Cactus |
| Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) |
| Total Submission(s): 56 Accepted Submission(s): 34 |
|
Problem Description
1. It is a Strongly Connected graph.
2. Each edge of the graph belongs to a circle and only belongs to one circle. We call this graph as CACTUS. 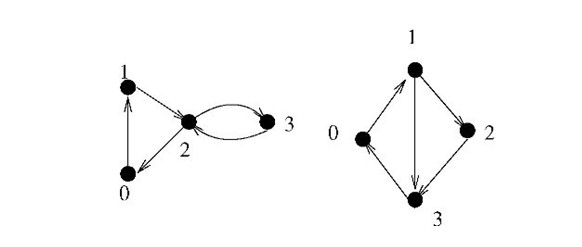 There is an example as the figure above. The left one is a cactus, but the right one isn’t. Because the edge (0, 1) in the right graph belongs to two circles as (0, 1, 3) and (0, 1, 2, 3). |
|
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line contains an integer T (1<=T<=10), representing the number of test cases.
For each case, the first line contains a integer n (1<=n<=20000), representing the number of points. The following lines, each line has two numbers a and b, representing a single-way edge (a->b). Each case ends with (0 0). Notice: The total number of edges does not exceed 50000. |
|
Output
For each case, output a line contains “YES” or “NO”, representing whether this graph is a cactus or not. |
|
Sample Input
2 4 0 1 1 2 2 0 2 3 3 2 0 0 4 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 0 1 3 0 0 |
|
Sample Output
YES NO |
|
Author
alpc91
|
|
Source
2010 ACM-ICPC Multi-University Training Contest(16)——Host by NUDT
|
|
Recommend
zhengfeng
|
/* 题意:给你一个强连通图,如果每条边都只属于一个圈,那么这个图就是仙人掌图。让你判断一下是不是仙人掌图。 初步思路:tarjan遍历边,每次遇到以前的边的时候,这个环中每个边都标记一下如果这条边标记两次,那么就不是仙人掌图 */ #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define N 20005 #define M 50005 using namespace std; /**************************强连通模板******************************/ struct node{ int from,to,next; }edge[M]; int tol,head[N],dfn[N],low[N],flag,Count,cnt,n; bool visit[N],vis[N]; stack<int>S; void add(int a,int b) { edge[tol].from=a;edge[tol].to=b;edge[tol].next=head[a];head[a]=tol++; } int min(int a,int b) { return a<b?a:b; } void tarjan(int u) { int j,v; dfn[u]=low[u]=cnt++; visit[u]=vis[u]=1; S.push(u); for(j=head[u];j!=-1;j=edge[j].next) { v=edge[j].to; if(!visit[v]) { tarjan(v); low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]); } else if(vis[v]) { low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[v]); if(dfn[v]!=low[v]) flag=1; } if(flag) return; } if(dfn[u]==low[u]) { Count++; do{ v=S.top(); S.pop(); vis[v]=0; }while(v!=u); } } /**************************强连通模板******************************/ int main() { int i,ncase,a,b; scanf("%d",&ncase); while(ncase--) { scanf("%d",&n); tol=0; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)!=EOF) { if(!a && !b) break; add(a,b); } memset(visit,0,sizeof(visit)); memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); flag=0; Count=0; cnt=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++) if(!visit[i]) tarjan(i); if(flag||Count!=1) printf("NO "); else printf("YES "); } return 0; }