个文件里面的内容就是记录此次操作的记录,当操作处理完成后改文件会自动删除。而master端会记录每次操作的详细信息,这个记录都是存到在Master端cache目录下的jobs下。
[root@linux-node1 ~]# cd /var/cache/salt/master/jobs/----->任务管理目录 [root@linux-node1 jobs]# pwd /var/cache/salt/master/jobs [root@linux-node1 jobs]# ls 07 0e 2f 3a 44 4c 53 5c 72 92 ac b2 bf e6 f4 0c 0f 34 3f 45 4e 5a 63 8b 93 ad b9 c1 e9 fb 0d 13 37 43 49 52 5b 64 8c a5 af be c4 f1 fe [root@linux-node1 linux-node1.example.com]# pwd /var/cache/salt/master/jobs/07/f8d6ec1380412c95718d931cfb300e793f6b7316d58ad3f34dd57052ca178f/linux-node1.example.com [root@linux-node1 linux-node1.example.com]# ll total 8 -rw------- 1 root root 10 Jan 20 09:39 out.p -rw------- 1 root root 1748 Jan 20 09:39 return.p---->结果返回 [root@linux-node1 ~]# grep "#keep_jobs: 24" /etc/salt/master #keep_jobs: 24 默认的缓存是24小时,可以进行修改。管理job是模块进行管理,由执行模块进行管理:SALT.MODULES.SALTUTIL salt '*' saltutil.clear_cache 清除缓存 salt '*' saltutil.find_job <job id> 查找当前在运行的job,并返回它的id salt '*' saltutil.is_running 查看当前在运行的job salt '*' saltutil.kill_job <job id> 杀死job
###############################################################
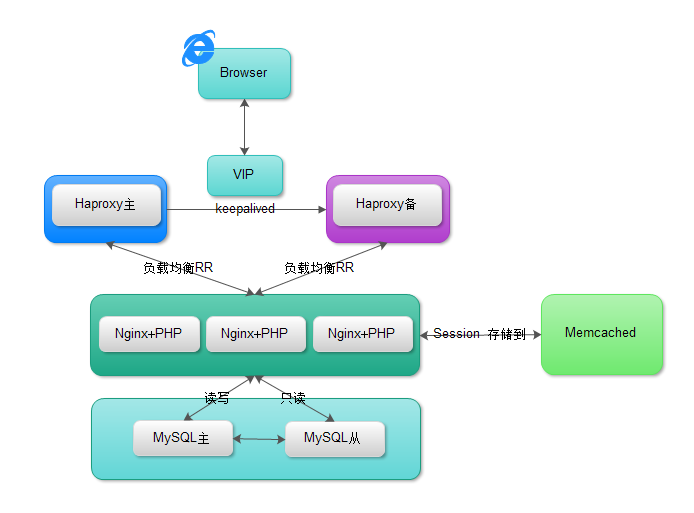
实验环境设置:
主机名 IP地址 角色 linux-node1.example.com 192.168.56.11 Master、Minion、Haproxy+Keepalived、Nginx+PHP linux-node2.example.com 192.168.56.12 Minion、Memcached、Haproxy+Keepalived、Nginx+PHP
SaltStack环境设置:
base环境用于存放初始化的功能,prod环境用于放置生产的配置管理功能
[root@linux-node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/master file_roots: base: - /srv/salt/base dev: - /srv/salt/dev test: - /srv/salt/test prod: - /srv/salt/prod pillar_roots: base: - /srv/pillar/base prod: - /srv/pillar/prod
1、系统初始化
当我们的服务器上架并安装好操作系统后,都会有一些基础的操作,所以生产环境中使用SaltStack,建议将所有服务器都会涉及的基础配置或者软件部署归类放在base环境下。此处,在base环境下创建一个init目录,将系统初始化配置的sls均放置到init目录下,称为“初始化模块”。
(1)需求分析和模块识别
| 初始化内容 | 模块使用 | 文件 |
| 关闭SElinux | file.managed | /etc/selinux/config |
| 关闭默认firewalld | service.disabled | |
| 时间同步 | pkg.installed | |
| 文件描述符 | file.managed | /etc/security/limits.conf |
| 内核优化 | sysctl.present | |
| SSH服务优化 | file.managed、service.running | |
| 精简开机系统服务 | service.dead | |
| DNS解析 | file.managed | /etc/resolv.conf |
| 历史记录优化history | file.append | /etc/profile |
| 设置终端超时时间 | file.append | /etc/profile |
| 配置yum源 | file.managed | /etc/yum.repo.d/epel.repo |
| 安装各种agent | pkg.installed 、file.managed、service.running | |
| 基础用户 | user.present、group.present | |
| 常用基础命令 | pkg.installed、pkgs | |
| 用户登录提示、PS1的修改 | file.append | /etc/profile |
(2)需求实现

1 [root@linux-node1 base]# pwd 2 /srv/salt/base 3 [root@linux-node1 base]# mkdir init/files -p 4 5 1、关闭selinux 6 #使用了file模块的managed方法 7 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim selinux.sls 8 selinux-config: 9 file.managed: 10 - name: /etc/selinux/config 11 - source: salt://salt/init/files/selinux-config 12 - user: root 13 - group: root 14 - mode: 0644 15 [root@linux-node1 init]# cp /etc/selinux/config files/selinux-config 16 17 2、关闭firewalld 18 #使用service模块的dead方法,直接关闭firewalld,并禁止开机启动 19 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim firewalld.sls 20 firewall-stop: 21 service.dead: 22 - name: firewalld.service 23 - enable: False 24 25 3、时间同步 26 #先使用pkg模块安装ntp服务,再使用cron模块加入计划任务 27 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim ntp.sls 28 ntp-install: 29 pkg.installed: 30 - name: ntpdate 31 32 cron-ntpdate: 33 cron.present: 34 - name: ntpdate time1.aliyun.com 35 - user: root 36 - minute: 5 37 38 4、修改文件描述符 39 #使用file模块的managed方法 40 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim limit.sls 41 limit-config: 42 file.managed: 43 - name: /etc/security/limits.conf 44 - source: salt://init/files/limits.conf 45 - user: root 46 - group: root 47 - mode: 0644 48 [root@linux-node1 init]# cp /etc/security/limits.conf files/ 49 [root@linux-node1 init]# echo "* - nofile 65535 50 " >> files/limits.conf 51 52 5、内核优化 53 #使用sysctl模块的present方法,此处演示一部分,这里没有使用name参数,所以id就相当于是name 54 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim sysctl.sls 55 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout: 56 sysctl.present: 57 - value: 2 58 59 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse: 60 sysctl.present: 61 - value: 1 62 63 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle: 64 sysctl.present: 65 - value: 1 66 67 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies: 68 sysctl.present: 69 - value: 1 70 71 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time: 72 sysctl.present: 73 - value: 600 74 75 6、SSH服务优化 76 #使用file.managed和service.running以及watch,对ssh服务进行优化配置 77 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim sshd.sls 78 sshd-config: 79 file.managed: 80 - name: /etc/ssh/sshd_config 81 - source: salt://init/files/sshd_config 82 - user: root 83 - gourp: root 84 - mode: 0600 85 service.running: 86 - name: sshd 87 - enable: True 88 - reload: True 89 - watch: 90 - file: sshd-config 91 [root@linux-node1 init]# cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config files/ 92 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim files/sshd_config 93 Port 8022 94 UseDNS no 95 PermitRootLogin no 96 PermitEmptyPasswords no 97 GSSAPIAuthentication no 98 99 7、精简开机启动的系统服务 100 #举例关闭postfix开机自启动 101 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim thin.sls 102 postfix: 103 service.dead: 104 - enable: False 105 106 8、DNS解析 107 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim dns.sls 108 dns-config: 109 file.managed: 110 - name: /etc/resolv.conf 111 - source: salt://init/files/resolv.conf 112 - user: root 113 - group: root 114 - mode: 644 115 [root@linux-node1 init]# cp /etc/resolv.conf files/ 116 117 9、历史记录优化history 118 #使用file.append扩展修改HISTTIMEFORMAT的值 119 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim history.sls 120 history-config: 121 file.append: 122 - name: /etc/profile 123 - text: 124 - export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T `whoami` " 125 - export HISTSIZE=5 126 - export HISTFILESIZE=5 127 128 10、设置终端超时时间 129 #使用file.append扩展修改TMOUT环境变量的值 130 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim tty-timeout.sls 131 ty-timeout: 132 file.append: 133 - name: /etc/profile 134 - text: 135 - export TMOUT=300 136 137 11、配置yum源 138 #拷贝yum源 139 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim yum-repo.sls 140 /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo: 141 file.managed: 142 - source: salt://init/files/epel.repo 143 - user: root 144 - group: root 145 - mode: 0644 146 147 12、安装各种agent(如安装zabbix-agent) 148 #相当于一个软件的安装、配置、启动,此处也使用了jinja模板和pillar 149 [root@linux-node1 base]# mkdir zabbix 150 [root@linux-node1 base]# vim zabbix/zabbix-agent.sls 151 zabbix-agent: 152 pkg.installed: 153 - name: zabbix22-agent 154 file.managed: 155 - name: /etc/zabbix_agentd.conf 156 - source: salt://zabbix/files/zabbix_agentd.conf 157 - template: jinja 158 - defaults: 159 ZABBIX-SERVER: {{ pillar['zabbix-agent']['Zabbix_Server'] }} 160 - require: 161 - pkg: zabbix-agent 162 service.running: 163 - enable: True 164 - watch: 165 - pkg: zabbix-agent 166 - file: zabbix-agent 167 zabbix_agent.conf.d: 168 file.directory: 169 - name: /etc/zabbix_agentd.conf.d 170 - watch_in: 171 - service: zabbix-agent 172 - require: 173 - pkg: zabbix-agent 174 - file: zabbix-agent 175 [root@linux-node1 srv]# vim pillar/base/zabbix.sls 176 zabbix-agent: 177 Zabbix_Server: 192.168.56.11 178 179 13、基础用户 180 #增加基础管理用户www,使用user.present和group.present 181 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim user-www.sls 182 www-user-group: 183 group.present: 184 - name: www 185 - gid: 1000 186 187 user.present: 188 - name: www 189 - fullname: www 190 - shell: /sbin/bash 191 - uid: 1000 192 - gid: 1000 193 194 14、常用基础命令 195 #这里因为各软件包会依赖源,所以使用include讲yum源包含进来,并在pkg.installed最后增加require依赖 196 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim pkg-base.sls 197 include: 198 - init.yum-repo 199 base-install: 200 pkg.installed: 201 - pkgs: 202 - screen 203 - lrzsz 204 - tree 205 - openssl 206 - telnet 207 - iftop 208 - iotop 209 - sysstat 210 - wget 211 - dos2unix 212 - lsof 213 - net-tools 214 - mtr 215 - unzip 216 - zip 217 - vim 218 - bind-utils 219 - require: 220 - file: /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo 221 222 15、用户登录提示、PS1的修改 223 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim tty-ps1.sls 224 /etc/bashrc: 225 file.append: 226 - text: 227 - export PS1=' [u@h w]$ ' 228 229 16、编写一个总的状态,并写入top file中 230 #将所有初始化所需要的功能编写完成,每个小功能都是一个sls文件,统一放在init目录下。此时再使用include把这些初始化的功能都包含进来。 231 [root@linux-node1 init]# vim init-all.sls 232 include: 233 - init.dns 234 - init.yum-repo 235 - init.firewalld 236 - init.history 237 - init.limit 238 - init.ntp 239 - init.pkg-base 240 - init.selinux 241 - init.sshd 242 - init.sysctl 243 - init.thin 244 - init.tty-timeout 245 - init.tty-ps1 246 - init.user-www 247 248 #在top.sls里面给Minion指定状态并执行,强烈建议先测试,确定SaltStack会执行哪些操作然后再应用状态到服务器上 249 [root@linux-node1 base]# vim top.sls 250 base: 251 '*': 252 - init.init-all 253 [root@linux-node1 base]# salt '*' state.highstate test=True 254 [root@linux-node1 base]# salt '*' state.highstate
2、MySQL主从
1.需求分析:
配置MySQL主从的有以下步骤:
(1)MySQL安装初始化—->mysql-install.sls
(2)MySQL的主配置文件my.cnf配置不同的server_id–>mariadb-server-master.cnf、mariadb-server-slave.cnf
(3)创建主从同步用户–>master.sls
(4)master获取bin-log和post值–>通过脚本实现
(5)slave上,change master && start slave–>slave.sls
2.需求实现:

(1)在prod环境下载创建modules和mysql目录 [root@linux-node1 prod]# pwd /srv/salt/prod [root@linux-node1 prod]# mkdir modules/mysql (2)配置安装和配置状态文件install.sls [root@linux-node1 mysql]# cat install.sls mysql-install: pkg.installed: - pkgs: - mariadb - mariadb-server mysql-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/my.cnf - source: salt://modules/mysql/files/my.cnf - user: root - gourp: root - mode: 644 [root@linux-node1 mysql]# cp /etc/my.cnf files/ (3)在主上配置mariadb-server.cnf,并更改server_id,以及创建主从用户 [root@linux-node1 mysql]# cat master.sls include: - modules.mysql.install master-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf - source: salt://modules/mysql/files/mariadb-server-master.cnf - user: root - group: root - mode: 0644 master-grant: cmd.run: - name: mysql -e "grant replication slave on *.* to repl@'192.168.56.0/255.255.255.0' identified by '123456';flush privileges;" [root@linux-node1 mysql]# cp /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf files/mariadb-server-master.cnf [root@linux-node1 mysql]# cp /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf files/mariadb-server-slave.cnf #修改主从的配置文件的server_id和开启主上的log-bin功能 [root@linux-node1 mysql]# vim files/mariadb-server-master.cnf [mysqld] server_id=1111 log-bin=mysql-bin [root@linux-node1 mysql]# vim files/mariadb-server-slave.cnf [mysqld] server_id=2222 (4)编写shell脚本获取bin-log值和pos值 [root@linux-node1 mysql]# cat files/start-slave.sh #!/bin/bash for i in `seq 1 10` do mysql -h 192.168.56.11 -urepl -p123456 -e "exit" if [ $? -eq 0 ];then Bin_log=`mysql -h 192.168.56.11 -urepl -p123456 -e "show master status;"|awk 'NR==2{print $1}'` POS=`mysql -h 192.168.56.11 -urepl -p123456 -e "show master status;"|awk 'NR==2{print $2}'` mysql -e "change master to master_host='192.168.56.11', master_user='repl', master_password='123456', master_log_file='$Bin_log', master_log_pos=$POS;start slave;" exit; else sleep 60; fi done (5)从库上配置slave,并启动 [root@linux-node1 mysql]# cat slave.sls include: - modules.mysql.install slave-config: file.managed: - name: /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf - source: salt://modules/mysql/files/mariadb-server-slave.cnf - user: root - group: root - mode: 0644 start-slave: file.managed: - name: /tmp/start-slave.sh - source: salt://modules/mysql/files/start-slave.sh - user: root - group: root - mode: 755 cmd.run: - name: /bin/bash /tmp/start-slave.sh
3、HAproxy+Keepalived
(1)pkg配置管理
[root@linux-node1 modules]# mkdir pkg [root@linux-node1 pkg]# vim pkg-init.sls pkg-init: pkg.installed: - names: - gcc - gcc-c++ - glibc - make - autoconf - openssl - openssl-devel [root@linux-node1 pkg]# salt 'linux-node1*' state.sls modules.pkg.pkg-init saltenv=prod test=True
(2)haproxy配置管理

[root@linux-node1 modules]# mkdir haproxy/files -p [root@linux-node1 haproxy]# cat haproxy.sls include: - pkg.pkg-init haproxy-install: file.managed: - name: /usr/local/src/haproxy-1.5.3.tar.gz - source: salt://modules/haproxy/files/haproxy-1.5.3.tar.gz - user: root - group: root - mode: 755 cmd.run: - name: cd /usr/local/src && tar -zxvf haproxy-1.5.3.tar.gz && cd haproxy-1.5.3 && make TARGET=linux26 PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy && make install PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy - unless: test -d /usr/local/haproxy - require: - pkg: pkg-init - file: haproxy-install /etc/init.d/haproxy: file.managed: - source: salt://modules/haproxy/files/haproxy.init - user: root - group: root - mode: 755 - require: - cmd: haproxy-install net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind: sysctl.present: - value: 1 haproxy-config-dir: file.directory: - name: /etc/haproxy - mode: 755 - user: root - group: root haproxy-init: cmd.run: - name: chkconfig --add haproxy - unless: chkconfig --list | grep haproxy - require: - file: /etc/init.d/haproxy [root@linux-node1 haproxy]# cp /usr/local/src/haproxy-1.5.3.tar.gz files/ [root@linux-node1 haproxy]# cp /usr/local/src/haproxy-1.5.3/examples/haproxy.init files/ [root@linux-node1 haproxy]# tree . ├── files │ ├── haproxy-1.5.3.tar.gz │ └── haproxy.init └── install.sls
(3)Keepalived配置管理

[root@linux-node1 keepalived]# vim install.sls include: - pkg.pkg-init keepalived-install: file.managed: - name: /usr/local/src/keepalived-1.2.17.tar.gz - source: salt://modules/keepalived/files/keepalived-1.2.17.tar.gz - user: root - gourp: root - mode: 755 cmd.run: - name: cd /usr/locall/src && tar -zxf keepalived-1.2.17.tar.gz && cd keepalived-1.2.17 && ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/keepalived --disable-fwmark && make && make install - unless: test -d /usr/local/keepalived - require: - pkg: pkg-init - file: keepalived-install /etc/sysconfig/keeplived: file.managed: - source: salt://modules/keepalived/files/keepalived-sysconfig - user: root - gourp: root - mode: 644 /etc/init.d/keepalived: file.managed: - sourcd: salt://modules/keepalived/files/keepalived.init - user: root - group: root - mode: 755 keepalive-init: cmd.run: - name: chkconfig --add keepalived - unless: chkconfig --list | grep keepalived - require: - file: /etc/init.d/keepalived /etc/keepalived: file.directory: - user: root - group: root [root@linux-node1 keepalived]# cp /usr/local/src/keepalived-1.2.17.tar.gz files/ [root@linux-node1 init.d]# pwd /usr/local/src/keepalived-1.2.17/keepalived/etc/init.d [root@linux-node1 init.d]# cp keepalived.init /srv/salt/prod/modules/keepalived/files/ [root@linux-node1 init.d]# cp keepalived.sysconfig /srv/salt/prod/modules/keepalived/files/ [root@linux-node1 keepalived]# tree . ├── files │ ├── keepalived-1.2.17.tar.gz │ ├── keepalived.init │ └── keepalived.sysconfig └── install.sls
4、Nginx+PHP
(1)Nginx配置管理

[root@linux-node1 modules]# mkdir pcre [root@linux-node1 pcre]# cat init.sls pcre-install: pkg.installed: - names: - pcre - pcre-devel [root@linux-node1 modules]# mkdir user [root@linux-node1 user]# cat www.sls www-user-group: group.present: - name: www - gid: 1000 user.present: - name: www - fullname: www - shell: /sbin/nologin - uid: 1000 - gid: 1000 [root@linux-node1 modules]# mkdir nginx/files -p [root@linux-node1 nginx]# cp /usr/local/src/nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz files/ [root@linux-node1 nginx]# tree . ├── files │ └── nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz └── install.sls [root@linux-node1 nginx]# cat install.sls include: - modules.pcre.init - modules.user.www - modules.pkg.pkg-init nginx-source-install: file.managed: - name: /usr/local/src/nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz - source: salt://modules/nginx/files/nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz - user: root - group: root - mode: 755 cmd.run: - name : cd /usr/local/src && tar -zxf nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz && cd nginx-1.12.2 && ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=www --group=www --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-file-aio --with-http_dav_module && make && make install && chown -R www.www /usrl/local/nginx - unless: test -d /usr/local/nginx - require: - user: www-user-group - file: nginx-source-install - pkg: pcre-install - pkg: pkg-init [root@linux-node1 nginx]# salt 'linux-node1*' state.sls modules.nginx.install saltenv=prod test=True
(2)PHP配置管理

[root@linux-node1 modules]# mkdir php/files -p [root@linux-node1 php]# cp /usr/local/src/php-5.6.9/sapi/fpm/init.d.php-fpm files/ [root@linux-node1 php]# cp /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf.default files/ [root@linux-node1 php]# cp /usr/local/src/php-5.6.9/php.ini-production files/ [root@linux-node1 php]# cp /usr/local/src/php-5.6.9.tar.gz files/ [root@linux-node1 php]# tree . ├── files │ ├── init.d.php-fpm │ ├── php-5.6.9.tar.gz │ ├── php-fpm.conf.default │ └── php.ini-production └── install.sls [root@linux-node1 php]# cat install.sls include: - modules.user.www pkg-php: pkg.installed: - names: - mysql-devel - openssl-devel - swig - libjpeg-turbo - libjpeg-turbo-devel - libpng - libpng-devel - freetype - freetype-devel - libxml2 - libxml2-devel - zlib - zlib-devel - libcurl - libcurl-devel php-source-install: file.managed: - name: /usr/local/src/php-5.6.9.tar.gz - source: salt://modules/php/files/php-5.6.9.tar.gz - user: root - gourp: root - mode: 755 cmd.run: - name: cd /usr/local/src && tar -zxf php-5.6.9.tar.gz && cd php-5.6.9 && ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/php -with-pdo-mysql=mysqlnd --with-mysqli=mysqlnd --with-mysql=mysqlnd --with-jpeg-dir --with-png-dir --with-zlib --enable-xml --with-libxml-dir --with-curl --enable-bcmath --enable-shmop --enable-sysvsem --enable-inline-optimization --enable-mbregex --with-openssl --enable-mbstring --with-gd --enable-gd-native-ttf --with-freetype-dir=/usr/lib64 --with-gettext=/usr/lib64 --enable-sockets --with-xmlrpc --enable-zip --enable-soap --disable-debug --enable-opcache --enable-zip --with-config-file-path=/usr/local/php-fastcgi/etc --enable-fpm --with-fpm-user=www --with-fpm-group=www && make && make install - require: - file: php-source-install - user: www-user-group - unless: test -d /user/local/php php-ini: file.managed: - name: /usr/local/php/etc/php.ini - source: salt://modules/php/files/php.ini-production - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 php-fpm: file.managed: - name: /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf - source: salt://modules/php/files/php-fpm.conf.default - user: root - group: root - mode: 644 php-service: file.managed: - name: /etc/init.d/php-fpm - source: salt://modules/php/files/init.d.php-fpm - user: root - group: root - mode: 755 cmd.run: - name: chkconfig --add php-fpm - unless: chkconfig --list | grep php-fpm - require: - file: php-service service.running: - name: php-fpm - enable: True - reload: True - require: - file: php-ini - file: php-fpm - file: php-service - cmd: php-service
统一使用的功能都抽象成一个模块,如安装以及基本配置(nginx中包含include,php中包含的include,那么就可以将nginx.conf放在功能模块,而虚拟主机配置文件,可以放在业务模块)。
其它配置和服务启动可以抽象在一个业务模块,每一个业务都是使用不同的配置文件。
服务全部使用www用户,统一id,只开放8080端口,对于web服务只开放ssh的8022端口以及web的8080端口。其余不用的端口一律不开启
这里将nginx,php都抽象成一个模块,把安装和基础配置都放在了modules中,在nginx衍生的业务模块web目录下,做一个bbs的虚拟主机。
[root@linux-node1 base]# vim top.sls prod: '*': - web.bbs [root@linux-node1 base]# salt '*' state.highstate