本节内容
1.使用基本SQL SELECT语句
2.运算符、逻辑符、比较符,其他操作符
3.使用别名 连接符
4.消除重复的行
5.条件查询
6.模糊查询
7.对查询结果排序
一、基本查询
语法: select 显示的列,.... from 表名
查询员工表中所有的数据
select * from employees; --*号代表显示所有的列
DUAL 是Oracle提供的一个小表,,它只有一行和一列,在句法必须正确(即:必须包括From子句),而数据库中又没有其他表可用于语句时,可使用表DUALL(虚表)
查询系统当前时间: sysdate
select sysdate from dual;

二、运算符、逻辑符、比较符,其他操作符
1.运算符 + - * / ()
在数据库中算术运算符中如果有空值参与运算结果为空
select (10+20*3)/5 from dual;

注意:
select (10+20*null)/5 from dual;
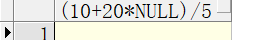
逻辑符: and or not
and 与
or 或
not 非
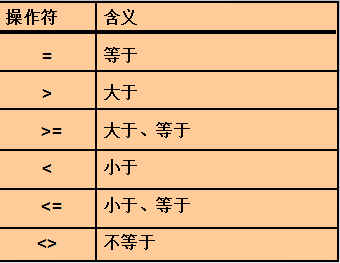
比较运算符:
三、使用别名
可以给列使用别名,也可以给表使用别名 这样方便使用,简化查询,保护表字段的安全。
语法: select employee_id e_id,salary as sal from employees emp;
列名 别名 或者 列名 as 别名
数据库中的连接符:
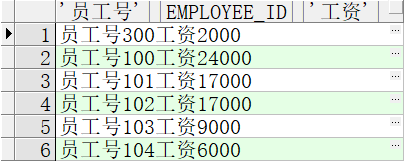
“||”把列与列,列与字符连接在一起。
select '员工号'||employee_id ||'工资'|| salary from employees
四、去重
关键词: DISTINCT 、UNIQUE
DISTINCT 关键词必须跟在select 之后
select distinct * from employees
select unique salary from employees
五、条件查询
我们的基本查询是全部查询,我们有时,可以说大多数情况下都是条件查询:条件查询的关键词 where
语法: select 显示的列 from 表名 where 条件
条件查询:条件可以使用 比较符、逻辑符、或者其他的运算符
例如:查询员工号大于105小于130的员工
select * from employees emp where emp.employee_id>=105 and emp.employee_id<=130;
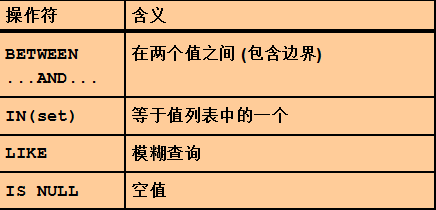
...between... and... 在....之间 包含边界
select * from employees emp where emp.employee_id between 105 and 130;
查询 100、130、400号员工
select * from employees emp where emp.employee_id=100 or emp.employee_id=130 or emp.employee_id=400;
使用 in(...)
select * from employees emp where emp.employee_id in(100,130,400)
你会发现他们的结果是一样的。
六、模糊查询
模糊查询:不提供确定的值,根据提供的值去匹配相符的显示。
使用关键词: like
_ 下划线: 一个下划线代表一个字符
% :代表0到多个字符。
查询:员工姓名以字母A开头的员工
select * from employees emp where emp.last_name like 'A%'
查询:员工姓名中包含字符A的员工
select * from employees emp where emp.last_name like '%A%'
查询:员工姓名第3个字母是A的员工
select * from employees emp where emp.last_name like '__A%'
七、排序:
数据库中的排序:order by
升序:asc (数据库默认是升序)
降序 : desc
SQL语句中order by 排序语句出现在最末尾。
对员工表中的员工工资排序降序:
select * from employees emp order by salary desc
多列排序
select * from employees emp order by salary desc,department_id asc