最近学了插头dp,准备陆续更新插头dp类练习。
学习论文还是cdq那篇《基于连通性状态压缩的动态规划问题》。
基本的想法都讲得很通透了,接下来就靠自己yy了。
还有感谢kuangbin大大的专题练习。
首先入门肯定写个n*m*state的插头dp,没为什么,这东西好写啊~
然后你就想着,当n*m特别大的时候我该怎么解决呢(m不可能特别大,因为他决定了状态数state)。
你会发现这个dp只针对前一种状态和后一种状态进行转移。
所以你能最后把他压缩成2*state的插头dp,当然这么写肯定是很麻烦的写法,但是极为节省空间。
首先是基础题:
Eat the Trees
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4168 Accepted Submission(s): 2091
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))
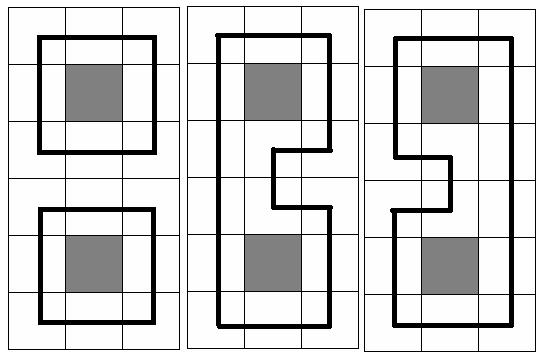
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
基础题嘛,很容易想到转移方程。鉴于我嫌麻烦,写了空间复杂度较高的代码:

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x)) 5 #define LL long long 6 using namespace std; 7 LL dp[20][20][1<<12+1]; 8 int mp[100][100]; 9 int main() 10 { 11 int T,n,m,k,t1,t2,kase=0; 12 scanf("%d",&T); 13 while(T--) 14 { 15 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 16 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 17 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) 18 scanf("%d",&mp[i][j]); 19 clr(dp); 20 dp[0][m][0]=1; 21 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 22 { 23 for(int k=0;k<(1<<m);k++) 24 { 25 dp[i][0][k<<1]=dp[i-1][m][k]; 26 } 27 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) 28 { 29 for(int k=0;k<(1<<(m+1));k++) 30 { 31 t2=1<<j; 32 t1=1<<(j-1); 33 if(mp[i][j]) 34 { 35 if(((k&t2)==0 && (k&t1)!=0) || ((k&t2)!=0 && (k&t1)==0)) 36 dp[i][j][k]+=dp[i][j-1][k]; 37 dp[i][j][k]+=dp[i][j-1][k^t1^t2]; 38 } 39 else 40 { 41 if((k&t1)==0&&(k&t2)==0)dp[i][j][k]+=dp[i][j-1][k]; 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 printf("Case %d: There are %lld ways to eat the trees. ",++kase,dp[n][m][0]); 47 } 48 return 0; 49 }
Pandora adventure
 Problem Description
Problem Description
The pollution of the earth is so serious that people can not survive any more. Fortunately, people have found a new planet that maybe has life, and we call it "Pandora Planet".
Leonardo Da Vinci is the only astronaut on the earth. He will be sent to the Pandora Planet to gather some plant specimens and go back. The plant specimen is important to the people to decide whether the planet is fit to live or not.
Assuming that Da Vinci can only move in an N×M grid. The positions of the plant specimens he wants to collect are all marked by the satellite. His task is to find a path to collect all the plant specimens and return to the spaceship. There are some savage beasts in the planet. Da Vinci can not investigate the grid with the savage beast. These grids are also marked by the satellite. In order to save time Da Vinci could only visit each grid exactly once and also return to the start grid, that is, you can not visit a grid twice except the start grid. You should note that you can choose any grid as the start grid.
Now he wants to know the number of different paths he can collect all the plant specimens. We only care about the path and ignore where the start grid is, so the two paths in Figure 1 are considered as the same.

 Input
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer T (T≤100), indicating the number of cases. Each case begins with a line containing two integers N and M (1≤N, M≤12), the size of the planet is N×M. Each of the following N lines contains M characters Gij(1≤i≤N, 1≤j≤M), Gij denotes the status of the grid in row i and column j, where 'X' denotes the grid with savage beast, '*' denotes the safe grid that you can decide to go or not, 'O' denotes the plant specimen you should collect. We guarantee that there are at least three plant specimens in the map.
 Output
Output
For each test case, print a line containing the test case number (beginning with 1) and the number of different paths he can collect all the plant specimens. You can make sure that the answer will fit in a 64-bit signed integer.
 Sample Input
Sample Input
 Sample Output
Sample Output
三种格子:必经过,不能经过,经不经过无所谓。然后求只有一条的欧拉回路。

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x)) 5 #define clr_1(x) memset(x,-1,sizeof(x)) 6 #define LL long long 7 #define HASH 10007 8 #define STATE 1000010 9 using namespace std; 10 struct hashmap 11 { 12 int size; 13 int next[STATE],state[STATE],head[HASH]; 14 LL fas[STATE]; 15 void init() 16 { 17 size=0; 18 clr_1(head); 19 } 20 void add(int st,LL solu) 21 { 22 int k=st%HASH; 23 for(int i=head[k];i!=-1;i=next[i]) 24 if(st==state[i]) 25 { 26 fas[i]+=solu; 27 return; 28 } 29 next[++size]=head[k]; 30 fas[size]=solu; 31 state[size]=st; 32 head[k]=size; 33 return ; 34 } 35 }dp[2]; 36 int maped[20][20],endflag; 37 char s[20]; 38 int code[20]; 39 void init(int n,int m) 40 { 41 clr(maped); 42 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 43 { 44 scanf("%s",s); 45 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) 46 { 47 if(s[j]=='*') 48 maped[i][j+1]=1; 49 if(s[j]=='O') 50 maped[i][j+1]=2; 51 } 52 } 53 return ; 54 } 55 void decode(int st,int *code,int m) 56 { 57 endflag=st&1; 58 st>>=1; 59 for(int i=m;i>=0;i--) 60 { 61 code[i]=st&3; 62 st>>=2; 63 } 64 return ; 65 } 66 int encode(int *code,int m) 67 { 68 int st=0; 69 for(int i=0;i<=m;i++) 70 { 71 st<<=2; 72 st|=code[i]; 73 } 74 st<<=1; 75 st|=endflag; 76 return st; 77 } 78 void shift(int *code,int m) 79 { 80 for(int i=m;i>0;i--) 81 code[i]=code[i-1]; 82 code[0]=0; 83 return ; 84 } 85 void dpblank(int i,int j,int cnt,int m) 86 { 87 int top,left,up; 88 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 89 { 90 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 91 left=code[j-1]; 92 up=code[j]; 93 if(endflag &&((dp[cnt].state[it]>>1)>0 || maped[i][j]==2)) continue; 94 if(left && up) 95 { 96 if(left!=up) 97 { 98 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 99 if(left==1) endflag=1; 100 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 101 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 102 } 103 else 104 { 105 if(left==2) 106 { 107 top=0; 108 for(int k=j-2;k>=0;k--) 109 { 110 if(code[k]==2) 111 top++; 112 if(code[k]==1) 113 if(top>0) 114 top--; 115 else 116 { 117 code[k]=2; 118 break; 119 } 120 } 121 } 122 else 123 { 124 top=0; 125 for(int k=j+1;k<=m;k++) 126 { 127 if(code[k]==1) 128 top++; 129 if(code[k]==2) 130 if(top>0) 131 top--; 132 else 133 { 134 code[k]=1; 135 break; 136 } 137 } 138 } 139 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 140 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 141 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 142 } 143 } 144 else if(left || up) 145 { 146 if(left) top=left; 147 else top=up; 148 if(maped[i][j+1]) 149 { 150 code[j-1]=0; 151 code[j]=top; 152 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 153 } 154 if(maped[i+1][j]) 155 { 156 code[j-1]=top; 157 code[j]=0; 158 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 159 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 160 } 161 } 162 else 163 { 164 if(maped[i][j+1] && maped[i+1][j]) 165 { 166 code[j-1]=1; 167 code[j]=2; 168 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 169 } 170 if(maped[i][j]==1) 171 { 172 code[j-1]=code[j]=0; 173 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 174 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 175 } 176 } 177 } 178 return ; 179 } 180 void dpnone(int i,int j,int cnt,int m) 181 { 182 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 183 { 184 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 185 if(endflag &&((dp[cnt].state[it]>>1)>0 || maped[i][j]==2)) continue; 186 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 187 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 188 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 189 } 190 return ; 191 } 192 LL solve(int n,int m) 193 { 194 int cnt=0; 195 LL ans=0; 196 dp[cnt].init(); 197 dp[cnt].add(0,1); 198 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 199 { 200 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) 201 { 202 dp[cnt^1].init(); 203 if(maped[i][j]==0) 204 dpnone(i,j,cnt,m); 205 else 206 dpblank(i,j,cnt,m); 207 cnt^=1; 208 /* for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 209 { 210 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 211 for(int k=0;k<=m;k++) 212 printf("%d:%d ",k,code[k]); 213 printf("FLAG:%d fas:%lld ",endflag,dp[cnt].fas[it]); 214 } 215 printf(" "); */ 216 } 217 } 218 for(int i=1;i<=dp[cnt].size;i++) 219 ans+=dp[cnt].fas[i]; 220 return ans; 221 } 222 int main() 223 { 224 int T,n,m; 225 scanf("%d",&T); 226 for(int kase=1;kase<=T;kase++) 227 { 228 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 229 init(n,m); 230 printf("Case %d: %lld ",kase,solve(n,m)); 231 } 232 return 0; 233 }
Pipes
Time Limit: 5000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 917 Accepted Submission(s): 448
Amodern office building ismade up of squaremodules, one on each floor being a service module from which (among other things) hot water is pumped out to the other modules through the heating pipes. Each module (including the service module) will have heating pipes connecting it to exactly two of its two to four neighboring modules. Thus, the pipes have to run in a circuit, from the service module, visiting each module exactly once, before finally returning to the service module. Due to different properties of the modules, having pipes connecting a pair of adjacent modules comes at different costs. For example, some modules are separated by thick walls, increasing the cost of laying pipes. Your task is to, given a description of a floor of an office building, decide the cheapest way to route the heating pipes.

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x)) 5 #define clr_1(x) memset(x,-1,sizeof(x)) 6 #define LL long long 7 #define HASH 10007 8 #define STATE 1000010 9 using namespace std; 10 struct hashmap 11 { 12 int size; 13 int next[STATE],head[HASH]; 14 LL state[STATE]; 15 LL fas[STATE]; 16 void init() 17 { 18 size=0; 19 clr_1(head); 20 } 21 void add(LL st,LL solu) 22 { 23 int k=st%HASH; 24 for(int i=head[k];i!=-1;i=next[i]) 25 if(st==state[i]) 26 { 27 if(fas[i]>solu) 28 fas[i]=solu; 29 return; 30 } 31 next[++size]=head[k]; 32 fas[size]=solu; 33 state[size]=st; 34 head[k]=size; 35 return ; 36 } 37 }dp[2]; 38 int maped[40][40],endflag; 39 char s[40]; 40 int code[40]; 41 void init(int n,int m) 42 { 43 clr(maped); 44 fgets(s,100,stdin); 45 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 46 { 47 fgets(s,100,stdin); 48 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) 49 { 50 if(s[j]==' ') 51 maped[i][j+1]=11; 52 if(s[j]>='0' && s[j]<='9') 53 maped[i][j+1]=s[j]-'0'+1; 54 } 55 } 56 return ; 57 } 58 void decode(LL st,int *code,int m) 59 { 60 endflag=st&1; 61 st>>=1; 62 for(int i=m;i>=0;i--) 63 { 64 code[i]=st&3; 65 st>>=2; 66 } 67 return ; 68 } 69 LL encode(int *code,int m) 70 { 71 LL st=0; 72 for(int i=0;i<=m;i++) 73 { 74 st<<=2; 75 st|=code[i]; 76 } 77 st<<=1; 78 st|=endflag; 79 return st; 80 } 81 void shift(int *code,int m) 82 { 83 for(int i=m;i>0;i--) 84 code[i]=code[i-1]; 85 code[0]=0; 86 return ; 87 } 88 void dpblank(int i,int j,int cnt,int m) 89 { 90 int top,left,up; 91 LL cost; 92 if(maped[i][j]==11) 93 cost=0; 94 else 95 cost=1LL*(maped[i][j]-1); 96 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 97 { 98 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 99 if(endflag &&((dp[cnt].state[it]>>1)>0 || maped[i][j]==2)) continue; 100 left=code[j-1]; 101 up=code[j]; 102 if(left && up) 103 { 104 if(left!=up) 105 { 106 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 107 if(left==1) endflag=1; 108 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 109 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 110 } 111 else 112 { 113 if(left==2) 114 { 115 top=0; 116 for(int k=j-2;k>=0;k--) 117 { 118 if(code[k]==2) 119 top++; 120 if(code[k]==1) 121 if(top>0) 122 top--; 123 else 124 { 125 code[k]=2; 126 break; 127 } 128 } 129 } 130 else 131 { 132 top=0; 133 for(int k=j+1;k<=m;k++) 134 { 135 if(code[k]==1) 136 top++; 137 if(code[k]==2) 138 if(top>0) 139 top--; 140 else 141 { 142 code[k]=1; 143 break; 144 } 145 } 146 } 147 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 148 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 149 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 150 } 151 } 152 else if(left || up) 153 { 154 if(left) top=left; 155 else top=up; 156 if(maped[i][j+1]) 157 { 158 code[j-1]=0; 159 code[j]=top; 160 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 161 } 162 if(maped[i+1][j]) 163 { 164 code[j-1]=top; 165 code[j]=0; 166 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 167 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 168 } 169 } 170 else 171 { 172 if(maped[i][j+1] && maped[i+1][j]) 173 { 174 code[j-1]=1; 175 code[j]=2; 176 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 177 } 178 if(maped[i][j]!=11) 179 { 180 code[j-1]=code[j]=0; 181 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 182 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 183 } 184 } 185 } 186 return ; 187 } 188 void dpnone(int i,int j,int cnt,int m) 189 { 190 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 191 { 192 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 193 if(endflag &&((dp[cnt].state[it]>>1)>0 || maped[i][j]==2)) continue; 194 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 195 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 196 } 197 return ; 198 } 199 LL solve(int n,int m) 200 { 201 int cnt=0; 202 LL ans=0; 203 dp[cnt].init(); 204 dp[cnt].add(0,0); 205 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 206 { 207 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) 208 { 209 dp[cnt^1].init(); 210 if(maped[i][j]==0) 211 dpnone(i,j,cnt,m); 212 else 213 dpblank(i,j,cnt,m); 214 cnt^=1; 215 /* for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 216 { 217 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 218 for(int k=0;k<=m;k++) 219 printf("%d:%d ",k,code[k]); 220 printf("FLAG:%d fas:%lld ",endflag,dp[cnt].fas[it]); 221 } 222 printf(" "); */ 223 } 224 } 225 for(int i=1;i<=dp[cnt].size;i++) 226 ans+=dp[cnt].fas[i]; 227 return ans; 228 } 229 int main() 230 { 231 int T,n,m; 232 scanf("%d",&T); 233 for(int kase=1;kase<=T;kase++) 234 { 235 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 236 n=2*n+1; 237 m=2*m+1; 238 init(n,m); 239 printf("%lld ",solve(n,m)); 240 } 241 return 0; 242 }
Plan
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1436 Accepted Submission(s): 517
Now they comes to the magical world and Lilish ask Resty to play with her.
The game is following :
Now the world is divided into a m * n grids by Lilith, and Lilith gives each grid a score.
So we can use a matrix to describe it.
You should come from cell(0, 0) to cell(m-1, n-1) (Up-Left to Down-Right) and try to colloct as more score as possible.
According to Lilish's rule, you can't arrive at each cell more than once.
Resty knows that Lilish will be easy to find the max score, and he doesn't want to lose the game.
So he want to find the game plan to reach the max score.
Your task is to calculate the max score that Lilish will find, the map is so small so it shouldn't be difficult for you, right?
Process to the END OF DATA.
For each test data :
the first live give m and n. (1<=m<=8, 1<=n<=9)
following m lines, each contain n number to give you the m*n matrix.
each number in the matrix is between -2000 and 2000
Don't print any empty line to the output
这题仍然可以用回路做,value数组存经过的贡献,maped存是否可走(可走,不可走,必过)。

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x)) 5 #define clr_1(x) memset(x,-1,sizeof(x)) 6 #define LL long long 7 #define HASH 10007 8 #define STATE 1000010 9 using namespace std; 10 struct hashmap 11 { 12 int size; 13 int next[STATE],head[HASH]; 14 LL state[STATE]; 15 LL fas[STATE]; 16 void init() 17 { 18 size=0; 19 clr_1(head); 20 } 21 void add(LL st,LL solu) 22 { 23 int k=st%HASH; 24 for(int i=head[k];i!=-1;i=next[i]) 25 if(st==state[i]) 26 { 27 if(fas[i]<solu) 28 fas[i]=solu; 29 return; 30 } 31 next[++size]=head[k]; 32 fas[size]=solu; 33 state[size]=st; 34 head[k]=size; 35 return ; 36 } 37 }dp[2]; 38 int maped[40][40],value[40][40],endflag; 39 char s[40]; 40 int code[40]; 41 void init(int &n,int &m) 42 { 43 clr(maped); 44 clr(value); 45 for(int i=2;i<=n+1;i++) 46 { 47 for(int j=2;j<=m+1;j++) 48 { 49 maped[i][j]=1; 50 scanf("%d",&value[i][j]); 51 } 52 } 53 n+=3; 54 m+=3; 55 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) 56 maped[i][0]=maped[i][m]=1; 57 for(int i=0;i<=m;i++) 58 maped[0][i]=maped[n][i]=1; 59 maped[1][2]=1; 60 maped[n-1][m-2]=1; 61 maped[2][2]=maped[n-2][m-2]=2; 62 maped[n][m]=2; 63 /* for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) 64 { 65 for(int j=0;j<=m;j++) 66 printf("%d ",maped[i][j]); 67 printf(" "); 68 }*/ 69 return ; 70 } 71 void decode(LL st,int *code,int m) 72 { 73 endflag=st&1; 74 st>>=1; 75 for(int i=m;i>=0;i--) 76 { 77 code[i]=st&3; 78 st>>=2; 79 } 80 return ; 81 } 82 LL encode(int *code,int m) 83 { 84 LL st=0; 85 for(int i=0;i<=m;i++) 86 { 87 st<<=2; 88 st|=code[i]; 89 } 90 st<<=1; 91 st|=endflag; 92 return st; 93 } 94 void shift(int *code,int m) 95 { 96 for(int i=m;i>0;i--) 97 code[i]=code[i-1]; 98 code[0]=0; 99 return ; 100 } 101 void dpblank(int i,int j,int cnt,int m) 102 { 103 int top,left,up; 104 LL cost=1LL*value[i][j]; 105 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 106 { 107 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 108 if(endflag &&((dp[cnt].state[it]>>1)>0 || maped[i][j]==2)) continue; 109 left=code[j-1]; 110 up=code[j]; 111 if(left && up) 112 { 113 if(left!=up) 114 { 115 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 116 if(left==1) endflag=1; 117 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 118 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 119 } 120 else 121 { 122 if(left==2) 123 { 124 top=0; 125 for(int k=j-2;k>=0;k--) 126 { 127 if(code[k]==2) 128 top++; 129 if(code[k]==1) 130 if(top>0) 131 top--; 132 else 133 { 134 code[k]=2; 135 break; 136 } 137 } 138 } 139 else 140 { 141 top=0; 142 for(int k=j+1;k<=m;k++) 143 { 144 if(code[k]==1) 145 top++; 146 if(code[k]==2) 147 if(top>0) 148 top--; 149 else 150 { 151 code[k]=1; 152 break; 153 } 154 } 155 } 156 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 157 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 158 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 159 } 160 } 161 else if(left || up) 162 { 163 if(left) top=left; 164 else top=up; 165 if(maped[i][j+1]) 166 { 167 code[j-1]=0; 168 code[j]=top; 169 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 170 } 171 if(maped[i+1][j]) 172 { 173 code[j-1]=top; 174 code[j]=0; 175 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 176 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 177 } 178 } 179 else 180 { 181 if(maped[i][j+1] && maped[i+1][j]) 182 { 183 code[j-1]=1; 184 code[j]=2; 185 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 186 } 187 if(maped[i][j]==1) 188 { 189 code[j-1]=code[j]=0; 190 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 191 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 192 } 193 } 194 } 195 return ; 196 } 197 void dpnone(int i,int j,int cnt,int m) 198 { 199 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 200 { 201 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 202 if(endflag &&((dp[cnt].state[it]>>1)>0 || maped[i][j]==2)) continue; 203 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 204 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 205 } 206 return ; 207 } 208 LL solve(int n,int m) 209 { 210 int cnt=0; 211 LL ans=0; 212 dp[cnt].init(); 213 dp[cnt].add(0,0); 214 for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) 215 { 216 for(int j=0;j<=m;j++) 217 { 218 dp[cnt^1].init(); 219 if(maped[i][j]==0) 220 dpnone(i,j,cnt,m); 221 else 222 dpblank(i,j,cnt,m); 223 cnt^=1; 224 /* for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 225 { 226 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 227 for(int k=0;k<=m;k++) 228 printf("%d:%d ",k,code[k]); 229 printf("FLAG:%d fas:%lld ",endflag,dp[cnt].fas[it]); 230 } 231 printf(" "); */ 232 } 233 } 234 for(int i=1;i<=dp[cnt].size;i++) 235 ans+=dp[cnt].fas[i]; 236 return ans; 237 } 238 int main() 239 { 240 int n,m,kase=0; 241 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF) 242 { 243 init(n,m); 244 printf("Case %d: %lld ",++kase,solve(n,m)); 245 } 246 return 0; 247 }
然后我之前是用独立插头做的,终于过了(78ms):

1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x)) 5 #define clr_1(x) memset(x,-1,sizeof(x)) 6 #define LL long long 7 #define HASH 10007 8 #define STATE 1000010 9 using namespace std; 10 struct hashmap//hash表存状态及大的数和 11 { 12 int size; 13 int next[STATE],head[HASH]; 14 LL state[STATE]; 15 LL fas[STATE]; 16 void init()//清空 17 { 18 size=0; 19 clr_1(head); 20 } 21 void add(LL st,LL solu)//状态加入,若已有该状态则取较大者 22 { 23 int k=st%HASH; 24 for(int i=head[k];i!=-1;i=next[i]) 25 if(st==state[i]) 26 { 27 if(fas[i]<solu) 28 fas[i]=solu; 29 return; 30 } 31 next[++size]=head[k]; 32 fas[size]=solu; 33 state[size]=st; 34 head[k]=size; 35 return ; 36 } 37 }dp[2]; 38 int maped[40][40]; 39 int code[40]; 40 void init(int n,int m)//初始化值,读入maped 41 { 42 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 43 { 44 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) 45 { 46 scanf("%d",&maped[i][j]); 47 } 48 } 49 return ; 50 } 51 void decode(LL st,int *code,int m)//解码,括号序列 52 { 53 for(int i=m;i>=0;i--) 54 { 55 code[i]=st&3; 56 st>>=2; 57 } 58 return ; 59 } 60 LL encode(int *code,int m)//编码,括号序列 61 { 62 LL st=0; 63 for(int i=0;i<=m;i++) 64 { 65 st<<=2; 66 st|=code[i]; 67 } 68 return st; 69 } 70 void shift(int *code,int m)//左移操作 71 { 72 for(int i=m;i>0;i--) 73 code[i]=code[i-1]; 74 code[0]=0; 75 return ; 76 } 77 void dpblank(int i,int j,int cnt,int n,int m)//空格子状态转移 78 { 79 int top,left,up; 80 LL cost; 81 cost=1LL*maped[i][j]; 82 if(i==1 &&j==1)//i=1 且 j=1时加入只有下独立插头 和 右独立插头的状态 83 { 84 decode(dp[cnt].state[1],code,m); 85 if(j+1<=m) 86 { 87 code[j-1]=0; 88 code[j]=3; 89 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[1]+cost); 90 } 91 if(i+1<=n) 92 { 93 code[j-1]=3; 94 code[j]=0; 95 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 96 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[1]+cost); 97 } 98 return ; 99 } 100 if(i==n &&j==m)//i=n 且 j=m时截止单个独立插头的状态 101 { 102 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 103 { 104 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 105 code[j-1]=code[j]=0; 106 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 107 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 108 } 109 return ; 110 } 111 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 112 { 113 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 114 left=code[j-1]; 115 up=code[j]; 116 if(left && up)//上插头和左插头都存在 117 { 118 if(left==3 || up==3)//存在一个独立插头 119 { 120 if(up==2|| left==2)//若另一个插头为右括号插头,则找到对应的左括号插头变为独立插头 121 { 122 top=0; 123 for(int k=j-2;k>=0;k--) 124 { 125 if(code[k]==2) 126 top++; 127 if(code[k]==1) 128 if(top>0) 129 top--; 130 else 131 { 132 code[k]=3; 133 break; 134 } 135 } 136 } 137 else if(up==1 ||left==1)//若另一个插头为左括号插头,则找到对应的右括号插头变为独立插头 138 { 139 top=0; 140 for(int k=j+1;k<=m;k++) 141 { 142 if(code[k]==1) 143 top++; 144 if(code[k]==2) 145 if(top>0) 146 top--; 147 else 148 { 149 code[k]=3; 150 break; 151 } 152 } 153 } 154 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 155 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 156 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 157 } 158 else if(left!=up)//两个括号插头 159 { 160 if(left==1)//左右括号插头,不允许形成回路 161 continue; 162 else//右左括号插头直接去掉 163 { 164 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 165 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 166 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 167 } 168 } 169 else 170 { 171 if(left==2)//都是左括号插头,找到对应的第一个右括号插头变为左括号插头 172 { 173 top=0; 174 for(int k=j-2;k>=0;k--) 175 { 176 if(code[k]==2) 177 top++; 178 if(code[k]==1) 179 if(top>0) 180 top--; 181 else 182 { 183 code[k]=2; 184 break; 185 } 186 } 187 } 188 else//都是右括号插头,找到对应的第一个左括号插头变为右括号插头 189 { 190 top=0; 191 for(int k=j+1;k<=m;k++) 192 { 193 if(code[k]==1) 194 top++; 195 if(code[k]==2) 196 if(top>0) 197 top--; 198 else 199 { 200 code[k]=1; 201 break; 202 } 203 } 204 } 205 code[j]=code[j-1]=0; 206 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 207 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 208 } 209 } 210 else if(left || up)//仅有一个插头,则延伸插头 211 { 212 if(left) top=left; 213 else top=up; 214 if(j+1<=m)//右延伸插头 215 { 216 code[j-1]=0; 217 code[j]=top; 218 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 219 } 220 if(i+1<=n)//下延伸插头 221 { 222 code[j-1]=top; 223 code[j]=0; 224 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 225 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 226 } 227 } 228 else//没有插头 229 { 230 if(j+1<=m && i+1<=n)//下插头和左插头 231 { 232 code[j-1]=1; 233 code[j]=2; 234 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]+cost); 235 } 236 //可经过可不经过点则可以保持原样,没有插头 237 code[j-1]=code[j]=0; 238 if(j==m) shift(code,m); 239 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].fas[it]); 240 } 241 } 242 return ; 243 } 244 LL solve(int n,int m) 245 { 246 int cnt=0; 247 LL ans=0; 248 if(n==1 && m==1) 249 return ans=1LL*maped[1][1]; 250 dp[cnt].init(); 251 dp[cnt].add(0,0); 252 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 253 { 254 for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) 255 { 256 dp[cnt^1].init(); 257 dpblank(i,j,cnt,n,m); 258 cnt^=1; 259 /* for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 260 { 261 decode(dp[cnt].state[it],code,m); 262 for(int k=0;k<=m;k++) 263 printf("%d:%d ",k,code[k]); 264 printf("fas:%lld ",dp[cnt].fas[it]); 265 } 266 printf(" "); */ 267 } 268 } 269 for(int i=1;i<=dp[cnt].size;i++) 270 ans+=dp[cnt].fas[i]; 271 return ans; 272 } 273 int main() 274 { 275 int n,m,kase=0; 276 while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF) 277 { 278 init(n,m); 279 printf("Case %d: %lld ",++kase,solve(n,m)); 280 } 281 return 0; 282 }
可见增加一维可能导致时间暴增,所以能少递推次数尽量少。
还有测过kuangbin的代码,178ms。状态数过多吧容易变慢。
Black and white
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 254 Accepted Submission(s): 76
Special Judge
You are to calculate how many ways there are to fill the remaining part of the grid under the constraints stated below to make the absolute of (sumBlack - sumWhite) minimum and output one of these ways (if any exist).
Each cell in the grid should be colored either black or white.
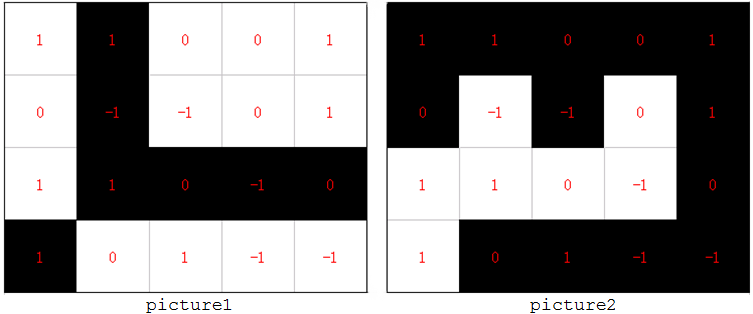
All black cells in the grid should be connected with each other, and all white cells should also be connected with each other.The pictures below show two filled grids where this constraint is only fulfilled in the picture2.
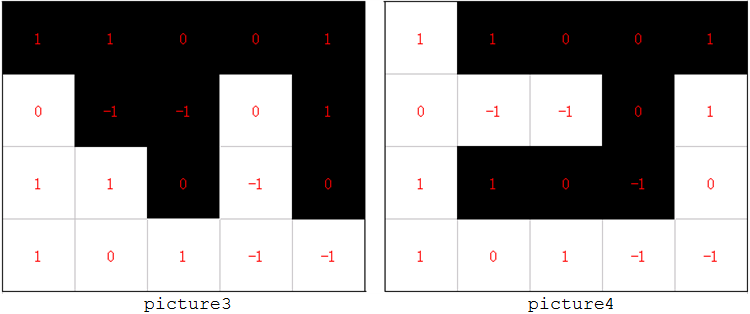
There must be no 2x2 blocks in the grid which consists of only white cells, or of only black cells.
The picture3 shows a grid with a black and a white 2x2 block, while the picture4 contains no such 2x2 block.
You are not allowed to change the color of any of the cells whose color has already been assigned in the input, and all cells must be colored.
Each case starts with two integers, N and M (2 ≤ N, M ≤ 8), the number of rows and columns respectively in the grid.
The next N lines contains M characters each and describes the grid using the following characters:
# - a cell which is colored black
o - a cell which is colored white
. - a cell which color has not yet been assigned
The next N lines contains M integers (-1 or 0 or 1) each indicating the number of this gird.
If there are at least one way, then output the minimum absolute of (sumBlack - sumWhite) and the number of ways to fill the grid make it minimum in a line and output one of these ways, using the same format for the grid as in the input.(anyone is ok)
If there is no way to fill the gird under the constraints stated , just output two zero.
Output a blank line after each case.(Special judge.If you not output a blank line after each case, you may get Wrong Answer)
转移状态较多,给出胡浩的题解:


1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x)) 6 #define clr_1(x) memset(x,-1,sizeof(x)) 7 #define LL long long 8 #define HASH 100003 9 #define STATE 100010 10 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 11 using namespace std; 12 char s[10][10]; 13 int value[10][10]; 14 int pre[65][100010]; 15 char sta[65][100010]; 16 int code[10],ch[10]; 17 int n,m; 18 struct hashmap//hash表存状态及大的数和 19 { 20 int size; 21 int next[STATE],head[HASH]; 22 int state[STATE],dif[STATE],col[STATE]; 23 LL fas[STATE]; 24 void init()//清空 25 { 26 size=0; 27 clr_1(head); 28 } 29 void add(int st,int difr,int colr,int prer,char chr,LL solu,int id) 30 { 31 int k=((st<<6)+colr+difr+2000)%HASH; 32 for(int i=head[k];i!=-1;i=next[i]) 33 if(st==state[i] && difr==dif[i] && colr==col[i]) 34 { 35 fas[i]+=solu; 36 return ; 37 } 38 state[++size]=st; 39 dif[size]=difr; 40 col[size]=colr; 41 fas[size]=solu; 42 pre[id][size]=prer; 43 sta[id][size]=chr; 44 next[size]=head[k]; 45 head[k]=size; 46 return ; 47 } 48 }dp[2]; 49 void init(int n,int m) 50 { 51 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 52 scanf("%s",s[i]); 53 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 54 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) 55 scanf("%d",&value[i][j]); 56 return ; 57 } 58 int encode(int *code,int m) 59 { 60 int st=0; 61 clr_1(ch); 62 int ct=-1; 63 for(int i=0;i<m;i++) 64 { 65 st<<=3; 66 if(ch[code[i]]==-1) ch[code[i]]= ++ ct; 67 st=st|ch[code[i]]; 68 } 69 return st; 70 } 71 void decode(int *code,int m,int st) 72 { 73 for(int i=m-1;i>=0;i--) 74 { 75 code[i]=st & 7; 76 st>>=3; 77 } 78 return ; 79 } 80 void print(int k) 81 { 82 for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--) 83 for(int j=m-1;j>=0;j--) 84 { 85 s[i][j]=sta[i*m+j][k]; 86 k=pre[i*m+j][k]; 87 } 88 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 89 printf("%s ",s[i]); 90 return ; 91 } 92 void dpblank(int i,int j,int cnt,int c) 93 { 94 int lt,up,ltup,col,s1,s2; 95 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size;it++) 96 { 97 decode(code,m,dp[cnt].state[it]); 98 col=dp[cnt].col[it]; 99 up=(i>0)?(col>>j&1)==c:0; 100 lt=(j>0)?(col>>(j-1) & 1)==c:0; 101 ltup=(i&&j)?(col >> m)==c:0; 102 if(i==n-1 && j==m-1 && !lt & !up & ltup) continue; 103 if(lt && up && ltup) continue; 104 if(i && !up) 105 { 106 s1=s2=0; 107 for(int k=0;k<m;k++) 108 { 109 if(code[k]==code[j]) 110 s1++; 111 if((col>>k&1)!=c) 112 s2++; 113 } 114 if(s1==1) 115 { 116 if(s2>1) continue; 117 if(i<n-1 || j<m-2) continue; 118 } 119 } 120 if(lt && up) 121 { 122 if(code[j]!=code[j-1]) 123 for(int k=0,x=code[j];k<m;k++) 124 if(code[k]==x) 125 code[k]=code[j-1]; 126 } 127 else if(lt & !up) 128 code[j]=code[j-1]; 129 else if(!lt && !up) 130 code[j]=m; 131 if(col & 1 << j) col |= 1 << m; 132 else col &= ~(1 << m); 133 if(c) col |= 1 << j; 134 else col &= ~(1 << j); 135 dp[cnt^1].add(encode(code,m),dp[cnt].dif[it]+ (c ? -value[i][j] : value[i][j]),col,it,(c==0?'o':'x'),dp[cnt].fas[it],i*m+j); 136 } 137 return ; 138 } 139 void solve(int n,int m) 140 { 141 int cnt=0; 142 dp[cnt].init(); 143 dp[cnt].add(0,0,0,0,0,1,0); 144 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 145 for(int j=0;j<m;j++) 146 { 147 dp[cnt^1].init(); 148 if(s[i][j]!='x') dpblank(i,j,cnt,0); 149 if(s[i][j]!='o') dpblank(i,j,cnt,1); 150 cnt^=1; 151 }; 152 int minx=INF,ctk; 153 LL ans=0; 154 int ct; 155 for(int it=1;it<=dp[cnt].size; it++) 156 { 157 int s1 = 0; 158 clr(ch); 159 decode(code,m,dp[cnt].state[it]); 160 for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++) if(!ch[code[j]]) ++s1, ch[code[j]] = 1; 161 if(s1 <= 2) 162 { 163 if(abs(dp[cnt].dif[it]) < minx) 164 minx=abs(dp[cnt].dif[it]),ans = dp[cnt].fas[it],ctk=it; 165 else if(abs(dp[cnt].dif[it])==minx) 166 ans+=dp[cnt].fas[it]; 167 } 168 } 169 if(minx==INF) printf("0 0 "); 170 else 171 { 172 printf("%d %lld ", minx,ans); 173 print(ctk); 174 } 175 return ; 176 } 177 int main() 178 { 179 int T; 180 scanf("%d",&T); 181 for(int kase=1;kase<=T;kase++) 182 { 183 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 184 init(n,m); 185 printf("Case %d: ",kase); 186 solve(n,m); 187 printf(" "); 188 } 189 return 0; 190 }
