个人博客网:https://wushaopei.github.io/ (你想要这里多有)
一、不可变对象-1
1、不可变对象需要满足的条件
① 对象创建以后其状态就不能修改
② 对象所有域都是final类型
③ 对象是正确创建的(在对象创建期间,this引用没有逸出)
2、final关键字:
final 关键字可以用来修饰:类、方法、变量
修饰类:不能被继承,final类中的成员方法都会被隐式的指定为final方法
修饰方法:1、锁定方法不被继承类修改;2、效率
注意:一个类的private方法会被隐式的指定为final方法
修饰变量:基本数据类型变量、引用类型变量
被final修饰的数值不能再被修改;被final修饰的引用类型不能再指向另一个对象。
重点:fianl修饰数据类型变量和引用类型变量的区别
3、fianl的使用代码演示:
执行结果:
分析:由图中可知,被final修饰的变量无法被重新赋值,被final修饰的map引用类型变量也不能指向新的内存引用。
又由代码执行结果可知,被final修饰的引用数据类型如map的值是可以改变的。
4、常见不可变对象
Collections.unmodifiableXXX : Collection 、List、Set、Map ..,
Guava : ImmutableXXX : Collection 、List、Set、Map....
注意:
使用Collections的unmodifiableXXX生成的引用变量就不能再被修改了;
使用Guava的ImmutableXXX生成的引用变量就不能再被修改了;
5、 Collections.unmodifiableXXX :代码演示:
执行结果:
由执行结果可知,被Collections.unmodifiableMap()修改过的map不能再被重新赋值,虽然声明时没有报错,但是编译运行时却抛出了异常。
二、不可变对象-2
1、从源码对原因进行分析:
unmodifiableMap调用了UnmodifiableMap方法;
在UnmodifiableMap方法中,进行了序列化已经使用final对传入参数m进行修饰:
相当于將原本的map使用另一个map进行替代,并将所有的更新方法在操作时进行异常的抛出,相关源码如下:
当第一次声明值时,会对引用变量的长度和数据进行副本备份,如果有第二次修改时,会进行校验,发现传入参数和底层取出的值不同时,抛出异常。
2、ImmutableXXX代码演示:
ImmutableList 重新赋值测试结果:
ImmutableMap重新赋值测试结果:
查询ImmutableMap的value值:
由结果可知,ImmutableXXX声明的对象为不可变对象,是线程安全的,同时不影响值的获取。
三、线程封闭-1
避免并发,除了设置不可变对象,还有线程封闭。
1、什么是线程封闭
所谓线程封闭,就是把对象锁定到一个线程里,只有这个线程可以看到对象,那么,这个对象就算不是线程安全的,也不会出现线程安全的问题了。因为它只能在一个线程内访问。
2、线程封闭共有三种:
第一种线程封闭:
Ad-hoc 线程封闭 : 程序控制实现,最糟糕,忽略
第二种线程封闭:
堆栈封闭:局部变量,无并发问题
多个线程访问一个方法的时候,局部变量都会被拷贝一份到线程的栈中,所以局部变量是不会被多个线程所共享的,因此也就不会出现并发问题。
全局的变量容易出现并发问题。
第三种线程封闭:
ThreadLocal线程封闭:特别好的封闭方法
原因:
ThreadLocal内部维护了一个map,map的key是每一个线程的名称,而map的值就是我们要封闭的对象,每个map中的对象都对应了一个线程中的值,也就是ThreadLocal利用map实现了线程封闭。
3、ThreadLocal线程封闭——代码演示:
Fitler :
四、线程封闭-2
1、HttpFilter.java
2、配置Filter,将HttpFilter添加到容器
3、Handler适配器实现接口实现前后的拦截、过滤操作:
4、在启动器中将HttpInterceptor 的Bean配置到容器中:
启动并执行测试接口:
由执行结果可知,使用ThreadLocal实现了线程封闭,以为着ThreadLocal是线程安全的。
5、分析:
实现流程:
当请求进来的时候,通过Filter将线程ID存储到了ThreadLocal里面,当接口被处理调用的时候,就可以从ThreadLocal里去取出线程ID,当接口处理完后,再通过HttpInterception适配器中的afterCompletion方法将线程ID给移除掉。
分析:
这里在使用ThreadLocal的时候,定义了三个方法,分别是从ThreaadLocal里面放数据、移除数据、获取数据,放数据一般是通过Filter来放数据,先拦截住接口,在拦截器里面把数据放进去,数据处理完之后在Interceptor里面将数据移除出去,避免内存泄露。
扩展:
线程封闭技术的常见应用:
数据库连接对应JDBC的Connection对象,Connection对象在实现时并没有对线程安全做太多的处理,在相应的JDBC规范里也没有要求Connection对象一定是线程安全的,实际上在服务器应用程序中线程从连接池获取了一个Connection对象,使用完之后再将对象返回给连接池,由于大多数请求都是采用单线程同步的方式处理的,在Connection对象返回之前,连接池不会将它分配给其他线程,因此这种管理模式在请求时隐含的将对象封闭在线程里面。我们使用Connnection对象虽然本身不是线程安全的,但是通过线程封闭也做到了线程安全。
五、线程不安全类与写法-1
线程不安全的类:如果一个类的对象同时可以被多个线程访问,如果你不做特殊的同步处理。那么,它就容易表现出线程不安全的现象。
如:抛出异常、逻辑处理错误等等。
这种类就成为线程不安全的类。
1、字符串拼接
StringBuilder - > StringBuffer
1) StringBuilder 线程安全代码演示:
如果线程安全的话,打印结果应该为5000!
执行打印结果:
由打印结果可知,size的值小于5000,意味着StringBuilder是线程不安全的类。
2) StringBuffer 线程安全代码演示:
执行打印结果:
由打印结果可知,size的值等于5000,意味着StringBuffer是线程安全的类。
3) StringBuffer和StringBuilder线程分析:
由截图可知,StringBuffer的底层实现方法都添加synchronized同步锁,是线程安全的。
而StringBuilder底层的方法没有添加synchronized同步锁,存在线程安全的问题。
4)为什么java要同时提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer两个类?
之所以java同时提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer两个线程安全和不安全的类,是因为在StringBuffer中,使用synchronized锁机制会导致同时只有一个线程可以操作该对象,对性能和效率有损耗。StringBuffer只有在多线程并发且声明为成员变量时使用就可以保证线程的安全;而在业务层逻辑方法中声明StringBuilder局部变量时,由于存在堆栈封闭的关系,同一时间内只会有一个线程调用该类变量,所以不存在线程安全的问题。
2、日期转换的类
SimpleDateFormat - > JodaTimie
1)SimpleDateFormat类线程安全测试:
执行结果:
由执行结果可知,SimpleDateFormat在进行并发执行时抛出了大量异常,这说明了SimpleDateFormat类的线程是不安全的。SimpleDateFormat声明的实例不能直接以成员变量的形式声明来被多线程使用。
正确使用SimpleDateFormat类,应该以局部变量的方式声明该类的实例:
代码如下:
执行结果没有抛出异常:
注意:多线程并发使用SimpleDateFormat类时,一定要在方法中以局部变量的方式声明该类的实例。从而避免线程安全的问题。
2)JodaTimie类线程安全测试:
导入依赖:
代码段:
由执行结果可知,虽然DateTimeFormatter 实例结果是乱序输出的,但是执行线程总数是完全符合要求的,所以DateTimeFormatter的线程是安全的。
六、线程不安全类与写法-2
ArrayList , HashSet , HashMap 等 Collections
1、ArrayList线程安全测试:
执行并打印结果:
由结果可知,size的长度不为5000,说明了ArrayList的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程不安全的。
2、HashSet线程安全测试:
执行并打印结果:
由结果可知,size的长度不为5000,说明了HashSet的add操作在多线程并发环境下也是线程不安全的。
3、HashMap线程安全测试:
执行并打印结果:
由结果可知,size的长度不为5000,说明了HashMap的add操作在多线程并发环境下也是线程不安全的。
4、扩展
先检查再执行: if(condition(a)) { handle(a) ; }
七、同步容器-1
线程安全的同步容器:
ArrayList - > Vecotr , Stack
HashMap - > HashTable (key 、value 不能为 null)
Collections.synchronizedXXX(List、Set、Map)
1、Vector线程安全测试:
测试执行结果:
由结果可知,size的长度为5000,说明了Vector的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
注意:即使是线程安全的Vector也可能发生线程不安全的情况,如下演示
执行结果:
如图,vector的多线程操作发生了异常,全都集中在执行get()操作时,一直发生数组索引越界的异常问题。
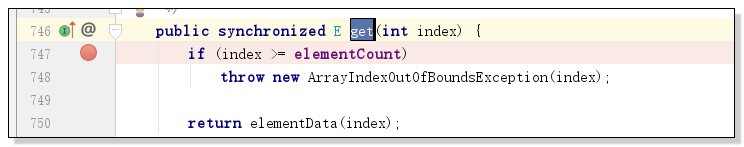
原因分析:vector 是一个线程同步容器,所有的remove操作都是有synchronized修饰的,get操作也是有synchronized修饰的,如图:
在Vector中由于有synchronized同步锁机制,保证了当前两个线程即thread1 和 thread2 是属于两个独立的同步线程;但是,在实际执行代码的过程中,当thread1执行了remove()删除操作时,thread2正好也执行到了get()方法,两者由于相对独立且同步,所以当thread1删除了某个索引的值时,thread2依旧会去get()获取那个索引位的值,但这时候对应的值已经被删除了,所以java会抛出索引越界的异常来提示用户,当前所要get()的值是不存在的。
2、将HashMap替换成Hashtable实现线程安全:
代码演示:
执行结果:
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了HashTable的put操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
源码查看:
由上图可知,HashTable的put、remove等方法的底层实现都是使用synchronized修饰的,是线程安全的。
八、同步容器-2
1、synchronizedList测试线程安全:
执行测试打印结果:
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了synchronizedList的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
2、synchronizedSet测试线程安全:
执行测试打印结果:
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了synchronizedSet的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
3、synchronizedMap测试线程安全:
执行测试打印结果:
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了synchronizedMap的put操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
九、并发容器及安全共享策略总结
ArrayList - > CopyOnWriteArrayList
HashSet 、TreeSet - > CopyOnWriteArraySet ConcurrentSkipListSet
HashMap 、 TreeMap - > ConcurrentHashMap ConcurrentSkipListMap
1、用CopyOnWriteArrayList 替代ArrayList
1) 使用原理:
写操作时复制,当有新元素添加到CopyOnWriteArrayList时,会从原有数组里面拷贝一份出来,在新的数组上用写操作,写完之后把原来的数组指向新的数组,CopyOnWriteArrayList的整个add()操作都是在锁的保护下进行的,主要是为了避免在多线程情况下复制出多个副本出来把数据搞乱,导致最终返回的数据结果不是我们所期待的。
2) 适用场景:
3) CopyOnWriteArrayList的设计思想:
第一点:读写分离,让读和写分开;
第二点:最终一致性,因为在copy的过程需要一些时间,而最终一致性保证了数据是对的;
第三点:使用时另外开辟空间,通过这种方式解决掉并发冲突。
CopyOnWriteArrayList读操作时是在原数组上读的,不需要加锁;而写操作的时候需要加锁,以避免产生多个副本出来,影响最终的数据结果。
4) 代码演示验证CopyOnWriteArrayList的写操作线程安全性:
执行测试打印结果:
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了CopyOnWriteArrayList的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
2、HashSet 、TreeSet - > CopyOnWriteArraySet ConcurrentSkipListSet
1) 代码演示验证CopyOnWriteArraySet的写操作线程安全性:
执行测试打印结果:
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了CopyOnWriteArraySet的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
2) 代码演示验证ConcurrentSkipListSet的写操作线程安全性:
执行测试打印结果:
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了ConcurrentSkipListSet的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
这里的线程安全仅限于做add操作时,如果是做remove操作,还需要其他锁机制保障线程安全。
3、HashMap 、 TreeMap - > ConcurrentHashMap ConcurrentSkipListMap
对并发要求比较高的时候,建议使用ConcurrentSkipListMap
1) 代码演示验证ConcurrentHashMap的写操作线程安全性:
执行测试打印结果:
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了ConcurrentHashMap的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
2) 代码演示验证ConcurrentSkipListMap的写操作线程安全性:
执行测试打印结果:
由结果可知:size的长度为5000,说明了ConcurrentSkipListMap的add操作在多线程并发环境下是线程安全的。
总结:
安全共享对象策略 - 总结:
线程限制:一个被线程限制的对象,由线程独占,并且只能被占有它的线程修改
共享只读:一个共享只读的对象,在没有额外同步的情况下,可以被多个线程并发访问,但是任何线程都不能修改它
线程安全对象:一个线程安全的对象或者容器,在内部通过同步机制来保证线程安全,所以其他线程无需额外的同步就可以通过公共接口随意访问它
被守护对象:被守护对象只能通过获取特定的锁来访问