AOP 是OOP 的延续,是Aspect Oriented Programming 的缩写,意思是面向切面编程。可以通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态统一添加功能的一种技术。AOP设计模式孜孜不倦追求的是调用者和被调用者之间的解耦,AOP 可以说也是这种目标的一种实现。我们现在做的一些非业务,如:日志、事务、安全等都会写在业务代码中(也即是说,这些非业务类横切于业务类),但这些代码往往是重复,复制——粘贴式的代码会给程序的维护带来不便,AOP 就实现了把这些业务需求与系统需求分开来做。这种解决的方式也称代理机制。
AOP 中必须明白的几个概念
1、切面(Aspect)
官方的抽象定义为“ 一个关注点的模块化,这个关注点可能会横切多个对象” 。“ 切面”在ApplicationContext 中<aop:aspect>来配置。连接点(Joinpoint) :程序执行过程中的某一行为,例如,MemberService .get 的调用或者MemberService .delete 抛出异常等行为。
2、通知(Advice)
“切面”对于某个“连接点”所产生的动作。其中,一个“切面”可以包含多个“Advice”。
3、切入点(Pointcut)
匹配连接点的断言,在AOP 中通知和一个切入点表达式关联。切面中的所有通知所关注的连接点,都由切入点表达式来决定。
4、目标对象(Target Object)
被一个或者多个切面所通知的对象。例如,AServcieImpl 和BServiceImpl,当然在实际运行时,SpringAOP 采用代理实现,实际AOP 操作的是TargetObject 的代理对象。
5、AOP 代理(AOP Proxy)
在Spring AOP 中有两种代理方式,JDK 动态代理和CGLib 代理。默认情况下,TargetObject 实现了接口时,则采用JDK 动态代理,例如,AServiceImpl;反之,采用CGLib 代理,例如,BServiceImpl。强制使用CGLib 代理需要将<aop:config>的proxy-target-class 属性设为true。通知(Advice)类型:
6、前置通知(Before Advice)
在某连接点(JoinPoint)之前执行的通知,但这个通知不能阻止连接点前的执行。ApplicationContext中在<aop:aspect>里面使用<aop:before>元素进行声明。例如,TestAspect 中的doBefore 方法。
7、后置通知(After Advice)
当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。ApplicationContext 中在<aop:aspect>里面使用<aop:after>元素进行声明。例如,ServiceAspect 中的returnAfter 方法,所以Teser 中调用UserService.delete 抛出异常时,returnAfter 方法仍然执行。
8、返回后通知(After Return Advice)
在某连接点正常完成后执行的通知,不包括抛出异常的情况。ApplicationContext 中在<aop:aspect>里面使用<after-returning>元素进行声明。
9、环绕通知(Around Advice)
包围一个连接点的通知,类似Web 中Servlet 规范中的Filter 的doFilter 方法。可以在方法的调用前后完成自定义的行为, 也可以选择不执行。ApplicationContext 中在<aop:aspect> 里面使用<aop:around>元素进行声明。例如,ServiceAspect 中的around 方法。
10、异常通知(After Throwing Advice)
在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。ApplicationContext 中在<aop:aspect> 里面使用<aop:after-throwing>元素进行声明。例如,ServiceAspect 中的returnThrow 方法。注:可以将多个通知应用到一个目标对象上,即可以将多个切面织入到同一目标对象。使用Spring AOP 可以基于两种方式,一种是比较方便和强大的注解方式,另一种则是中规中矩的xml配置方式。
如下是基于springBoot的注解方式
@Component //声明这是一个切面Bean @Aspect public class AnnotaionAspect { private final static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AnnotaionAspect.class); //配置切入点,该方法无方法体,主要为方便同类中其他方法使用此处配置的切入点 @Pointcut("execution(* com.wuzz.demo.aop.web..*(..))") public void aspect() { } /* * 配置前置通知,使用在方法aspect()上注册的切入点 * 同时接受JoinPoint 切入点对象,可以没有该参数 */ @Before("aspect()") public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) { //获取目标方法的参数信息 Object[] obj = joinPoint.getArgs(); //AOP代理类的信息 joinPoint.getThis(); //代理的目标对象 joinPoint.getTarget(); //用的最多 通知的签名 Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature(); //代理的是哪一个方法 System.out.println(signature.getName()); //AOP代理类的名字 System.out.println(signature.getDeclaringTypeName()); //AOP代理类的类(class)信息 signature.getDeclaringType(); //获取RequestAttributes RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); //从获取RequestAttributes中获取HttpServletRequest的信息 HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) requestAttributes.resolveReference(RequestAttributes.REFERENCE_REQUEST); //如果要获取Session信息的话,可以这样写: //HttpSession session = (HttpSession) requestAttributes.resolveReference(RequestAttributes.REFERENCE_SESSION); Enumeration<String> enumeration = request.getParameterNames(); Map<String,String> parameterMap = new HashMap(); while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()){ String parameter = enumeration.nextElement(); parameterMap.put(parameter,request.getParameter(parameter)); } String str = JSON.toJSONString(parameterMap); if(obj.length > 0) { System.out.println("请求的参数信息为:"+str); } log.info("before 通知" + joinPoint); } //配置后置通知,使用在方法aspect()上注册的切入点 @After("aspect()") public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) { log.info("after 通知" + joinPoint); } //配置环绕通知,使用在方法aspect()上注册的切入点 @Around("aspect()") public Object around(JoinPoint joinPoint) { long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { Object proceed = ((ProceedingJoinPoint) joinPoint).proceed(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("around 通知" + joinPoint + " Use time : " + (end - start) + " ms!"); return proceed; } catch (Throwable e) { long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); log.info("around 通知" + joinPoint + " Use time : " + (end - start) + " ms with exception : " + e.getMessage()); } return null; } //配置后置返回通知,使用在方法aspect()上注册的切入点 @AfterReturning("aspect()") public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint) { log.info("afterReturn 通知" + joinPoint); } //配置抛出异常后通知,使用在方法aspect()上注册的切入点 @AfterThrowing(pointcut = "aspect()", throwing = "ex") public void afterThrow(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) { log.info("afterThrow 通知" + joinPoint + " " + ex.getMessage()); } }
应该说学习Spring AOP 有两个难点,第一点在于理解AOP 的理念和相关概念,第二点在于灵活掌握和使用切入点表达式。概念的理解通常不在一朝一夕,慢慢浸泡的时间长了,自然就明白了,下面我们简单地介绍一下切入点表达式的配置规则吧。通常情况下,表达式中使用”execution“就可以满足大部分的要求。表达式格式如下:
execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern? name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?
- modifiers-pattern:方法的操作权限
- ret-type-pattern:返回值
- declaring-type-pattern:方法所在的包
- name-pattern:方法名
- parm-pattern:参数名
- throws-pattern:异常
其中, 除ret-type-pattern 和name-pattern 之外, 其他都是可选的。上例中, execution(* com.wuzz.demo.aop.web..*(..))表示com.wuzz.demo.aop.web 包下,返回值为任意类型;方法名任意;参数不作限制的所有方法。最后说一下通知参数,可以通过args 来绑定参数,这样就可以在通知(Advice)中访问具体参数了。例如,<aop:aspect>配置如下:
<aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="xmlAspect"> <aop:pointcut id="simplePointcut" expression="execution(* com.gupaoedu.aop.service..*(..)) and args(msg,..)" /> <aop:after pointcut-ref="simplePointcut" Method="after"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
上面的代码args(msg,..)是指将切入点方法上的第一个String 类型参数添加到参数名为msg 的通知的入参上,这样就可以直接使用该参数啦。在上面的Aspect 切面Bean 中已经看到了,每个通知方法第一个参数都是JoinPoint。其实,在Spring中,任何通知(Advice)方法都可以将第一个参数定义为org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint 类型用以接受当前连接点对象。JoinPoint 接口提供了一系列有用的方法, 比如getArgs() (返回方法参数)、getThis() (返回代理对象)、getTarget() (返回目标)、getSignature() (返回正在被通知的方法相关信息)和toString() (打印出正在被通知的方法的有用信息)。
Spring AOP 源码
Spring 的AOP 是通过接入BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器开始的,它是Spring IOC 容器经常使用到的一个特性,这个Bean 后置处理器是一个监听器,可以监听容器触发的Bean 声明周期事件。后置处理器向容器注册以后,容器中管理的Bean 就具备了接收IOC 容器事件回调的能力。BeanPostProcessor 的使用非常简单,只需要提供一个实现接口BeanPostProcessor 的实现类,然后在Bean 的配置文件中设置即可。
1、BeanPostProcessor 源码
public interface BeanPostProcessor { //为在Bean 的初始化前提供回调入口 @Nullable default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { return bean; } //为在Bean 的初始化之后提供回调入口 @Nullable default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { return bean; } }
这两个回调的入口都是和容器管理的Bean 的生命周期事件紧密相关,可以为用户提供在Spring IOC容器初始化Bean 过程中自定义的处理操作。
2、AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 类对容器生成的Bean 添加后置处理器
BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器的调用发生在Spring IOC 容器完成对Bean 实例对象的创建和属性的依赖注入完成之后,在对Spring 依赖注入的源码分析过程中我们知道,当应用程序第一次调用getBean()方法(lazy-init 预实例化除外)向Spring IOC 容器索取指定Bean 时触发Spring IOC 容器创建Bean 实例对象并进行依赖注入的过程, 其中真正实现创建Bean 对象并进行依赖注入的方法是AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 类的doCreateBean()方法,主要源码如下:
//真正创建Bean 的方法 protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException { ...... try { //将Bean 实例对象封装,并且Bean 定义中配置的属性值赋值给实例对象 //,对Bean 属性的依赖注入进行处理。 populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); //初始化Bean 对象 exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { throw (BeanCreationException) ex; } else { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); } } ...... return exposedObject; }
从上面的代码中我们知道,为Bean 实例对象添加BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器的入口的是initializeBean()方法。
3、initializeBean()方法为容器产生的Bean 实例对象添加BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器
同样在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory 类中,initializeBean()方法实现为容器创建的Bean实例对象添加BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器,源码如下:
//初始容器创建的Bean 实例对象,为其添加BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器 protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { //JDK 的安全机制验证权限 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { //为Bean 实例对象包装相关属性,如名称,类加载器,所属容器等信息 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { //对BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器的postProcessBeforeInitialization //回调方法的调用,为Bean 实例初始化前做一些处理 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { //调用Bean 实例对象初始化的方法,这个初始化方法是在Spring Bean 定义配置 //文件中通过init-Method 属性指定的 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { //对BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器的postProcessAfterInitialization //回调方法的调用,为Bean 实例初始化之后做一些处理 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; } //调用BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器实例对象初始化之前的处理方法 @Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; //遍历容器为所创建的Bean 添加的所有BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器 for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { //调用Bean 实例所有的后置处理中的初始化前处理方法,为Bean 实例对象在 //初始化之前做一些自定义的处理操作 Object current = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result; } //调用BeanPostProcessor 后置处理器实例对象初始化之后的处理方法 @Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { Object current = beanProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result;
}
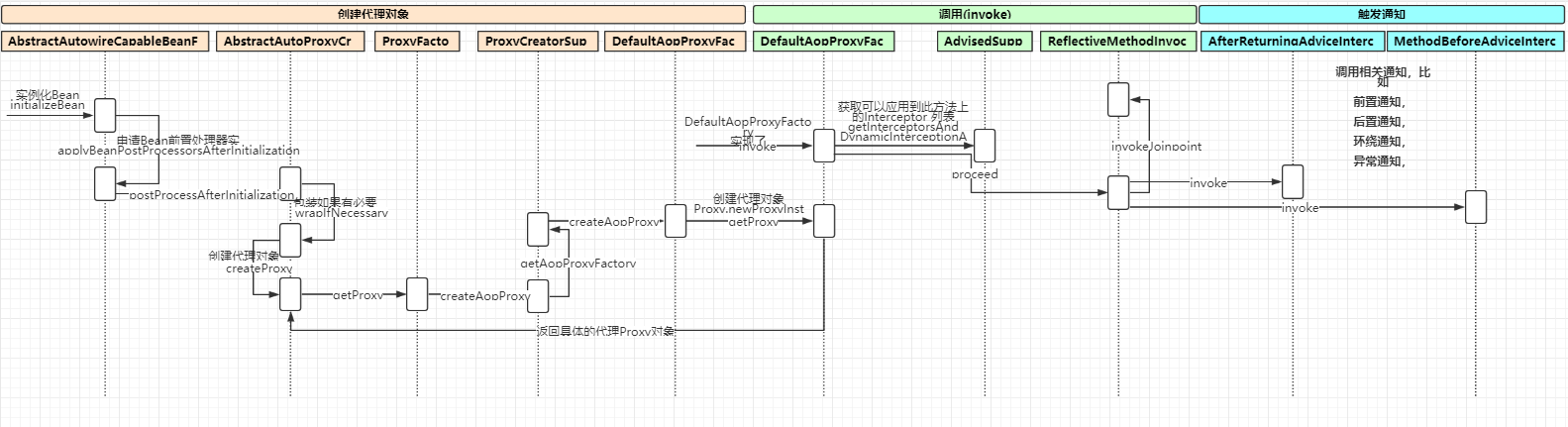
BeanPostProcessor 是一个接口,其初始化前的操作方法和初始化后的操作方法均委托其实现子类来实现,在Spring 中,BeanPostProcessor 的实现子类非常的多,分别完成不同的操作,如:AOP 面向切面编程的注册通知适配器、Bean 对象的数据校验、Bean 继承属性、方法的合并等等,我们以最简单的AOP 切面织入来简单了解其主要的功能。下面我们来分析其中一个创建AOP 代理对象的子类AbstractAutoProxyCreator 类。该类重写了postProcessAfterInitialization()方法。
选择代理策略
以后置处理器为例,进入postProcessAfterInitialization()方法,我们发现调到了一个非常核心的方法wrapIfNecessary(),其源码如下:
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } // 判断是否不应该代理这个bean if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } /*判断是否是一些InfrastructureClass 或者是否应该跳过这个bean。 所谓InfrastructureClass 就是指Advice/PointCut/Advisor 等接口的实现类。 shouldSkip 默认实现为返回false,由于是protected 方法,子类可以覆盖。 */ //扫描所有的相关的方法 pointCut原始方法 if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } // Create proxy if we have advice. // 获取这个bean 的advice Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); // 创建代理 Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//获取代理工厂
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
整个过程跟下来,我发现最终调用的是proxyFactory.getProxy()方法。到这里我们大概能够猜到proxyFactory 有JDK 和CGLib 的,那么我们该如何选择呢?最终调用的是DefaultAopProxyFactory的createAopProxy()方法:
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable { @Override
//创建AOP代理 public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation."); } if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); }//Cglib代理 return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else {
//JDK代理 return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } } /** * Determine whether the supplied {@link AdvisedSupport} has only the * {@link org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy} interface specified * (or no proxy interfaces specified at all). */ private boolean hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(AdvisedSupport config) { Class<?>[] ifcs = config.getProxiedInterfaces(); return (ifcs.length == 0 || (ifcs.length == 1 && SpringProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(ifcs[0]))); } }
调用代理方法,分析调用逻辑之前先上类图,看看Spring 中主要的AOP 组件:
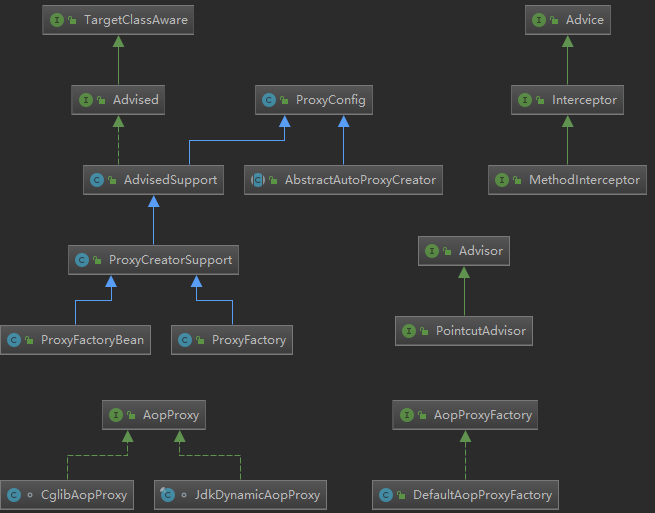
上面我们已经了解到Spring 提供了两种方式来生成代理方式有JDKProxy 和CGLib。下面我们来研究一下Spring 如何使用JDK 来生成代理对象,具体的生成代码放在JdkDynamicAopProxy 这个类中,直接上相关代码:
/** * 获取代理类要实现的接口,除了Advised 对象中配置的,还会加上SpringProxy, Advised(opaque=false) * * 检查上面得到的接口中有没有定义equals 或者hashcode 的接口 * * 调用Proxy.newProxyInstance 创建代理对象 */ public JdkDynamicAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null"); if (config.getAdvisors().length == 0 && config.getTargetSource() == AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) { throw new AopConfigException("No advisors and no TargetSource specified"); } this.advised = config; }
通过注释我们应该已经看得非常明白代理对象的生成过程,此处不再赘述。下面的问题是,代理对象生成了,那切面是如何织入的?我们知道InvocationHandler 是JDK 动态代理的核心,生成的代理对象的方法调用都会委托到InvocationHandler.invoke()方法。而从JdkDynamicAopProxy 的源码我们可以看到这个类其实也实现了InvocationHandler,下面我们分析Spring AOP 是如何织入切面的,直接上源码看invoke()方法:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { MethodInvocation invocation; Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource; Object target = null; try { //eqauls()方法,具目标对象未实现此方法 if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) { return equals(args[0]); } //hashCode()方法,具目标对象未实现此方法 else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself. return hashCode(); } //Advised 接口或者其父接口中定义的方法,直接反射调用,不应用通知 else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) { // There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config. return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised); } else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() && method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) { // Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config... return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args); } Object retVal; if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { // Make invocation available if necessary. oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; }//获得目标对象的类 target = targetSource.getTarget(); Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null); // Get the interception chain for this method. //获取可以应用到此方法上的Interceptor 调用链列表 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);//如果没有可以应用到此方法的通知(Interceptor),此直接反射调用Method.invoke(target, args) if (chain.isEmpty()) { Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); } else {//创建MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain. retVal = invocation.proceed(); } Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) { retVal = proxy; } else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) { throw new AopInvocationException( "Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method); } return retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { // Must have come from TargetSource. targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } }
主要实现思路可以简述为:首先获取应用到此方法上的通知链(Interceptor Chain)。如果有通知,则应用通知,并执行JoinPoint;如果没有通知,则直接反射执行JoinPoint。而这里的关键是通知链是如何获取的以及它又是如何执行的呢?现在来逐一分析。首先,从上面的代码可以看到,通知链是通过Advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice()这个方法来获取的,我们来看下这个方法的实现逻辑:
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method); List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey); if (cached == null) { cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice( this, method, targetClass); this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached); } return cached; }
通过上面的源码我们可以看到, 实际获取通知的实现逻辑其实是由AdvisorChainFactory 的getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice()方法来完成的,且获取到的结果会被缓存。下面来分析getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice()方法的实现:
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice( Advised config, Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { // This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first, // but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list. List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>(config.getAdvisors().length); Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass()); //查看是否包含IntroductionAdvisor boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass); //这里实际上注册一系列AdvisorAdapter,用于将Advisor 转化成MethodInterceptor AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance(); for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) { if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { // Add it conditionally. PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { //这个地方这两个方法的位置可以互换下 //将Advisor 转化成Interceptor MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); //检查当前advisor 的pointcut 是否可以匹配当前方法 MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher(); if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) { if (mm.isRuntime()) { // Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method // isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains. for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) { interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm)); } } else { interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } } } else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor; if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } else { Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } return interceptorList; }
这个方法执行完成后,Advised 中配置能够应用到连接点(JoinPoint)或者目标类(Target Object)的Advisor 全部被转化成了MethodInterceptor,接下来我们再看下得到的拦截器链是怎么起作用的。
//如果没有可以应用到此方法的通知(Interceptor),此直接反射调用Method.invoke(target, args) if (chain.isEmpty()) { Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); } else { // We need to create a method invocation... //创建MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain. retVal = invocation.proceed(); }
从这段代码可以看出, 如果得到的拦截器链为空, 则直接反射调用目标方法, 否则创建MethodInvocation,调用其proceed()方法,触发拦截器链的执行,来看下具体代码:
public Object proceed() throws Throwable { // We start with an index of -1 and increment early. //如果Interceptor 执行完了,则执行joinPoint if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) { return invokeJoinpoint(); } Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice = this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex); if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) { // Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have // been evaluated and found to match. //如果要动态匹配joinPoint InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm = (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice; //动态匹配:运行时参数是否满足匹配条件 if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) { return dm.interceptor.invoke(this); } else { // Dynamic matching failed. // Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain. //动态匹配失败时,略过当前Intercetpor,调用下一个Interceptor return proceed(); } } else { // It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have // been evaluated statically before this object was constructed. //执行当前Intercetpor return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this); } }
至此,通知链就完美地形成了。我们再往下来看invokeJoinpointUsingReflection()方法,其实就是反射调用:
public static Object invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(@Nullable Object target, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { // Use reflection to invoke the method. try { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method); return method.invoke(target, args); } ....... }
触发通知
在为AopProxy 代理对象配置拦截器的实现中,有一个取得拦截器的配置过程,这个过程是由DefaultAdvisorChainFactory 实现的,这个工厂类负责生成拦截器链,在它的getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice 方法中,有一个适配器和注册过程,通过配置Spring 预先设计好的拦截器,Spring 加入了它对AOP 实现的处理。
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice( Advised config, Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) { // This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first, // but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list. List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>(config.getAdvisors().length); Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass()); //查看是否包含IntroductionAdvisor boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass); //这里实际上注册一系列AdvisorAdapter,用于将Advisor 转化成MethodInterceptor AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance(); for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) { if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { // Add it conditionally. PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { //这个地方这两个方法的位置可以互换下 //将Advisor 转化成Interceptor MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); //检查当前advisor 的pointcut 是否可以匹配当前方法 MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher(); if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) { if (mm.isRuntime()) { // Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method // isn't a problem as we normally cache created chains. for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) { interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm)); } } else { interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } } } else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor; if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) { Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } else { Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor); interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors)); } } return interceptorList; }
GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry 负责拦截器的适配和注册过程。而GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry 起到了适配器和单例模式的作用,提供了一个DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry,它用来完成各种通知的适配和注册过程。
public abstract class GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry { /** * Keep track of a single instance so we can return it to classes that request it. */ private static AdvisorAdapterRegistry instance = new DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry(); /** * Return the singleton {@link DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry} instance. */ public static AdvisorAdapterRegistry getInstance() { return instance; } /** * Reset the singleton {@link DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry}, removing any * {@link AdvisorAdapterRegistry#registerAdvisorAdapter(AdvisorAdapter) registered} * adapters. */ static void reset() { instance = new DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry(); } }
DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry 设置了一系列的是配置,正是这些适配器的实现,为Spring AOP 提供了编织能力。
public class DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry implements AdvisorAdapterRegistry, Serializable { private final List<AdvisorAdapter> adapters = new ArrayList<>(3); /** * Create a new DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry, registering well-known adapters. */ public DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry() { registerAdvisorAdapter(new MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter()); registerAdvisorAdapter(new AfterReturningAdviceAdapter()); registerAdvisorAdapter(new ThrowsAdviceAdapter()); } @Override //包装 public Advisor wrap(Object adviceObject) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException { if (adviceObject instanceof Advisor) { return (Advisor) adviceObject; } if (!(adviceObject instanceof Advice)) { throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(adviceObject); } Advice advice = (Advice) adviceObject; if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) { // So well-known it doesn't even need an adapter. return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(advice); } for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) { // Check that it is supported. if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) { return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(advice); } } throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advice); } @Override //获取方法拦截器,即我们配置的切面方法处理 public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException { List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(3); Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice(); if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) { interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice); } for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) { if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) { interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor)); } } if (interceptors.isEmpty()) { throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice()); } return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]); } @Override //注册通知适配器 public void registerAdvisorAdapter(AdvisorAdapter adapter) { this.adapters.add(adapter); } }
下面以MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter 为例,看具体的实现:
class MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter implements AdvisorAdapter, Serializable { @Override public boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice) { return (advice instanceof MethodBeforeAdvice); } @Override public MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor) { MethodBeforeAdvice advice = (MethodBeforeAdvice) advisor.getAdvice(); return new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(advice); } }
Spring AOP 为了实现advice 的织入,设计了特定的拦截器对这些功能进行了封装。我们接着看MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor 如何完成封装的?
public class MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable { private MethodBeforeAdvice advice; /** * Create a new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor for the given advice. * @param advice the MethodBeforeAdvice to wrap */ public MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(MethodBeforeAdvice advice) { Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null"); this.advice = advice; } @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis() ); return mi.proceed(); } }
可以看到,invoke 方法中,首先触发了advice 的before 回调,然后才是proceed。AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor 的源码:
public class AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, AfterAdvice, Serializable { private final AfterReturningAdvice advice; /** * Create a new AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor for the given advice. * @param advice the AfterReturningAdvice to wrap */ public AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(AfterReturningAdvice advice) { Assert.notNull(advice, "Advice must not be null"); this.advice = advice; } @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { Object retVal = mi.proceed(); this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis()); return retVal; } }
ThrowsAdviceInterceptor 的源码:
@Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable { try { return mi.proceed(); } catch (Throwable ex) { Method handlerMethod = getExceptionHandler(ex); if (handlerMethod != null) { invokeHandlerMethod(mi, ex, handlerMethod); } throw ex; } } private void invokeHandlerMethod(MethodInvocation mi, Throwable ex, Method method) throws Throwable { Object[] handlerArgs; if (method.getParameterCount() == 1) { handlerArgs = new Object[] { ex }; } else { handlerArgs = new Object[] {mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis(), ex}; } try { method.invoke(this.throwsAdvice, handlerArgs); } catch (InvocationTargetException targetEx) { throw targetEx.getTargetException(); } }
其实就是在调用方法的时候,先后调用通知的方法拦截器以达到增强方法的功能,最后来一张时序图