时间:2017-1-6 16:53
修改struts.xml配置文件不需要重启服务器。
Struts2框架
一、
* 介绍Struts2
* 关于Struts2配置(关于Action配置)
* 关于Struts2结果类型
二、
* Struts2处理请求参数
* Struts2的类型转换(了解)
* Struts2的校验
三、
* Struts2的国际化
* Struts2的拦截器
* Struts2文件上传与下载
* Struts2中ognl与valuestack
四、
* ognl与valuestack
* Struts2中的防止表单重复提交
* Struts2中的Ajax插件
五、
* 练习(增删改查)
——什么是Struts2
1、Struts2是一个非常优秀的MVC框架,基于Model2设计模型,只能在JavaWeb项目中应用。
2、由传统Struts1和WebWork两个经典框架发展而来。
3、Struts2核心功能
* 允许POJO(Plain Old Java Object)对象作为Action。
* Action的excute方法不再与Servlet API耦合,更容易测试。
* 支持更多视图技术(JSP、FreeMarker、Velocity)。
* 基于Spring AOP思想的拦截器机制,更易扩展。
* 更强大、更易用的输入校验功能。
* 整合Ajax支持
4、Struts2核心:WebWork
WebWork核心是XWork,XWork提供了很多核心功能:前端拦截器(Interceptor),运行时表单属性验证,类型转换,强大的表达式语言,(OGNL - the Object Graph Navigation Language),IoC(Inversion of Control 反转控制)容器等。
——Struts2的下载和安装
1、到http://struts.apache.org/download.cgi 去下载Struts2最新版本。
2、Struts2目录结构
* apps:该文件包含了基于Struts2的示例应用。
* docs:该文件夹下包含了Struts2相关文档,包括Struts2快速入门、Struts2的文档以及API等文档。
* lib:该文件夹下包含了Struts2框架和核心类库,以及Struts2第三方插件类库
* src:该文件夹下包含了Struts框架的全部源代码。
> core:Struts2的源代码
> xwork-core:xwork的源代码
3、开发时没必要将lib目录下的jar文件全部复制到项目中。
可以到:struts-2.3.15.1appsstruts2-blankWEB-INFlib目录下找到必要jar包。
——Struts2之HelloWorld
Struts2的Web项目尽量使用JavaEE5.0版本,因为Struts2是基于配置文件进行开发的。
1、导入jar包
struts-2.3.15.1appsstruts2-blankWEB-INFlib目录下找到必要jar包即可。
2、创建index.jsp、hello.jsp页面
3、对Struts2框架进行配置
1)web.xml文件中配置前端控制器(核心控制器),其实就是一个Filter,目的是使Struts2框架生效。
该过滤器的init()方法加载了Struts2框架必要的配置文件。
2)创建一个struts.xml配置文件,这个是Struts2框架的配置文件,目的是使Struts2的流程可以执行。
名称:struts.xml
位置:src文件夹下(classes文件夹下)
4、创建一个HelloAction类
要求:在HelloAction类中创建一个返回值是String类型的无参方法。
5、在struts.xml文件中配置HelloAction
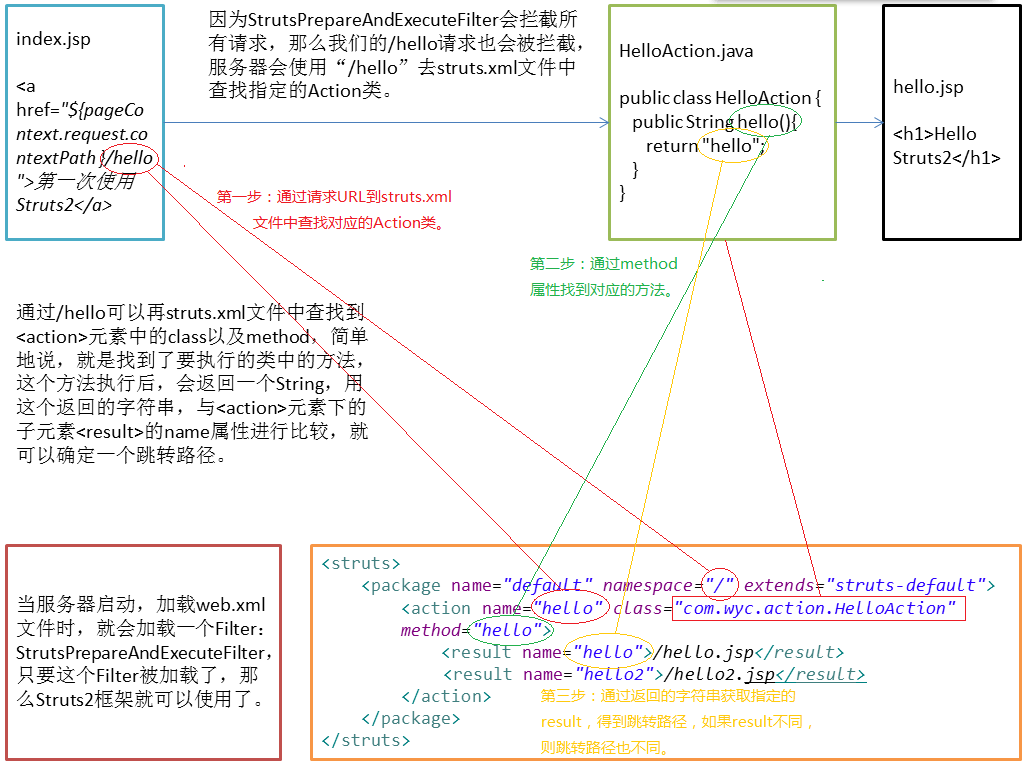
6、在index.jsp中添加链接,进行测试:
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/hello" >第一次使用Struts2</a>
在地址栏中输入:http://localhost/struts2_day01/index.jsp,访问超链接,就可以看到HelloAction类中的hello方法执行了,并且跳转到了hello.jsp页面。
7、流程分析:
8、手写代码实现Struts2功能
1)创建一个Filter:StrutsFilter
2)在web.xml文件中配置StrutsFilter
3)在StrutsFilter中拦截操作,并访问Action中的方法,跳转到hello.jsp页面。
=============================================================================
示例代码:
struts.xml文件:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
StrutsFilter:
// 得到项目名
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HelloAction.java
——Struts2的流程分析与工具配置
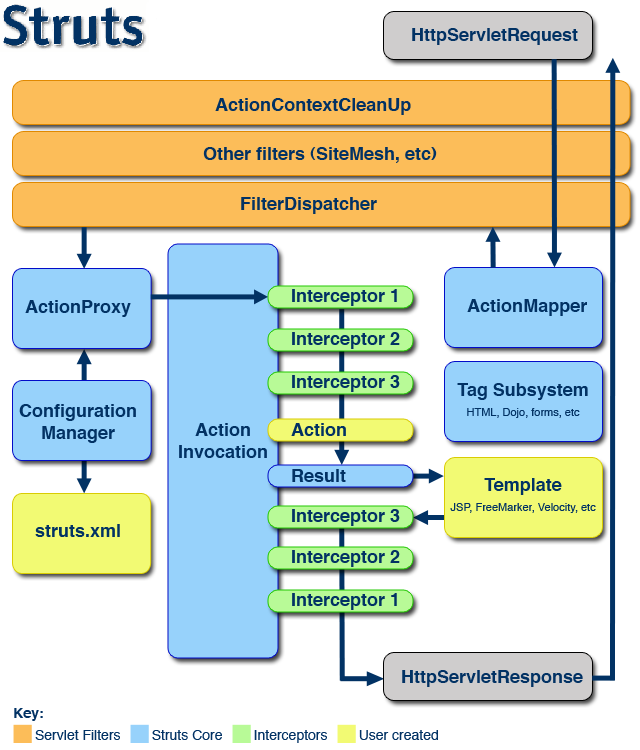
1、运行流程:
请求 --> StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter(核心控制器、核心拦截器、前端控制器、前端拦截器) --> Interceptors(拦截器,实现代码功能,核心是AOP动态代理) --> Action的execute --> Result(结果页面)
拦截器:在struts-default.xml中定义
执行拦截器:在defaultStack中引用拦截器
可以通过源码级别断点调试,证明拦截器执行了(学会导入源码,选中完整类名,然后ctrl + t)。
2、手动配置struts.xml文件中提示操作
1)复制http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd
到该目录中查找dtd文件:struts-2.3.15.1srccoresrcmain
esources
2)在Windows —— Preferences —— 输入XML —— XML Catalog —— Add ——在Location中填入dtd文件路径 ——Key type选择URI —— URI中填入(名称空间):http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd —— OK
导入DTD时,应该和配置DTD版本一致。
3、关联Struts2的源文件
Ctrl + Shift + t,输入类名查找对应类,然后关联源码。
如果是com.opensymphony.xxx,就在xwork-core目录中查找。
如果是org.apache.struts2.xxx,就在core目录中查找
4、使用ConfigBroswer插件(了解)
提供在浏览器中查看Struts2配置加载情况。
将解压后的struts2/lib/struts2-config-browser-plugin-2.3.7.jar复制到WEB-INF/lib目录下
访问:localhost:8080/struts2_day01/config-browser/index.action查看struts2配置加载情况。
——Struts2配置(重点)
1、Struts2配置文件加载顺序:
1)Struts2框架要想执行,必须先加载StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter
在StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter类的init()方法中对Dispatcher进行了初始化操作。
在Dispatcher类中定义的init()方法内就描述了Struts2配置文件的加载顺序:
第一个加载的文件:default.properties文件
作用:定义了Struts2框架中所有常量。
位置:org/apache/struts2/default.properties
properties文件定义键值对,定义值。
XML文件定义关系。
第二个加载的文件:
struts-default.xml:
作用:配置了bean, interceptor, result等信息。
位置:struts2-core-2.3.15.1.jara包中。
struts-plugin.xml
它是struts2框架中所使用的插件的配置文件。
struts.xml
使用struts2框架所使用的配置文件。
第三个加载的文件:自定义的struts.properties
可以自定义常量,而不是用struts.properties中定义的常量。
第四个加载的文件:web.xml
在开发中,后加载文件中的配置会将先加载文件中的配置覆盖。
——关于Action的配置(重点)
1、struts.xml
1)<package>:
用于声明一个包,管理Action类。(通常情况下一个模块一个package)
Struts2所有action都通过package管理。
struts-default是struts-default.xml定义的一个package,其中包含大量拦截器和结果集。
Action的访问路径 = namespace + action的name属性
* name
包名,用于声明一个包名,包名不能重复。
* namespace
与<action>元素的name属性合并,确定了一个唯一可以访问Action类的路径。
* extends
表示继承的包名。
* abstract
可以取值为true或false,(true)表示可以用于继承。
2)<action>
用于声明一个Action类。
* name
表示一个Action类的名称,在同一个包内,Action的名称是唯一的。
它与<package>元素中的namespace属性确定了一个访问Action类的路径。
* class
Action类的完整包名
* method(请求处理方法)
表示要访问的Action类中的方法的名称。
3)<result>
用于确定返回结果。
* name
与Action类中的方法返回值做对比,确定跳转路径。
* type
确定跳转处理方式。
2、关于Action配置其他细节
1)默认值:
<package namespace="默认值">
* namespace的默认值是"/";
<action class="默认值" method="默认值">
* class的默认值:com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport
* method默认值:ActionSupport类中的execute()方法
<result name="默认值">
* name的默认值是execute()方法的返回值return SUCCESS;,也就是"success"。
2)关于访问Action的路径问题
现在的Action配置是:
<package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default">
<action name="hello" class="com.wyc.action.DefaultAction">
<resule>/hello.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
当输入:http://localhost/Struts2_day01_2/a/b/c/hello时,也可以访问到Action类。
因为:Struts2中的Action被访问时,它会首先查找:
1: namespace="/a/b/c" action的name=hello,没有找到
2: namespace="/a/b" action的name=hello,没有找到
3: namespace="/a" action的name=hello,没有找到
4: namespace="/" action的name=hello,找到了
如果最后也查找不到,会报404错误。
3)默认的处理请求Action
作用:处理其他Action处理不了的路径。
<default-action-ref name="action的name属性" />
配置这个元素后,当所有的Action无法处理访问路径时,会执行name指定的<action>元素。
只在同包中有效。
4)Action的默认处理类
在Action配置时,如果不写class属性,默认是:comm.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport。
<default-class-ref class="com.wyc.action.DefaultAction"/>
配置这个元素后,在当前包中,如果<action>元素不写class属性,那么默认处理Action请求的处理类就为class指定的类。
只在同包中有效。
3、关于Struts2中的常量配置
在default.properties文件中声明了Struts2中的常量。
可以在哪些文件中配置常量?
* struts.xml(应用最多)
> <constant name="常量名称" value="常量值"></constant>
* struts.properties(基本不用)
* web.xml(了解)
> 在<filter>元素下通过<init-param>初始化参数进行配置。
> 在web.xml文件中配置的常量会覆盖struts.xml文件中的配置。
1)常用常量:
* struts.action.extension=action,,
这个常量用于指定Struts2框架默认拦截的后缀名,例如:
localhost/Struts2_day01/hello.action(可以访问)
localhost/Struts2_day01/hello(可以访问)
localhost/Struts2_day01/hello.abc(不可以访问)
在struts.xml文件中设置:
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="abc,,"></constant>
运行结果如下:
localhost/Struts2_day01/hello.action(不可以访问)
localhost/Struts2_day01/hello(可以访问)
localhost/Struts2_day01/hello.abc(可以访问)
* struts.i18n.encoding=UTF-8
相当于request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");,可以解决POST请求的乱码问题。
* struts.serve.static.browserCache=false
false表示不缓存,true表示浏览器会缓存静态内容,产品环境设置true,开发环境设置false。
* struts.devMode=true
DevelopModel,开发模式,相当于热部署。
修改struts.xml文件后不需要重启服务器。
提供详细报错页面,而不是只显示404等错误信息。
* struts.configuration.xml.reload=true
当struts的配置文件修改后,系统是否自动重新加载该文件,默认值为false(生产环境下使用),开发阶段最好打开
4、struts.xml文件的分离
因为多个模块的package太多会影响阅读,为了方便阅读,所以可以让一个模块保存一个配置文件,将多个package分离,使用时引入配置文件即可。
引入方式:
<include file="文件路径" />
——Action类的创建方式
1、有三种创建方式:
1)创建一个POJO类(直接创建一个class)
POJO类表示没实现任何接口,没继承任何父类,除了Object类。
优点:无耦合。
缺点:所有工作都要自己实现,代码量大。
底层通过反射来实现:
Struts2框架读取struts.xml获得完整Action类名 —— object = Class.forName(完整类名).newInstance() —— Method m = obj.getMethod("execute"); —— m.invoke(obj); 通过反射执行execute()方法。
2)实现Action接口
为了让用户开发的Action更加规范,Struts2提供了一个Action接口。
创建一个类,实现Action接口:com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action
优点:耦合低,提供了五种逻辑视图(字符串常量),定义了一个行为方法(execute())。
缺点:所有工作都要自己实现,但是已经得到标准规范。
五种逻辑视图:(Action处理数据后进行页面跳转)
public static final String SUCCESS = "success"; // 数据处理成功(成功页面)
public static final String NONE = "none"; // 页面不跳转,与return null 效果相同
public static final String ERROR = "error"; // 数据处理发送错误(错误页面)
public static final String INPUT = "input"; // 用户输入数据有误,通常用于校验表单数据
public static final String LOGIN = "login"; // 主要权限认证(登录页面)
示例代码:
public class HelloAction implements Action {
3)继承ActionSupport(推荐)
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport类实现了Action接口。
优点:功能比较完善,ActionSupport支持校验(实现Validateable接口)、错误信息设置、支持国际化(实现LocaleProvider接口)
缺点:耦合度高。
示例代码:
——关于Action的访问
如果没有指定method属性,则默认执行execute()方法。
1、通过设置method的属性值,来确定访问action类中的哪一个方法。
当访问book_add时,会调用BookAction类中的add方法,以此类推。
2、使用通配符来简化配置
1)在struts.xml文件中配置:
<action name="*_*" class="com.wyc.action.{1}Action" method="{2}"></action>
2)在JSP页面中创建两个页面:book.jsp、product.jsp
book.jsp:
<body>
product.jsp:
<body>
当访问book add时,这时的路径是:Book_add,那么对于struts.xml文件中第一个“*”就是Book,第二个“*”就是add。
对于{1}Action就相当于BookAction,对于method="{2}",就相当于method="add"
3)、使用通配符配置时注意事项:
* 必须定义一个统一的命名规范
* 不建议使用过多的通配符,影响阅读性
3、动态方法调用(了解)
在struts.xml文件中配置:
<action name="book" class="com.wyc.action.BookAction"></action>
访问:http://localhost/Struts2_day01_2/book!add
就可以访问到BookAction类中的add方法了。
book!add就是动态方法调用,叹号后面写的就是方法名。
注意:
Struts2框架支持动态方法调用,可以在default.properties中设置动态方法调用为true
struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation = true
——在Struts2框架中获取Servlet API
对于Struts2框架,不建议直接使用Servlet API。
在Struts2中获取Servlet API有三种方式:
1、通过ActionContext获取
* 获取一个ActionContext对象
> ActionContext context = ActionContext();
* 获取Servlet API
> 通过ActionContext获取到的不是真正的Servlet API,而是一个Map集合,集合中存放的就是对象(用键值对)存放的数据。
2、通过注入方式获取
3、通过ServletActionContext获取
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1、Action访问Servlet
在Action中用解耦和方式使用ActionContext对象间接访问Servlet API。
在Struts2中Action API已经与Servlet API解耦和了(没有依赖关系)。
Servlet API常见操作:
* 获取表单提交请求参数
* 向request, session, application三个作用域存取数据
开发中应优先使用ActionContext,这样可以避免耦合。
ActionContext方法:
* Map getParameters()
获取所有请求参数的Map集合。
Map底层是一个HashMap。
* void put(String key, Object value)
对request域存放数据。
* Map getApplication()
获取ServletContext数据Map,对应用访问存取数据。
* Map getSession()
获取session数据Map,对Session范围存取数据。
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2、使用接口注入的方式操作Servlet API(耦合)
这种方式能够真正获取到Web对象。
步骤:
1)要求Action类必须实现指定接口:
ServletContextAware接口:注入ServletContext对象
ServletRequestAware接口:注入request对象
ServletResponseAware接口:注入response对象
2)重写接口中指定的方法:
public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request)
3)声明一个web对象,使用接口中的方法对声明的web对象赋值
private HttpServletRequest request;
public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request){
this.request = request;
}
示例代码:
/*
分析其实现方法:
通过Struts2的interceptor实现的。
struts-default.xml:
<interceptor name="servletConfig" class="org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletConfigInterceptor"/>
源码:
org.apache.struts2.interceptor.ServletConfigInterceptor拦截器中的intercept()方法:
public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception {
// 因为action是Object类型,所以需要强转
.......
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3、通过ServletActionContext获取Servlet API
在ServletActionContext中方法都是静态的。
该类的父类是ActionContext,其内部代码也是通过ActionContext获取到的。
方法概要:
static PageContext getPageContext()
获取PageContext对象。
static HttpServletRequest getRequest()
获取request对象。
static HttpServletResponse getResponse()
获取response对象。
static ServletContext getServletContext()
获取ServletContext对象。
没有getSession()方法,但是可以通过getPageContext().getSession()获得。
有了pageContext,其它八个对象都可以得到。
示例代码:
——Result结果类型
在:struts-default.xml文件中定义。
1、理解处理结果
* Action处理完用户请求后,会返回一个普通字符串。
* 整个普通字符串就是一个逻辑视图名。
* Struts2根据逻辑视图名,决定运行哪个结果。
* Struts2处理结果使用<result>元素进行配置。
> 局部结果:将<result>作为<action>的子元素进行配置
> 全局结果:将<result>作为<global-result>的子元素进行配置
* 配置<result>元素通常需要指定两个属性
> name:该属性指定配置逻辑视图名
> type:该属性指定结果类型(跳转方式、处理方式)
2、<result>标签属性:
* name属性:
与action中的method的返回值匹配,获取跳转路径,进行跳转。
* type属性:
作用是定义跳转方式。
对于type属性的取值范围有以下几种:(可以在struts-default.xml文件中查看)
> chain:请求转发,一般情况下用于从一个Action跳转到另一个Action。
> dispatcher:请求转发,是默认值,一般用于从Action跳转到jsp页面。
> freemarker:模板技术,将页面与数据分离,通过freemarker将数据和页面整合到一起。
> httpheader
> plainText
> redirect:重定向,一般用于从Action重定向到页面。
> redirectAction:重定向,一般用于从Action重定向到另一个Action。
redirectAction有两个参数:
actionname:指定目标Action的名称,它是默认属性。
namespace:用来指定目标Action的名称空间,默认为"/"。
> stream:代表从服务器端返回一个流,一般用于下载。
> velocity:模板引擎
> xslt
</package>
必须掌握:
chain、dispatcher、redirect、redirectAction、stream
两个转发、两个重定向、一个流。
了解:freemarker、velocity
3、局部结果页面与全局结果页面
当多个action中都是用了相同的result,这时可以把result定义为全局结果页面。
<!-- 如果当前action下没有result,那么就会到全局中查找 -->
</action>
——练习:登录操作
1、需求:
用户通过表单进行登录,登陆失败将页面转发到login.jsp,并显示错误信息。
登录成功后将用户存储到Session中,重定向到success.jsp页面,并展示用户信息。
2、所需页面
login.jsp
> 提供登录表单
> 登录失败时显示错误信息
success.jsp
> 登录成功后通过session获取用户信息并显示到页面
3、所需类
LoginAction
> 获取Servlet API,获取表单信息
> 校验用户信息
> 登录成功,重定向到success.jsp
> 登录失败,转发到login.jsp
User类
实体类
> private String username;
> private String password;
——总结
1、Struts2环境搭建
* 导入jar包:
> struts2/apps/strut_blank.war文件
* web.xml如何配置:
> 配置StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter
> 在src目录下(classes)
* 如何通过反射执行action
* 每个配置文件的用途是什么
1)default.properties
2)struts-default.xml struts-plugin.xml struts.xml
3)struts.properties
4)web.xml
* package:用于管理action
> namespace:与action的name属性确定访问action的路径。
> extends:继承的包名,一般继承struts-default
* action:声明一个action
> name:action名称,在同一个包下不能重名
> class:action完整类名,默认是ActionSupport
> method:action类中的方法名,要求无参,返回值为String,默认值为execute
* result:结果视图
> name:与action的method方法的返回值进行匹配确定跳转路径
> type:跳转方式
在struts-default.xml文件中定义:
chain, dispatcher, redirect, redirectAction, stream
5、Action的三种创建方式
* POJO
* 指定method属性
* 通配符
* ActionContext
* <result>标签的type属性取值。
9、自定义常量
* 在struts.xml文件中定义
> <constant name="" value="" />
* 在struts.properties文件中定义
* 在web.xml文件中定义
> <init-param></initparam>
从struts2.1开始,struts2 引入了Convention插件来支持零配置