虚树听起来是一个很高大上的东西,实际上实现起来是比较简单的。
大致的意思是说,对于一棵树而言,也许每次询问我们只需要用到其中的部分节点,因此如果每次询问我们要对全部的节点都做一次处理的话,显然会造成浪费,且很可能会超时。
这时就需要虚树了。
因为有些节点是完全无用的,但你又不能因此毁了原树——说不定下次询问还要用呢?
所以我们可以提取出需要用到的部分节点,重新建一棵树。
我们把需要用到的节点称之为关键点。
比如对于这样一张图:
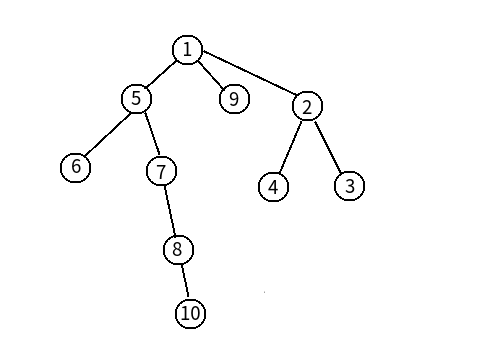
如果给定关键点是1, 6, 10, 那么建出来的虚树是这样的:
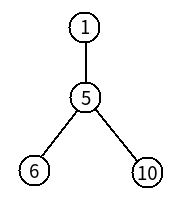
除了给定的关键点外,我们还需要加入一些其他的点作为关键点,来把各个关键点联系起来,而这些新加入的点就是相邻2点的LCA。
那么如何构建出这棵虚树呢?
如果我们按照dfn的顺序来加入节点,这样的话就跟树链剖分有点类似了。
对于这棵还没有构建出来的虚树,我们可以将其剖分成几条链,分别连接,这样的话我们就相当于加入节点的时候只需要维护一条链,而不是树。
而因为我们在树上进行DP等操作时肯定要用到点到root的路径,因此这条链应该是这个点到达root的路径。
但用重儿子来剖分显然是不行的,毕竟你都不知道重儿子会不会是关键点。但是用dfn的话既有明确的顺序,又可以保证在后面加入的点一定不会是前面的点的父亲,因此我们选用dfn。
首先我们依次加入1 6这2个点,现在它们构成了一条链。
然后加入10这个点,这时我们发现,10这个点的LCA是5,而5在1的下面,因此如果我们要得到10到root的路径,1是必须保留的,5作为LCA显然也是必须保留的。
而6对于我现在要维护的新链并没有什么用,因此我们要舍弃掉6,并连上5 ---> 6,然后把5和10依次加入栈。
这时我们发现没有新的点要加入了,于是弹出栈内所有元素,并且每弹出一个元素,就要把这个元素和上一个元素连一条边
于是我们就建好了一棵虚树。
不过有时我们并不需要把树实实在在的建出来
因为既然我们已经可以根据一个序列建出一棵虚树了,其实也完全可以通过这个序列来遍历这棵树,而不是把它建出来再遍历。
但是这种方法适用性没有那么广。
(下面的代码是消耗战(入门题)的)

1 // luogu-judger-enable-o2 2 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define R register int 5 #define AC 250010 6 #define ac 500100 7 #define LL long long 8 9 int n, m, timer, cnt, k; 10 int p[ac], t[ac], st[ac][20], dfn[AC], dep[AC], num[ac], first[AC]; 11 LL f[AC], val[AC], len[ac];//error !!!这里应该是ac!!! 12 int d[AC], s[AC], top; 13 int Head[AC], date[ac], Next[ac], tot;//原树,用完可以重复利用来建虚树 14 15 inline int read() 16 { 17 int x = 0;char c = getchar(); 18 while(c > '9' || c < '0') c = getchar(); 19 while(c >= '0' && c <= '9') x = x * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar(); 20 return x; 21 } 22 23 inline void add1(int f, int w, LL S) 24 { 25 date[++tot] = w, Next[tot] = Head[f], Head[f] = tot, len[tot] = S; 26 date[++tot] = f, Next[tot] = Head[w], Head[w] = tot, len[tot] = S; 27 } 28 29 inline void add2(int f, int w) 30 { 31 date[++tot] = w, Next[tot] = Head[f], Head[f] = tot; 32 date[++tot] = f, Next[tot] = Head[w], Head[w] = tot; 33 //printf("%d ---> %d ", f, w); 34 } 35 36 void dfs1(int x)//求出dfn和一些附带信息 37 { 38 int now; 39 dfn[x] = ++timer, num[++cnt] = x, first[x] = cnt; 40 for(R i = Head[x]; i; i = Next[i])//存下第一次出现的位置 41 { 42 now = date[i]; 43 if(dfn[now]) continue; 44 dep[now] = dep[x] + 1; 45 val[now] = min(len[i], val[x]);//求出这个点到root这条链上的最小代价 46 dfs1(now); 47 num[++cnt] = x;//应该是每次到达这个节点都要计入 48 } 49 //num[++cnt] = x;//存下遍历序列 50 } 51 52 void pre() 53 { 54 int a, b, c; 55 n = read(), val[1] = 1e18; 56 for(R i = 1; i < n; i ++) 57 { 58 a = read(), b = read(), c = read(); 59 add1(a, b, c); 60 } 61 dep[1] = 1; 62 dfs1(1); 63 } 64 65 int Max(int x, int y) 66 { 67 if(dep[num[x]] < dep[num[y]]) return x; 68 else return y; 69 } 70 71 int Min(int x, int y) 72 { 73 if(x < y) return x; 74 else return y; 75 } 76 77 void build()//建出st表 78 {//查询的应该是遍历序列上的深度最小值 79 for(R i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++) st[i][0] = i; 80 int tmp = 1, rnt = 0; 81 for(R i = 1; i <= cnt; i ++) 82 { 83 if(i == tmp * 2) tmp <<= 1, ++rnt; 84 p[i] = tmp, t[i] = rnt;//p[i]表示小于等于i的最大的2的次幂 85 } 86 tmp = 1; 87 for(R i = 1; i <= 19; i ++)//枚举长度 88 { 89 for(R j = 1; j <= cnt; j ++) 90 st[j][i] = Max(st[j][i - 1], st[Min(j + tmp, cnt)][i - 1]); 91 tmp <<= 1; 92 } 93 } 94 95 int LCA(int x, int y) 96 { 97 if(x > y) swap(x, y); 98 int len = y - x + 1; 99 return num[Max(st[x][t[len]], st[y - p[len] + 1][t[len]])]; 100 } 101 102 void dfs2(int x, int fa) 103 { 104 int now;LL tmp = 0; 105 f[x] = val[x]; 106 for(R i = Head[x]; i; i = Next[i]) 107 { 108 now = date[i]; 109 if(now == fa) continue; 110 dfs2(now, x); 111 tmp += f[now]; 112 } 113 Head[x] = 0; 114 if(tmp && tmp < f[x]) f[x] = tmp; 115 } 116 117 inline bool cmp(int a, int b) 118 { 119 return dfn[a] < dfn[b]; 120 } 121 122 void get() 123 { 124 int rnt = 1; 125 //memset(Head, 0, sizeof(Head)); 126 k = read(), tot = 0; 127 for(R j = 1; j <= k; j ++) d[j] = read(); 128 sort(d + 1, d + k + 1, cmp); 129 s[1] = top = 1; 130 for(R i = 2 ; i <= k; i ++) 131 if(LCA(first[d[i]], first[d[rnt]]) != d[rnt]) d[++rnt] = d[i]; 132 for(R i = 1; i <= rnt; i ++) 133 { 134 int lca = LCA(first[d[i]], first[s[top]]); 135 while(1) 136 { 137 if(dfn[lca] > dfn[s[top - 1]]) 138 { 139 if(lca != s[top]) add2(lca, s[top]), -- top; 140 if(lca != s[top]) s[++top] = lca;//因为top已经-1了,所以这里的top是上面的top-1 141 break; 142 } 143 add2(s[top - 1], s[top]), -- top;//否则就还要一直弹出 144 } 145 s[++top] = d[i]; 146 } 147 while(top > 1) add2(s[top - 1], s[top]), --top; 148 //printf("--------------"); 149 } 150 151 void work() 152 { 153 m = read(); 154 for(R i = 1; i <= m; i ++) 155 { 156 get(); 157 dfs2(1, 0); 158 printf("%lld ", f[1]); 159 } 160 } 161 162 int main() 163 { 164 // freopen("in.in", "r", stdin); 165 pre(); 166 build();//构建st数组 167 memset(Head, 0, sizeof(Head)); 168 work(); 169 // fclose(stdin); 170 return 0; 171 }
