react脚手架:
全局安装:npm i create-react-app -g
查看脚手架版本:create-react-app -V
脚手架创建项目:
create-react-app myrouter(要求node版本最低是v10.14.2)
react路由:
安装:npm i react-router-dom
基本使用:
1、路由的形式:
hash路由:HashRouter
history路由:BrowserRouter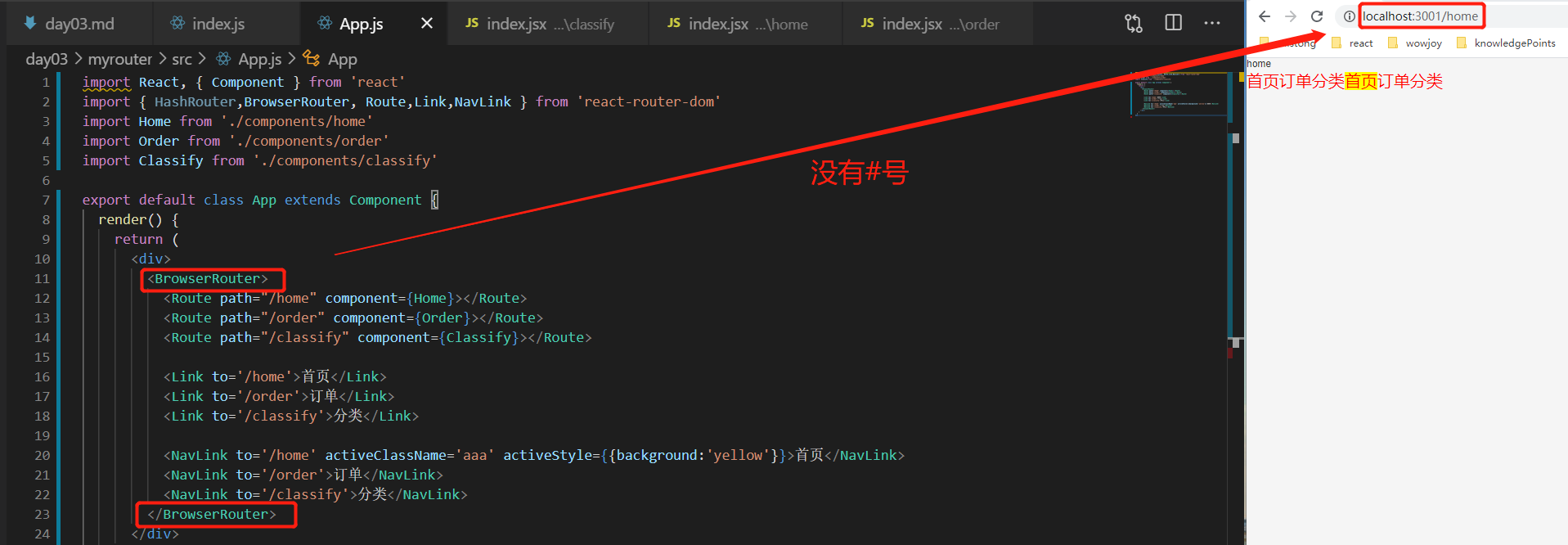
路由的所有配置必须在HashRouter或BrowserRouter的包裹范围之内
2、路由的显示:
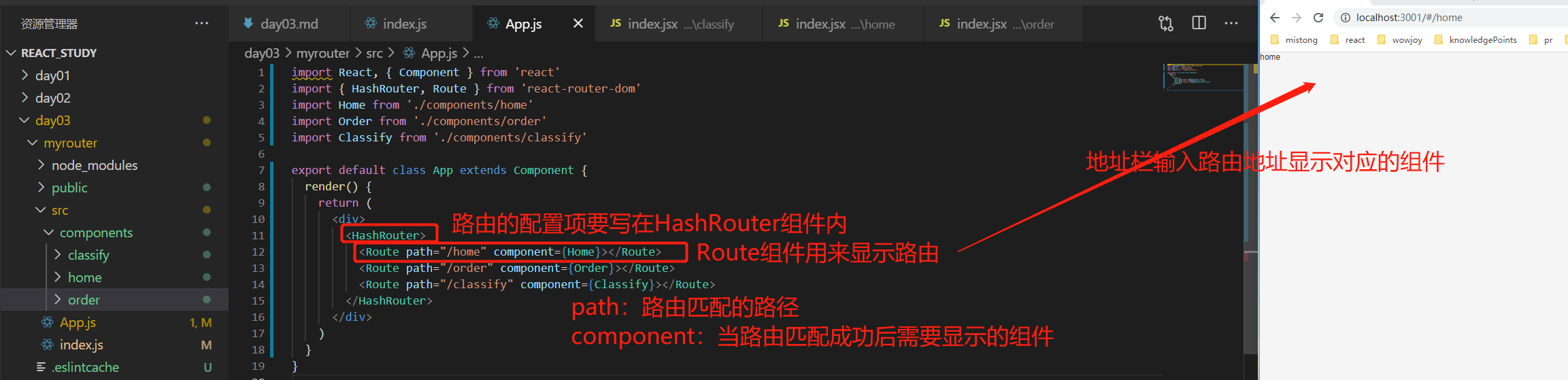
route:
作用:用来配置路由以及路由的显示
配置项:
path:路由匹配的路径
component:当路径匹配成功后需要渲染的组件(值为组件名称)
render:当路径匹配成功后需要渲染的组件(值是一个函数)
exact:完全匹配
3、路由跳转的方式:
①a标签
<a href="#/home">首页</a>
<a href="#/classify">分类</a>
<a href="#/order">订单</a>
②Link(没有选中标识的,使用场景:返回)
<Link to='/home'>首页</Link>
<Link to='/order'>订单</Link>
<Link to='/classify'>分类</Link>
如果重复点击某个路由会报警告:

警告:哈希历史不能推送相同的路径;新的条目不会被添加到历史堆栈中
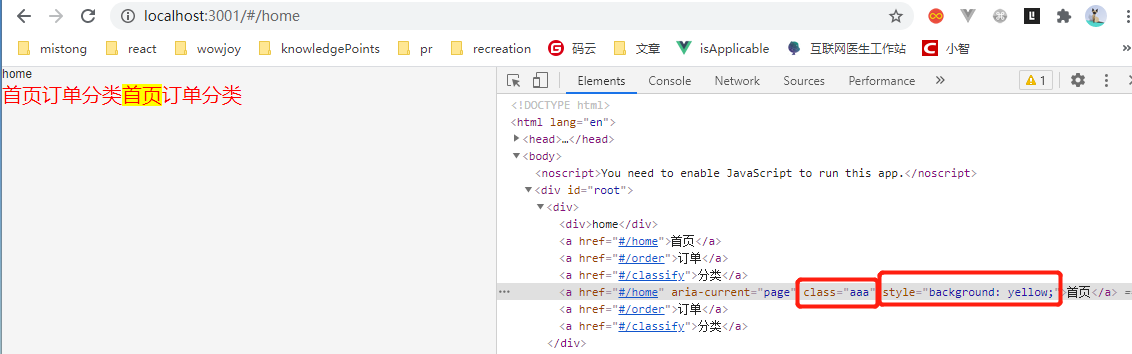
③NavLink(使用场景:底部导航、有选中标识的导航)
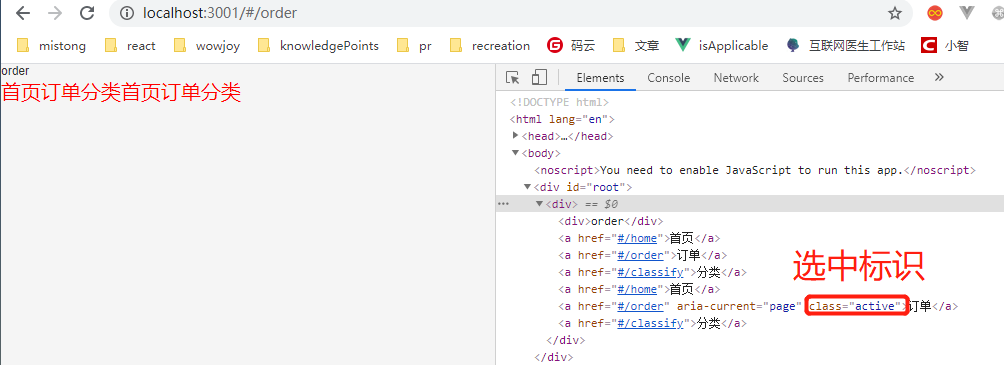
<NavLink to='/home' activeClassName='aaa' activeStyle={{background:'yellow'}}>首页</NavLink>
<NavLink to='/order'>订单</NavLink>
<NavLink to='/classify'>分类</NavLink>
配置项:
to:需要跳转的路径
activeClassName:更改选中后的标识
activeStyle:选中后的样式
④编程式导航
4、路由传值:
①动态路由:(地址栏上有参数:details/xxx/xxx,刷新不丢失)
在定义的时候通过 /:属性 的方式来定义传递的属性

在路由跳转的时候通过 /值 的方式进行传值

在需要接收数据的页面通过 this.props.match.params 来接收

②query传值:(地址栏上有参数:details?id=xxx&name=xxx,刷新不丢失)
路由:
在路由跳转的时候通过 query 进行传值

在需要接收数据的页面通过 this.props.location.search 来接收(?id=0&name=%E9%A6%99%E8%95%89)

③内存传值:(地址栏上没有参数,刷新会丢失)
路由:
在路由跳转的时候通过 to={{pathname:'', query:{}}} 进行传值

在需要接收的页面通过 this.props.location.query 来接收

5、路由嵌套:

6、编程式导航:
this.props.history.push()

this.props.history.goBack()
this.props.history.goForward()
this.props.history.go()
this.props.history.replace()
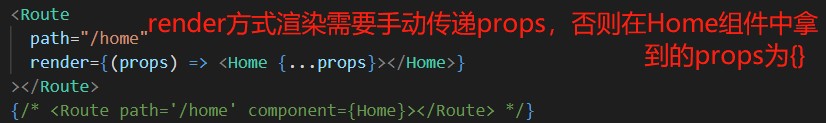
7、component渲染和render渲染的区别:
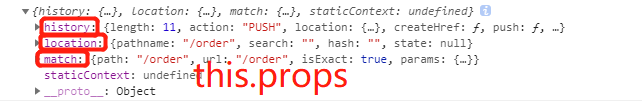
①在route组件中通过component属性进行页面渲染的时候会默认的给当前组件传递三个值(history match location)

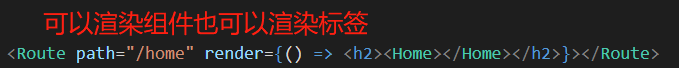
②render渲染的时候可以渲染组件也可以渲染标签
③render渲染的时候可以进行传值

④一般情况下会通过render的方式进行路由的嵌套
⑤render可以进行更多的业务逻辑
8、路由重定向:
import {Redirect} from 'react-router-dom'

9、Switch
作用:只匹配一个路由
10、路由懒加载:
①安装:npm i react-loadable
②引入并使用:
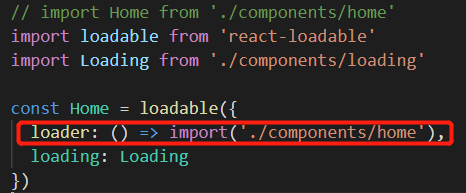
11、withRouter:
高阶组件:
作用:可以给当前组件的props传入一个对象,这个对象就是路由的三个值{history match location}
当使用render方式渲染组件时,如果没有手动去传路由的三个值:

此时在order组件中的this.props是一个空对象:
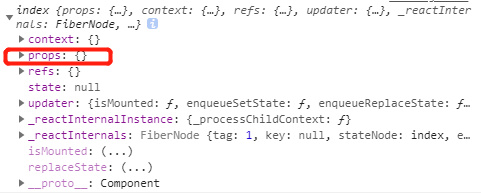
使用withRouter将组件包裹:
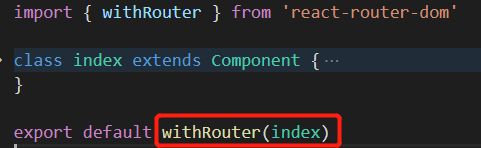
此时再打印this:
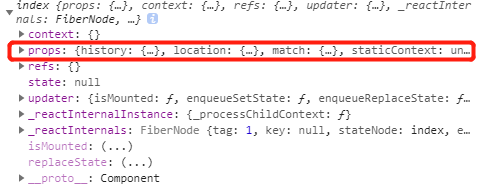
说明withRouter给当前被包裹的组件传递了路由的三个值,就可以正常使用编程式导航等功能了。
路由表封装:
1、在components中新建index.js文件,将所有的页面都用懒加载的方式引入,整体导出出去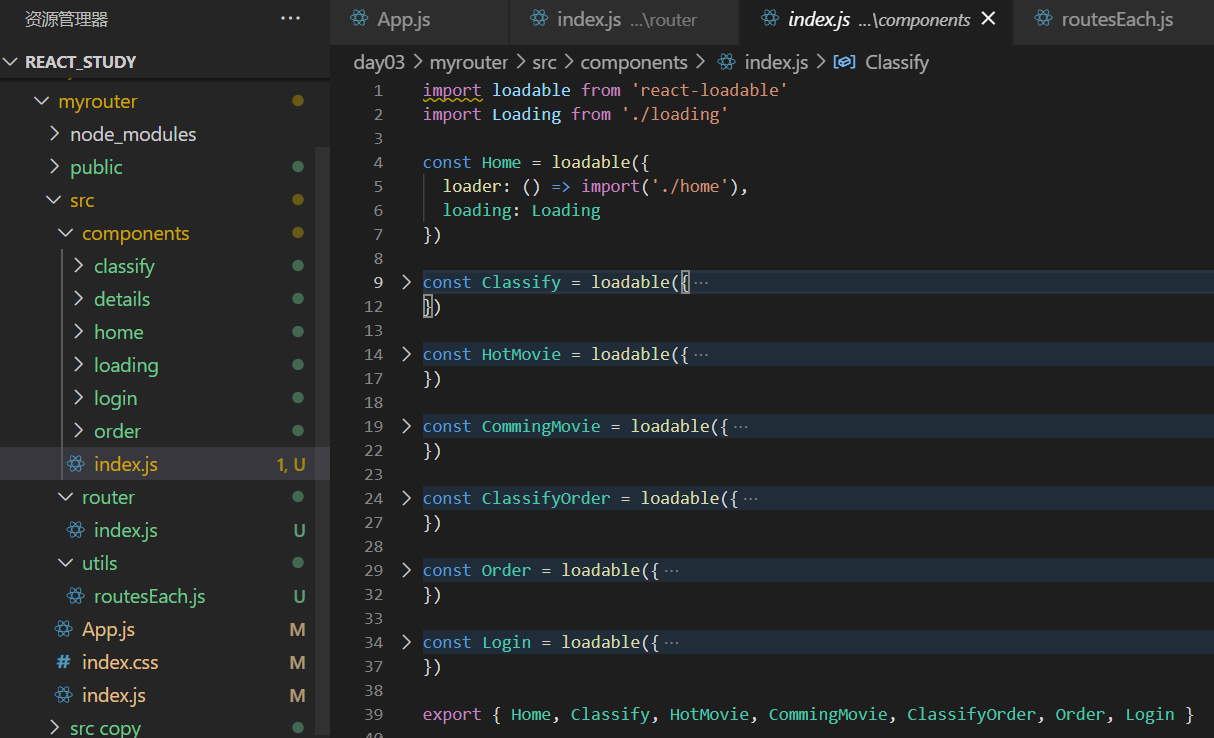
2、src下新建router/index.js:将路由放入路由表中
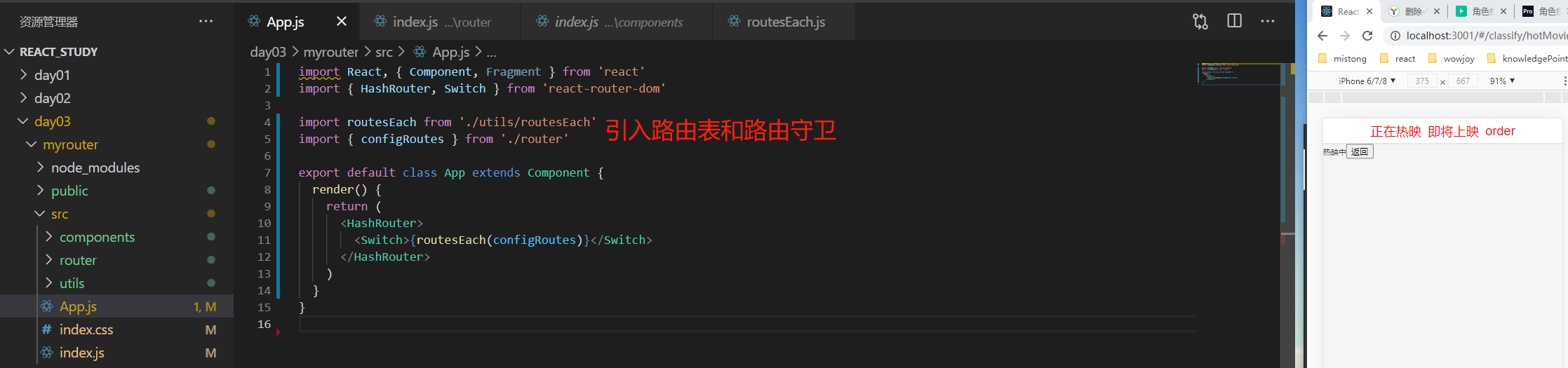
import { Home, Classify, HotMovie, CommingMovie, ClassifyOrder, Order, Login } from '../components' // 有layout布局的路由表 export const layoutRoutes = [ { path: '/home', component: Home, icon: '', meta: {} }, { path: '/classify', component: Classify, icon: '', meta: {}, children: [ { path: '/classify/hotMovie', component: HotMovie, meta: {} }, { path: '/classify/commingMovie', component: CommingMovie, meta: {} }, { path: '/classify/order', component: ClassifyOrder, meta: {} } ] }, { path: '/order', component: Order, icon: '', meta: {} } ] // 没有layout布局的路由表 export const notLayoutRoutes = [ { path: '/login', component: Login, meta: {} } ] // 所有路由的配置项 export const configRoutes = layoutRoutes.concat(notLayoutRoutes)
3、src下新建utils/routesEach.js:传入路由表返回对应的组件,并且模拟vue中路由守卫
import React, { Fragment } from 'react'
import { Switch, Redirect, Route } from 'react-router-dom'
export default (routes) => {
function routesEach(routeConfig) {
return routeConfig.map((item) => {
if (item.children) {
return (
<Route
path={item.path}
key={item.path}
render={() => {
return (
<Fragment>
<Route component={item.component}></Route>
<Switch>
<Redirect
from={item.path}
to={item.children[0].path} // 重定向到第一个路由
exact
></Redirect>
{item.children.map((child) => {
return (
<Route
path={child.path}
key={item.path}
render={() => {
return isAuthRequired(child) // 权限验证
}}
></Route>
)
})}
</Switch>
</Fragment>
)
}}
></Route>
)
} else {
return (
<Route
path={item.path}
key={item.path}
render={() => {
return isAuthRequired(item)
}}
></Route>
)
}
})
}
// 权限验证:路由守卫
function isAuthRequired(item) {
// 先判断当前路由是否需要权限验证
if (item.meta.authRequired) {
// 当前路由需要权限验证,判断token是否存在
if (localStorage.getItem('token')) {
return <item.component></item.component>
} else {
return <Redirect to="/login"></Redirect>
}
} else {
return <item.component></item.component> // 不需要权限验证的路由可以直接返回
}
}
return routesEach(routes)
}
4、app.js