Promise 仅仅只是个对象,主要用它来处理异步的数据
在Promise中,有三种状态
pending(等待,处理中)--》resolve(完成)
或
pending(等待,处理中)--》rejected(失败)
即一旦状态改变,就不会再变,任何时候都可以得到这个结果。
如果不设置回调函数,Promise 内部抛出的错误,不会反应到外部
参数:
resolve:成功时触发的回调函数
reject:失败时触发的回调函数
创建Promise对象
const pro = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){ if(/*成功*/){ resolve(value); //value为成功时,传出的值 }else{ reject(err); //err为失败时,传出的值 } })
Promise创建的实例,可以调用then来接收pro的值,并执行对应的回调函数
写法
then()方法接收两个参数,第一个参数是一个为成功时执行的回调函数,第二个参数为可选参数,失败时执行的回调函数。需要注意的地方是then方法是异步执行的。
//调用then方法
pro.then(function(val){ //成功时,调用成功的回调函数
console.log("成功时,接收数据为"+val) //成功时,接收数据为123
},function(err){ //失败时,调用失败的回调函数
console.log("失败时,接收数据为"+err)
})
调用then方法后返回的还是Promise对象,然后又可以调用then方法
const pro = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
if(123){
resolve(123);
}else{
reject(456);
}
})
pro.then(function(val){ //成功时,调用成功的回调函数
console.log("成功时,接收数据为"+val)
return val //链式调用then时需要return val,将值传递到下一层回调函数
},function(err){ //失败时,调用失败的回调函数
console.log("失败时,接收数据为"+err)
}).then(function(val){
console.log("又是成功时调用了then"+val) //成功时,接收数据为123
},function(err){
console.log("又是失败时调用了then"+err) //又是成功时调用了then123
})
catch()
catch()在链式写法中可以捕获前面then中发送的异常。
写法
const pro = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){ reject("错误") }) pro.then(function(){}).catch(function(err){ console.log(err) //错误 })
或
pro.catch(function(err){ console.log(err) //错误 })
resolve(),reject()
resolve()返回一个成功时的Promise对象
reject()返回一个失败时的Promise对象
写法
const pro = Promise.reject("错误");
const pro2 = Promise.resolve("成功");
const pro3 =Promise.resolve(pro2);
pro.then(function(val){ console.log(val) },function(err){ console.log(err) //错误
})
pro2.then(function(val){
console.log(val) //成功
})
pro3.then(function(val){
console.log(val) //成功
})
all
作为参数的几个promise对象一旦有一个的状态为rejected,则all的返回值就是rejected。
写法:
例子1
const pro = Promise.reject("错误");
const pro2 = Promise.resolve("成功")
const pro3 = Promise.resolve("成功")
Promise.all([pro,pro2,pro3]).then(function(val){
console.log(val)
},function(err){
console.log(err) //错误
})
例子2
const pro = Promise.resolve("成功");
const pro2 = Promise.resolve("成功")
const pro3 = Promise.resolve("成功")
Promise.all([pro,pro2,pro3]).then(function(val){
console.log(val) // ["成功", "成功", "成功"]
},function(err){
console.log(err)
})
race
哪个Promise对象传值较快就接收哪个
例子
const p1 = new Promise(function(resolve,reject){ setTimeout(resolve,100,"100") }) const p2 = new Promise(function (resolve,reject){ setTimeout(resolve,500,"500") }) Promise.race([p1,p2]).then(function(val){ console.log(val) })
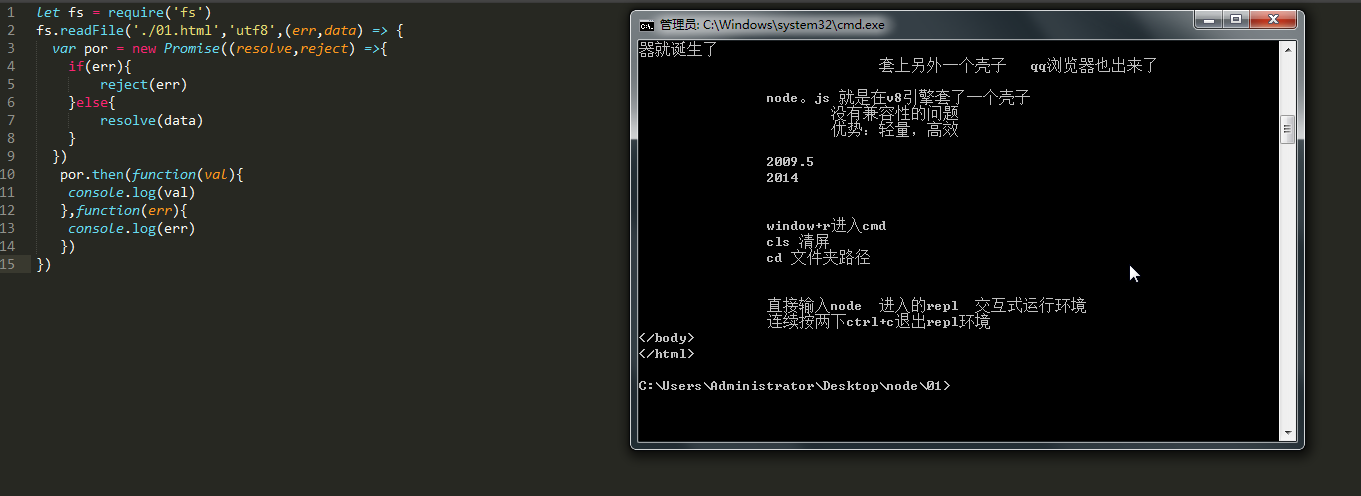
Promise对象在node中的玩法之一
let fs = require('fs')
fs.readFile('./01.html','utf8',(err,data) => {
var por = new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
if(err){
reject(err)
}else{
resolve(data)
}
})
por.then(function(val){
console.log(val)
},function(err){
console.log(err)
})
})
成功时
let fs = require('fs')
fs.readFile('./01dff.html','utf8',(err,data) => {
var por = new Promise((resolve,reject) =>{
if(err){
reject(err)
}else{
resolve(data)
}
})
por.then(function(val){
console.log(val)
},function(err){
console.log(err)
})
})
失败时

Promise与ajax组合运用
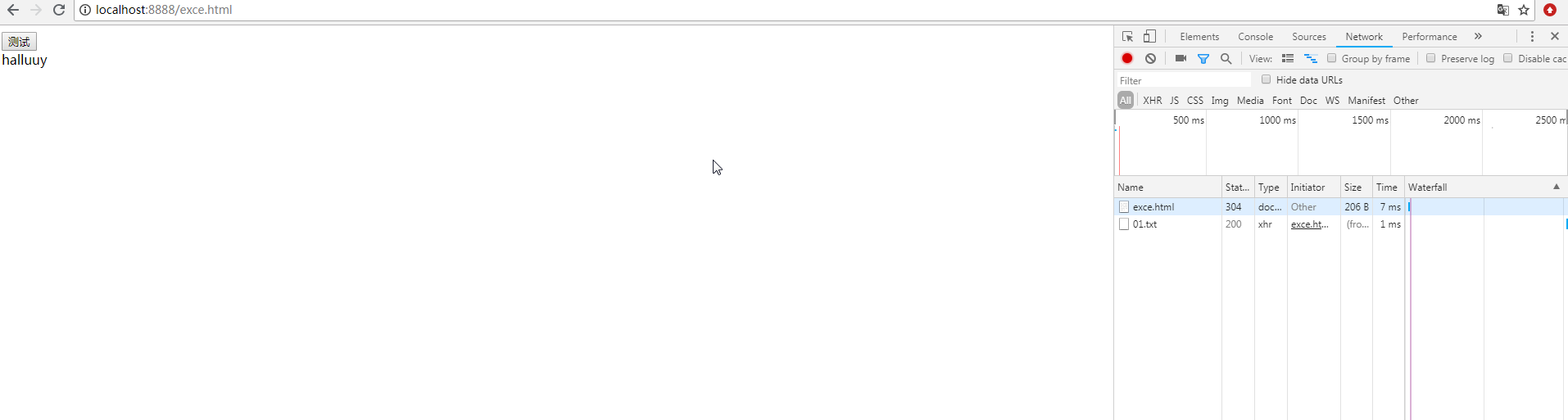
<body> <button id="btn">测试</button> <div id="box"></div> <script> var btn = document.getElementById('btn') var box = document.getElementById('box') function ajax(url,res,rej) { var xhr; if (window.XMLHttpRequest){ xhr=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else{ xhr=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xhr.open('GET',url,true) xhr.send() xhr.onload = function () { if (xhr.status == 200 && xhr.readyState == 4) { res(xhr.responseText); } else { rej(xhr.status) } } } btn.onclick = function(){ var pro = new Promise((resolve,reject) => { ajax("01.txt",function(data){ resolve(data) },function(err){ reject(err) }) }) pro.then(function(data){ box.innerHTML = data; },function(err){ box.innerHTML = err; }) } </script> </body>
ajax发送请求成功时:
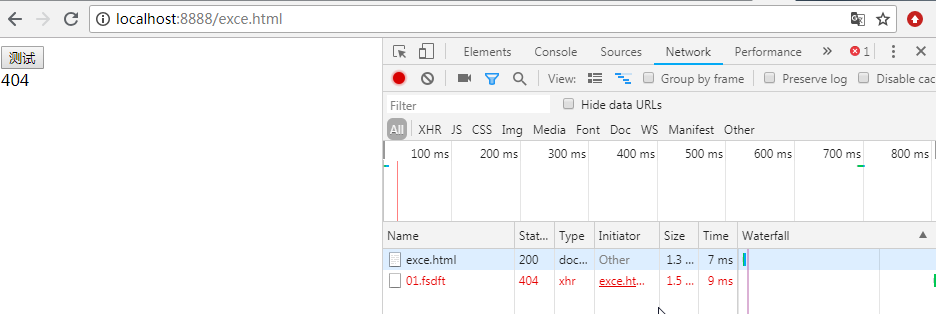
ajax失败时
<body> <button id="btn">测试</button> <div id="box"></div> <script> var btn = document.getElementById('btn') var box = document.getElementById('box') function ajax(url,res,rej) { var xhr; if (window.XMLHttpRequest){ xhr=new XMLHttpRequest(); } else{ xhr=new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); } xhr.open('GET',url,true) xhr.send() xhr.onload = function () { if (xhr.status == 200 && xhr.readyState == 4) { res(xhr.responseText); } else { rej(xhr.status) } } } btn.onclick = function(){ var pro = new Promise((resolve,reject) => { ajax("01.fsdft",function(data){ resolve(data) },function(err){ reject(err) }) }) pro.then(function(data){ box.innerHTML = data; },function(err){ box.innerHTML = err; }) } </script> </body>