BST的定义
在二叉查找(搜索)树中:
- 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
- 没有键值相等的节点。
- 若对它进行中序遍历,则是一个递增的排好序的序列
作用:
用来进行搜索
二叉搜索树注意事项:
进行中序遍历,可以得到一个有序的序列
树中最左侧节点一定是最小的节点,最右侧节点一定是最大的
二叉搜索树的实现
节点
public class BSTree<T extends Comparable<T>> { private BSTNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点 public class BSTNode<T extends Comparable<T>> { T key; // 关键字(键值) BSTNode<T> left; // 左孩子 BSTNode<T> right; // 右孩子 BSTNode<T> parent; // 父结点 public BSTNode(T key, BSTNode<T> parent, BSTNode<T> left, BSTNode<T> right) { this.key = key; this.parent = parent; this.left = left; this.right = right; } } ...... }
遍历
遍历包含前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历3种方式。
¶前序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
- 访问根结点;
- 先序遍历左子树;
- 先序遍历右子树。
private void preOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if(tree != null) { System.out.print(tree.key+" "); preOrder(tree.left); preOrder(tree.right); } } public void preOrder() { preOrder(mRoot); }
中序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
- 中序遍历左子树;
- 访问根结点;
- 中序遍历右子树。
private void inOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if(tree != null) { inOrder(tree.left); System.out.print(tree.key+" "); inOrder(tree.right); } } public void inOrder() { inOrder(mRoot); }
后序遍历
若二叉树非空,则执行以下操作:
- 后序遍历左子树;
- 后序遍历右子树;
- 访问根结点。
private void postOrder(BSTNode<T> tree) { if(tree != null) { postOrder(tree.left); postOrder(tree.right); System.out.print(tree.key+" "); } } public void postOrder() { postOrder(mRoot); }
------------------------------------------------此处为分割线(#^.^#)------------------------------------------------
下面这颗树的各种遍历方式:
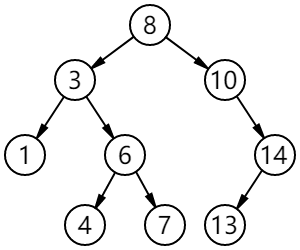
对于上面的二叉树而言,
- 前序遍历结果: 8 3 1 6 4 7 10 14 13
- 中序遍历结果: 1 3 4 6 7 8 10 13 14
- 后序遍历结果: 1 4 7 6 3 13 14 10 8
取最大值和最小值
/* * 查找最大结点: 返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最大结点。 */ private BSTNode<T> maximum(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return null; while(tree.right != null) tree = tree.right; return tree; } public T maximum() { BSTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot); if (p != null) return p.key; return null; }
/* * 查找最小结点: 返回tree为根结点的二叉树的最小结点。 */ private BSTNode<T> minimum(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree == null) return null; while(tree.left != null) tree = tree.left; return tree; } public T minimum() { BSTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot); if (p != null) return p.key; return null; }
查找
/* * (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点 */ private BSTNode<T> search(BSTNode<T> x, T key) { if (x==null) return x; int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) return search(x.left, key); else if (cmp > 0) return search(x.right, key); else return x; } public BSTNode<T> search(T key) { return search(mRoot, key); }
前驱和后继
节点的前驱: 是该节点的左子树中的最大节点。 节点的后继: 是该节点的右子树中的最小节点。
取得前驱结点:
/* * 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。 */ public BSTNode<T> predecessor(BSTNode<T> x) { // 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。 if (x.left != null) return maximum(x.left); // 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y!=null) && (x==y.left)) { x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; }
取得后继节点
/* * 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"二叉树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。 */ public BSTNode<T> successor(BSTNode<T> x) { // 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。 if (x.right != null) return minimum(x.right); // 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y!=null) && (x==y.right)) { x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; }
插入新节点
/* * 将结点插入到二叉树中 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的 * z 插入的结点 */ private void insert(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) { int cmp; BSTNode<T> y = null; BSTNode<T> x = bst.mRoot; // 查找z的插入位置 while (x != null) { y = x; cmp = z.key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) x = x.left; else x = x.right; } z.parent = y; if (y==null) bst.mRoot = z; else { cmp = z.key.compareTo(y.key); if (cmp < 0) y.left = z; else y.right = z; } } /* * 新建结点(key),并将其插入到二叉树中 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的根结点 * key 插入结点的键值 */ public void insert(T key) { BSTNode<T> z=new BSTNode<T>(key,null,null,null); // 如果新建结点失败,则返回。 if (z != null) insert(this, z); }
删除节点
/* * 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点 * * 参数说明: * bst 二叉树 * z 删除的结点 */ private BSTNode<T> remove(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z) { BSTNode<T> x=null; BSTNode<T> y=null; if ((z.left == null) || (z.right == null) ) y = z; else y = successor(z); if (y.left != null) x = y.left; else x = y.right; if (x != null) x.parent = y.parent; if (y.parent == null) bst.mRoot = x; else if (y == y.parent.left) y.parent.left = x; else y.parent.right = x; if (y != z) z.key = y.key; return y; } /* * 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点 * * 参数说明: * tree 二叉树的根结点 * z 删除的结点 */ public void remove(T key) { BSTNode<T> z, node; if ((z = search(mRoot, key)) != null) if ( (node = remove(this, z)) != null) node = null; }
打印
/* * 打印"二叉查找树" * * key -- 节点的键值 * direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点; * -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子; * 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。 */ private void print(BSTNode<T> tree, T key, int direction) { if(tree != null) { if(direction==0) // tree是根节点 System.out.printf("%2d is root ", tree.key); else // tree是分支节点 System.out.printf("%2d is %2d's %6s child ", tree.key, key, direction==1?"right" : "left"); print(tree.left, tree.key, -1); print(tree.right,tree.key, 1); } } public void print() { if (mRoot != null) print(mRoot, mRoot.key, 0); }
销毁树
/* * 销毁二叉树 */ private void destroy(BSTNode<T> tree) { if (tree==null) return ; if (tree.left != null) destroy(tree.left); if (tree.right != null) destroy(tree.right); tree=null; } public void clear() { destroy(mRoot); mRoot = null; }
代码实现
package Tree.BSTree; public class BSTree<T extends Comparable<T>> { private BSTNode<T> mRoot; //根节点 /** * 构建BST * @param <T> */ public class BSTNode<T extends Comparable<T>>{ T key; //键值 BSTNode<T> left; BSTNode<T> right; BSTNode<T> parent; public BSTNode(T key, BSTNode<T> parent,BSTNode<T> left, BSTNode<T> right){ this.key = key; this.parent = parent; this.left = left; this.right = right; } public T getKey(){ return key; } public String toString(){ return "key:" + key; } } public BSTree(){ mRoot = null; } /** * 前序遍历 */ private void preOrder(BSTNode<T> tree){ if(tree != null){ System.out.print(tree.key + " "); preOrder(tree.left); preOrder(tree.right); } } public void preOrder(){ preOrder(mRoot); } /** * 中序遍历 */ private void inOrder(BSTNode<T> tree){ if(tree != null){ inOrder(tree.left); System.out.print(tree.key + " "); inOrder(tree.right); } } public void inOrder(){ inOrder(mRoot); } /** * 后序遍历 */ private void postOrder(BSTNode<T> tree){ if(tree != null){ postOrder(tree.left); postOrder(tree.right); System.out.print(tree.key+" "); } } public void postOrder(){ postOrder(mRoot); } /* * (递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点 */ private BSTNode<T> search(BSTNode<T> x, T key) { if (x==null) return x; int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) return search(x.left, key); else if (cmp > 0) return search(x.right, key); else return x; } public BSTNode<T> search(T key) { return search(mRoot, key); } /* * (非递归实现)查找"二叉树x"中键值为key的节点 */ private BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(BSTNode<T> x, T key) { while (x!=null) { int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) x = x.left; else if (cmp > 0) x = x.right; else return x; } return x; } public BSTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) { return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key); } /** * 查找最大节点 */ private BSTNode<T> maximum(BSTNode<T> tree){ if(tree == null) return null; while (tree.right != null) tree = tree.right; return tree; } public T maximum(){ BSTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot); if(p != null) return p.key; return null; } /** * 查找最小节点 */ private BSTNode<T> minimum(BSTNode<T> tree){ if(tree == null) return null; while (tree.left != null) tree = tree.left; return tree; } public T minimum(){ BSTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot); if(p != null) return p.key; return null; } /** * 查找前驱 */ public BSTNode<T> predecessor(BSTNode<T> x){ // 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。 if(x.left != null) return maximum(x.left); // 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y!=null) && (x == y.left)){ x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; } /** * 查找后继 */ public BSTNode<T> successor(BSTNode<T> x){ // 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。 if(x.right != null) return minimum(x.right); // 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能: // (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。 // (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。 BSTNode<T> y = x.parent; while ((y != null) && (x == y.right)){ x = y; y = y.parent; } return y; } /** * 二叉树插入节点 */ private void insert(BSTree<T> bst,BSTNode<T> z){ int cmp; BSTNode<T> y = null; BSTNode<T> x = bst.mRoot; //查找z插入的位置 while(x != null){ y = x; cmp = z.key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) x = x.left; else x = x.right; } z.parent = y; if(y == null) bst.mRoot = z; else{ cmp = z.key.compareTo(y.key); if(cmp < 0) y.left = z; else y.right = z; } } public void insert(T key){ BSTNode<T> z = new BSTNode<T>(key,null,null,null); //如果新建节点失败,则返回 if(z != null) insert(this,z); } /** * 删除节点 */ private BSTNode<T> remove(BSTree<T> bst, BSTNode<T> z){ BSTNode<T> x = null; BSTNode<T> y = null; if((z.left == null) || (z.right == null)) y = z; else y = successor(z); if(y.left != null) x = y.left; else x = y.right; if(x != null) x.parent = y.parent; if(y.parent == null) bst.mRoot = x; else if(y == y.parent.left) y.parent.left = x; else y.parent.right = x; if(y != z) z.key = y.key; return y; } public void remove(T key){ BSTNode<T> z,node; if((z = search(mRoot,key)) != null) if((node = remove(this,z)) != null) node = null; } /** * 打印 */ private void print(BSTNode<T> tree,T key,int direction){ if(tree != null){ if(direction == 0) System.out.printf("%2d is root ",tree.key); else System.out.printf("%2d is %2d's %6s child ",tree.key,key,direction==1?"right":"left"); print(tree.left, tree.key,-1); print(tree.right,tree.key,1); } } public void print(){ if(mRoot != null) print(mRoot,mRoot.key,0); } /** * 销毁二叉树 */ private void destory(BSTNode<T> tree){ if(tree == null) return; if(tree.left != null) destory(tree.left); if(tree.right != null) destory(tree.right); tree = null; } public void clear(){ destory(mRoot); mRoot = null; } }
测试代码
package Tree.BSTree; public class BSTreeTest { private static final int arr[] = {1,5,4,3,2,6}; public static void main(String[] args){ int i,ilen; BSTree<Integer> tree = new BSTree<>(); System.out.print("=== 依次添加:"); ilen = arr.length; for(i=0 ;i<ilen; i++){ System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); tree.insert(arr[i]); } System.out.print(" == 前序遍历:"); tree.preOrder();; System.out.print(" == 中序遍历:"); tree.inOrder(); System.out.print(" == 后序遍历:"); tree.postOrder(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("== 最小值:" + tree.minimum()); System.out.println("== 最大值:" + tree.maximum()); System.out.println("== 树的详细信息:"); tree.print(); System.out.print(" == 删除根节点:" + arr[3]); tree.remove(arr[3]); System.out.print(" == 中序遍历:"); tree.inOrder(); System.out.println(); //销毁 tree.clear(); } }