例1:缺参补全
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot([5, 6, 8, 10])
plt.ylabel('some numbers')
plt.show()
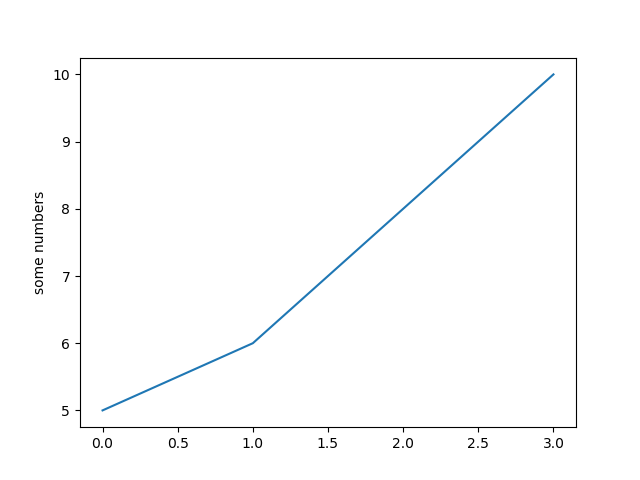
你会很好奇,为什么x轴范围在0-3而y轴的范围在5-10。因为如果你仅仅只提供一个列表给plot()命令,matplotlib
会默认这是y值,再按照len(y)=4,即y的长度给x从0开始分配相应长度的列表[0,1,2,3]。
例2.给定坐标轴范围
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 4, 9, 16], 'ro') plt.axis([0, 6, 0, 20]) plt.show()
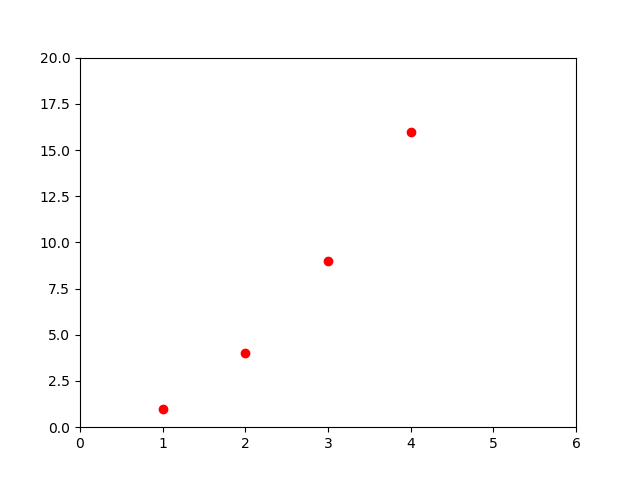
plot()命令中参数'ro'表示红色的实心圆点
axis()命令即给定x,y轴的范围
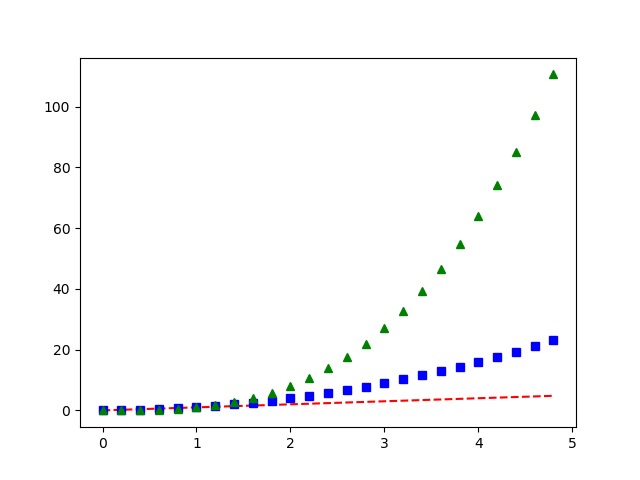
例3.与numpy中array的配合
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt t = np.arange(0., 5., 0.2) # [0. 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1. 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2. 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3. 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4. 4.2 4.4 4.6 4.8] # red的--, blue的方框 and green的尖尖 plt.plot(t, t, 'r--', t, t ** 2, 'bs', t, t ** 3, 'g^') plt.show()
例4:控制线的属性
1.线的粗细
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4], linewidth=10) plt.show()
2.抗锯齿
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt line, = plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4], '-') line.set_antialiased(False) # 关闭抗锯齿 plt.show()
3.设置多属性
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt lines = plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]) # 同时设置线的多个属性 plt.setp(lines, color='r', linewidth=2.0, alpha=0.2) plt.show()
属性大全:
| Property | Value Type |
|---|---|
| alpha | float |
| animated | [True | False] |
| antialiased or aa | [True | False] |
| clip_box | a matplotlib.transform.Bbox instance |
| clip_on | [True | False] |
| clip_path | a Path instance and a Transform instance, a Patch |
| color or c | any matplotlib color |
| contains | the hit testing function |
| dash_capstyle | ['butt' | 'round' | 'projecting'] |
| dash_joinstyle | ['miter' | 'round' | 'bevel'] |
| dashes | sequence of on/off ink in points |
| data | (np.array xdata, np.array ydata) |
| figure | a matplotlib.figure.Figure instance |
| label | any string |
| linestyle or ls | [ '-' | '--' | '-.' | ':' | 'steps' | ...] |
| linewidth or lw | float value in points |
| lod | [True | False] |
| marker | [ '+' | ',' | '.' | '1' | '2' | '3' | '4' ] |
| markeredgecolor or mec | any matplotlib color |
| markeredgewidth or mew | float value in points |
| markerfacecolor or mfc | any matplotlib color |
| markersize or ms | float |
| markevery | [ None | integer | (startind, stride) ] |
| picker | used in interactive line selection |
| pickradius | the line pick selection radius |
| solid_capstyle | ['butt' | 'round' | 'projecting'] |
| solid_joinstyle | ['miter' | 'round' | 'bevel'] |
| transform | a matplotlib.transforms.Transform instance |
| visible | [True | False] |
| xdata | np.array |
| ydata | np.array |
| zorder | any number |
例5:多图
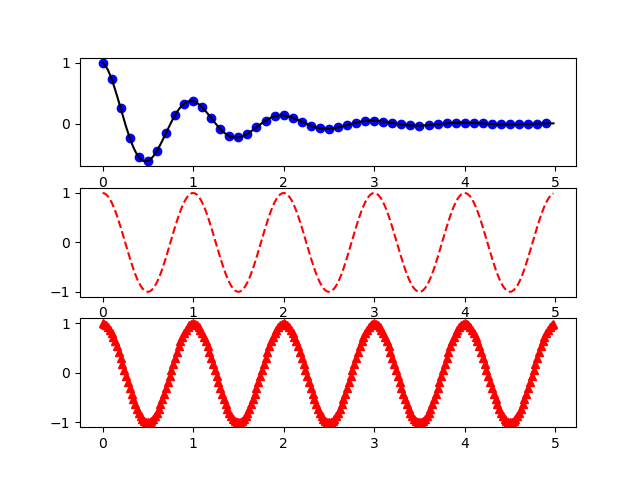
1.图中多图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(t):
return np.exp(-t) * np.cos(2 * np.pi * t)
t1 = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.1)
t2 = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.02)
plt.figure(1)
plt.subplot(311)
plt.plot(t1, f(t1), 'bo', t2, f(t2), 'k')
plt.subplot(312)
plt.plot(t2, np.cos(2 * np.pi * t2), 'r--')
plt.subplot(313)
plt.plot(t2, np.cos(2 * np.pi * t2), 'r^')
plt.show()
2.多图齐出
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.figure(1) # the first figure plt.subplot(211) # the first subplot in the first figure plt.plot([1, 2, 3]) plt.subplot(212) # the second subplot in the first figure plt.plot([4, 5, 6]) plt.figure(2) # a second figure plt.plot([4, 5, 6]) # creates a subplot(111) by default plt.show()
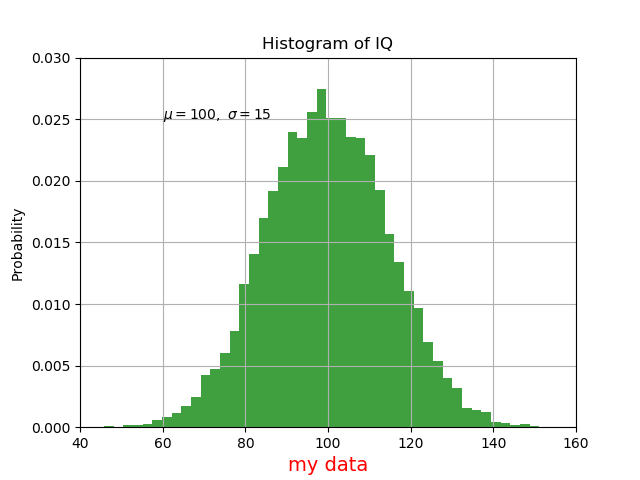
例6:图中插字
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
mu, sigma = 100, 15
x = mu + sigma * np.random.randn(10000)
# the histogram of the data
n, bins, patches = plt.hist(x, 50, normed=1, facecolor='g', alpha=0.75)
t = plt.xlabel('my data', fontsize=14, color='red')
plt.ylabel('Probability')
plt.title('Histogram of IQ')
plt.text(60, .025, r'$mu=100, sigma=15$')
plt.axis([40, 160, 0, 0.03])
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
1.使用数学表达式
plt.title(r'$sigma_i=15$')
2.注释语
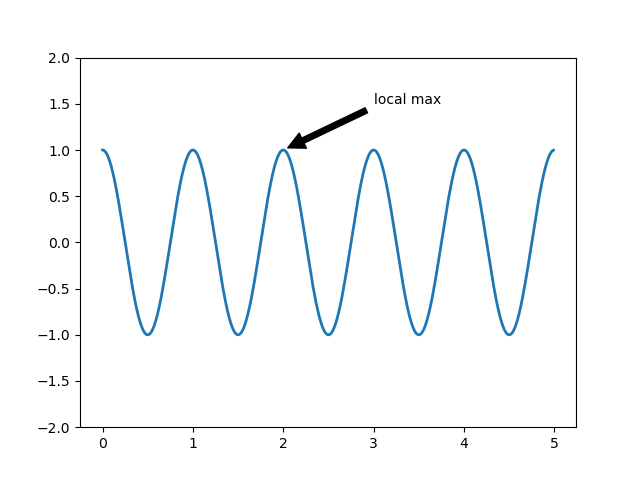
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ax = plt.subplot(111)
t = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.01)
s = np.cos(2 * np.pi * t)
line, = plt.plot(t, s, lw=2)
plt.annotate('local max', xy=(2, 1), xytext=(3, 1.5),
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),
)
plt.ylim(-2, 2)
plt.show()