组件传值:
父传子:
传递:给子组件标签上绑定一个自定义属性,值为需要传递的数据
<One username={this.state.name}></One>
接收:在子组件render函数中通过props接收
let { username } = this.props
* react中如何限制传递来的数据类型和设置初始值:
①下载插件:npm i prop-types 从v15.5开始,React.PropTypes助手函数被弃用,使用 prop-types 库来定义 contextTypes
②在子组件中引入:import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
③对当前组件进行类型限制和默认值的设置
// propTypes是组件上的属性,PropTypes是数据类型检测 Two.propTypes = { name: PropTypes.string } Two.defaultProps = { name: '吴小明' }
* vue中是怎样限制类型和设置初始值的:

子传父:
传递:在子组件中通过 this.props.事件函数 来进行传值
<button onClick={this.handleAdd.bind(this)}>点击发送给父组件</button>
handleAdd() {
this.props.toApp('我是从two组件传来的')
}
接收:在子组件标签上绑定一个自定义属性,值为需要接收参数的函数
<Two toApp={this.handle2.bind(this)}></Two>
handle2(value) {
this.setState({
towValue: value
})
}
非父子:
1、通过onserver传值
①定义observer.js

const eventList = {} const $on = function(eventName, callback) { if (!eventList[eventName]) { eventList[eventName] = [] } eventList[eventName].push(callback) } const $emit = function(eventName, params) { if (eventList[eventName]) { var arr = eventList[eventName] arr.forEach((cb) => { cb(params) }) } } const $off = function(eventName, callback) { if (eventList[eventName]) { if (callback) { var index = eventList[eventName].indexOf(callback) eventList[eventName].splice(index, 1) } else { eventList[eventName].length = 0 } } } export default { $on, $emit, $off }
②在需要传递的组件中引入observer.js
import Observer from '../observer'
通过Observer.$emit()传值:
<button onClick={this.handleClick.bind(this,'传个值给Two组件')}>传个值给Two组件</button>
handleClick(value){ Observer.$emit('abcd',value) }
③在需要接收的组件中引入observer.js
import Observer from '../observer'
通过Observer.$on()接收值
constructor() { super() this.state = { value: '' } Observer.$on('abcd', (value) => { this.setState({ value }) }) }
2、通过context传值
vue中:provide/inject
react中:通过context创建一个生产者,再创建一个消费者供组件使用。其中生产者是父级,消费者是子级。
实践step:
①创建createContext.js文件
import React, { createContext } from 'react'
export let { Provider, Consumer } = createContext() // Provider生产者,Consumer消费者
②在父级中引入Provider并将当前根节点包裹,Provider标签中value属性中是一个对象,用于传值
import { Provider } from './createContext'
render() {
return (
// Provider包裹所有的子级
<Provider
value={{
name: '孙艺珍',
age: 18
}}
>
<div className="app">
<One></One>
</div>
</Provider>
)
}
③在自己中引入Consumer并将当前根节点包裹,Consumer中是一个函数返回一个jsx
import { Consumer } from '../createContext'
render() {
return (
// Consumer包裹的组件接收Provider传来的值,Consumer中是一个函数返回一个jsx语法
<Consumer>
{(props) => {
let { name, age } = props
return (
<div className="Two">
<h1>Two组件</h1>
接收到来自Provider传来的name为:{name},age为:{age}
<Three></Three>
</div>
)
}}
</Consumer>
)
}
利用高阶组件对Consumer进行二次封装:
①src下创建connect/createContext.js
import React, { createContext } from 'react'
export let { Provider, Consumer } = createContext()
②src下创建高阶组件:hoc/connect.js 用于封装Consumer
import React from 'react' import { Consumer } from '../connect/createContext' export const connect = (WrapperComponent) => { return class extends React.Component { render() { return ( <Consumer> {(props) => { return <WrapperComponent {...props}></WrapperComponent> }} </Consumer> ) } } }
③在父组件中通过Provider传值
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Two from './two'
import { Provider } from '../connect/createContext'
class One extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Provider value={{ name: '孙艺珍', sex: '女' }}>
<div className="One">
<h1>One组件</h1>
<Two></Two>
</div>
</Provider>
)
}
}
export default One
如果用原来的Consumer接收:
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Three from './three'
import { Consumer } from '../connect/createContext'
class Two extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Consumer>
{(props) => {
let { name, sex } = props
return (
<div className="Two">
<h1>Two组件</h1>
姓名:{name},性别:{sex}
<Three></Three>
</div>
)
}}
</Consumer>
)
}
}
export default Two
④用封装好的Consumer接收:
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { connect } from '../hoc/connect'
class Three extends Component {
render() {
let { name, sex } = this.props
return (
<div className="Three">
<h1>Three组件</h1>
姓名:{name},性别:{sex}
</div>
)
}
}
export default connect(Three)

3、redux:公共状态管理
组件分类:
1、类组件 - class App extends React.Component {render (){}}
2、函数组件 - function fn (){return (<div>我是一个函数组件</div>)}
3、ui组件
4、容器组件
5、高阶组件
6、受控组件 - input加上value属性和onChange事件后变为受控组件
7、非受控组件 - input加上defaultValue依旧可以输入内容,此时为非受控组件
react中函数组件和类组件的区别:
函数组件:相比较类组件来说比较轻便、速度较快(16.8中引入hooks来解决函数组件的这个问题)
类组件:有属于自己的生命周期,可以在指定的时间做指定的事,可以存储属于自己的状态
高阶组件:
高阶组件是一个函数,它接收一个组件返回一个相对增强性的组件,简称HOC
react中的插槽:
只需在子组件中通过 this.props.children 进行嵌套的内容。
1、子组件标签中的内容默认是不显示的:
import React from 'react' import Header from './Header' class App extends React.Component { render() { return ( <div className="app"> <Header> <h2>标题</h2> </Header> </div> ) } } export default App
2、子组件中通过 this.props.children 接收
import React from 'react' import './index.css' class Header extends React.Component { render() { return <div className="header">{this.props.children}</div> } } export default Header
生命周期:
1、constructor:
1、当前生命周期是组件在初始化的时候执行的,在constructor中必须要写super()否则this的指向会发生错误
2、可以在当前生命周期中存放当前组件所需的一些状态,这些状态必须要放到this.state中
3、在当前生命周期中访问不到this.props,如果要访问this.props必须要在constructor中传入props
constructor(props) { super(props) this.state = { msg: '孙艺珍' } console.log('constructor', props,this.props) // 在super中传入props才可以用this.props接收到数据 }
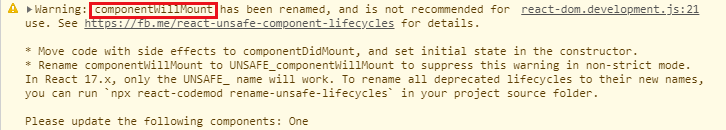
2、componentWillMount:
1、当前生命周期是组件挂载前。此时数据和模板还未结合,因此可以在当前生命周期中做数据最后的更改
2、当前生命周期中可以接收到外部的数据,可以访问到this.props
3、在v17.0中被废除,使用时页面会报警告
3、render:(多次执行)
1、当前生命周期是一个渲染函数,是数据和模板相结合的一个函数。当前生命周期在执行的时候会将渲染好的模板在缓存中存储一份,这就是diff算法比较(diff算法:新旧两个虚拟DOM的对比)
2、当前生命周期会多次执行,当this.setState()或者this.props发生改变的时候就会执行
3、可以通过控制shouldComponentUpdate来减少render函数渲染的次数来优化性能
4、componentDidMount:
1、当前生命周期是数据和模板已经结合完毕并且挂载到页面上,因此我们可以在当前生命周期中获取到真实的DOM结构
2、通常会在当前生命周期中进行前后端数据的交互和方法的实例化(swiper)
react中如何访问到DOM节点:
第一种:<h2 ref='h2'></h2>
this.refs.h2
第二种:<h2 ref={(h2)=>{this.h2=h2}}></h2>
this.h2
render() { return ( <div> <h1>One组件</h1> <h2 ref="h2">h2标签</h2> <h3 ref={(h3) => (this.h3 = h3)}>h3标签</h3> </div> ) } componentDidMount() { console.log('挂载后', this.refs.h2,this.h3) // <h2>h2标签</h2> <h3>h3标签</h3> }
5、componentWillReceiveProps:(多次执行)
1、当props的数据发生改变的时候会执行当前生命周期,在当前生命周期函数中有个参数,该参数是新的props
2、当前生命周期在v17.x的版本中被废除
6、shouldComponentUpdate:(多次执行)
1、当前生命周期书写的时候必须return一个布尔值,当值为true时继续执行下面的生命周期;如果为false不执行下面的生命周期
2、当前生命周期中有2个参数,一个是新的props,一个是新的state,可以根据新的props/state与旧的props/state比较减少render函数的渲染次数
3、当前生命周期决定render函数是否渲染,而不是决定数据是否更新
shouldComponentUpdate(newProps, newState) { console.log('决定数据是否更新', newProps, newState) if (this.state.msg === newState.msg) { return false } else { return true } }
7、componentWillUpdate:(多次执行)
1、当前生命周期在数据更新时执行,有2个参数,一个是新的props,一个是新的state
2、可以在当前生命周期中对数据进行最后的更改
注意:
1、尽量不要在当前生命周期中调用this.setState(),死循环
2、当前生命周期在v17.0中被废除
8、componentDidUpdate:(多次执行)
1、当前生命周期在数据更新完后执行,可以在这里获取到数据更新后最新的DOM结构(一定要加边界条件)
2、当前生命周期中有2个参数,一个是旧的props,一个是旧的state
9、componentWillUnmount:
当前生命周期在组件被卸载时执行,可以在当前生命周期做性能的优化:事件的解绑、定时器的移除……
react中如何强制更新数据:
this.forceUpdate()
注:vue中通过this.$forceUpdate()
常见的生命周期面试题:
1、react中哪些生命周期会执行一次,哪些会执行多次
执行一次:
constructor
componentWillMount
componentDidMount
componentWillUnmount
执行多次:
componentWillReceiveProps
shouldComponentUpdate
componentWillUpdate
render
componentDidUpdate
2、react中第一次执行的生命周期有哪些
constructor
componentWillMount
render
componentDidMount
3、render什么时候被触发
当this.props或this.setState()发生改变的时候触发
4、谈谈对shouldComponentUpdate的理解
5、当this.props或this.setState()执行的时候会触发哪些生命周期
this.props:
componentWillReceiveProps
shouldComponentUpdate
componentWillUpdate
render
componentDidUpdate
this.setState():
shouldComponentUpdate
componentWillUpdate
render
componentDidUpdate
css in js:styled-components 将css组件化
安装插件:npm install styled-components
新建styled.js:
import styled, { keyframes } from 'styled-components'
import logo from '../../logo.png' // 图片的引入
// 定义动画
const move = keyframes`
0%{
transform:rotate(0deg);
}
100%{
transform:rotate(360deg);
}
`
export const HeaderContainer = styled.div`
100%;
height: 1rem;
background-color: ${(props) => props.color}; /* 可以传参 */
color: #fff;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
/* 像sass和less一样嵌套 */
button {
background-color: yellow;
border: 0;
animation: ${move} 3s 1s;
}
button.a {
background-color: #c33;
}
`
// 可以接收父组件传来的值渲染
export const SerachInput = styled.input.attrs((props) => ({
type: props.type,
value: props.value
}))`
60%;
height: 0.5rem;
border: 0;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc;
background-image: url(${logo}); /* 图片的使用 */
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-size: 100% 100%;
`
export const MyButton = styled.button`
100px;
height: 40px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 40px;
color: black;
background-color: yellow;
border: 0;
animation: ${move} 3s 1s;
`
// 继承
export const ChildrenButton = styled(MyButton)`
background-color: green;
`
index.jsx中引入和使用:
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import {
HeaderContainer,
SerachInput,
MyButton,
ChildrenButton
} from './styled'
class Header extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
inputVal: '请输入'
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<HeaderContainer color="deeppink">
猫眼电影
<SerachInput
type="text"
value={this.state.inputVal}
onChange={this.onChange.bind(this)}
></SerachInput>
{/* <MyButton>按钮</MyButton>
<ChildrenButton>子按钮</ChildrenButton> */}
<button>按钮</button>
<button className="a">按钮</button>
</HeaderContainer>
</div>
)
}
onChange() {}
}
export default Header
