00.前言:
- 本次作业链接
- 队友博客链接
- github仓库链接
- 结对成员:031602605 陈浩 and 031602634 吴志鸿
01.分工:
- 031602605 陈浩:负责词频分析部分,在原WordCount的基础上进行升级,添加新的命令行参数支持更多的功能包括自定义输入输出文件,权重词频统计,词组统计等新功能的设计。
- 031602634 吴志鸿:负责关于爬虫部分的所有设计,从CVPR2018官网爬取今年的论文列表,以及其他拓展功能的设计。
02.PSP表格:
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 25 |
| • Estimate | • 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 25 |
| Development | 开发 | 480 | 600 |
| • Analysis | • 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 120 |
| • Design Spec | • 生成设计文档 | 35 | 30 |
| • Design Review | • 设计复审 | 20 | 20 |
| • Coding Standard | • 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 25 |
| • Design | • 具体设计 | 120 | 150 |
| • Coding | • 具体编码 | 120 | 120 |
| • Code Review | • 代码复审 | 120 | 150 |
| • Test | • 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 120 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 90 | 120 |
| • Test Repor | • 测试报告 | 30 | 45 |
| • Size Measurement | • 计算工作量 | 10 | 15 |
| • Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | • 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 35 |
| 合计 | 1225 | 1600 |
03.解题思路描述与设计实现说明:
解题思路简述:
- 本次作业主要分成两个步骤,先是根据题目需要,按照格式要求爬取论文列表;之后在对爬取的论文列表进行词频分析。实现对WordCount的升级。
- 爬虫使用
- 工具:Python 3.6
- 思路:一开始是先去CVPR2018官网检查页面元素观察规律;发现每一篇论文都有对应一个超链接,并且点开后就有论文的基本信息。之后就按照特征进行爬取即可。
- 如下图 id = content的块里存储了所需的论文列表,ptitle里存储了论文的具体网址

- 如下图 id = content的块里存储了所需的论文列表,ptitle里存储了论文的具体网址
- 思路:一开始是先去CVPR2018官网检查页面元素观察规律;发现每一篇论文都有对应一个超链接,并且点开后就有论文的基本信息。之后就按照特征进行爬取即可。
关键代码
- 读取网页内容
target_url = 'http://openaccess.thecvf.com/CVPR2018.py'
target_req = request.Request(url = target_url, headers = head)
target_response = request.urlopen(target_req)
target_html = target_response.read().decode('utf-8')
#创建BeautifulSoup对象
listmain_soup = BeautifulSoup(target_html,'lxml')
#搜索文档树,找出div标签中id为content的所有子标签
chapters = listmain_soup.find_all('div',id = 'content')
#使用查询结果再创建一个BeautifulSoup对象,对其继续进行解析
download_soup = BeautifulSoup(str(chapters), 'lxml')
- 依次打开对应论文网址进行爬取,内容读入到文件
file = open('.\result.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8')
numbers = len(download_soup.dl.contents)
index = 0
#开始记录内容标志位,只要正文卷下面的链接,最新章节列表链接剔除
begin_flag = True
#遍历dl标签下所有子节点
for child in download_soup.dl.children:
#滤除回车
if(child != '
' and child.name != "dd"):
print(child.name)
#爬取链接下载链接内容
if begin_flag == True and child.a != None:
download_url = "http://openaccess.thecvf.com/" + child.a.get('href')
download_req = request.Request(url = download_url, headers = head)
download_response = request.urlopen(download_req)
download_html = download_response.read().decode('utf-8')
download_name = child.a.string
soup_texts = BeautifulSoup(download_html, 'lxml')
#改
texts = soup_texts.find_all('div',id = 'content')
soup_text = BeautifulSoup(str(texts), 'lxml')
write_flag = True
file.write(str(index) +'
')
#将爬取内容写入文件
file.write('Title: '+download_name + '
')
#作者信息
# authors=soup_text.find('div',id = 'authors')
# file.write('Title: 'authors.string + '
')
abstract=soup_text.find('div',id = 'abstract')
file.write('Abstract: '+abstract.string[1:] + '
')
file.write('
')
index += 1
file.close()
-
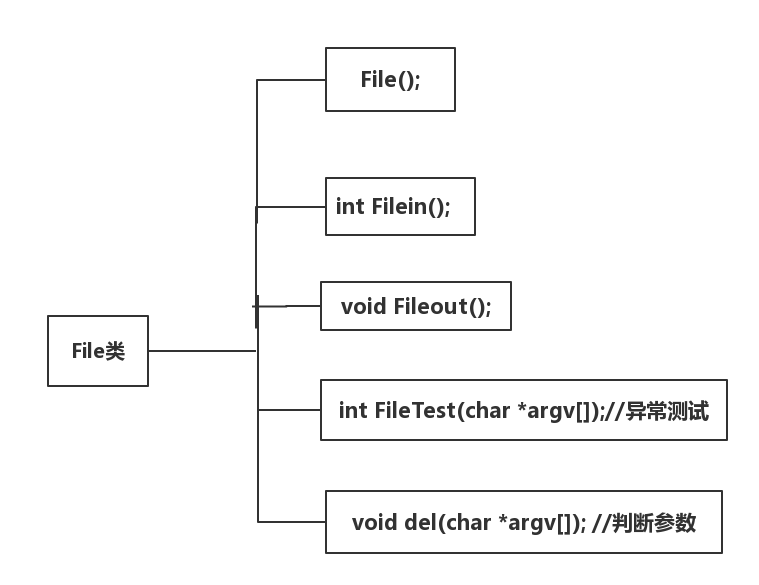
代码组织与内部实现设计(类图)
- 主要由两个类组成
- Word类用于实现词频分析的功能

- FIle类用于实现对命令行参数的解析,实现对文本的输入输出
-
说明算法的关键与关键实现部分流程图
-
主要说明新加三个功能
-
1.解析命令行参数:
- 遍历*argv[]数组- 遇到 -i 时 读取后面的输入路径字符,并写入输入路径中
- 遇到 -o 时 读取后面的输出路径字符,并写入输出路径中
- 遇到 -m 时 读取后面的字符串,并利用函数转换成正整数,存储数值
- 遇到 -n 时 读取后面的字符串,并利用函数转换成正整数,存储数值
- 遇到 -w 时 读取后面的字符串,并利用函数转换成正整数,存储数值
-
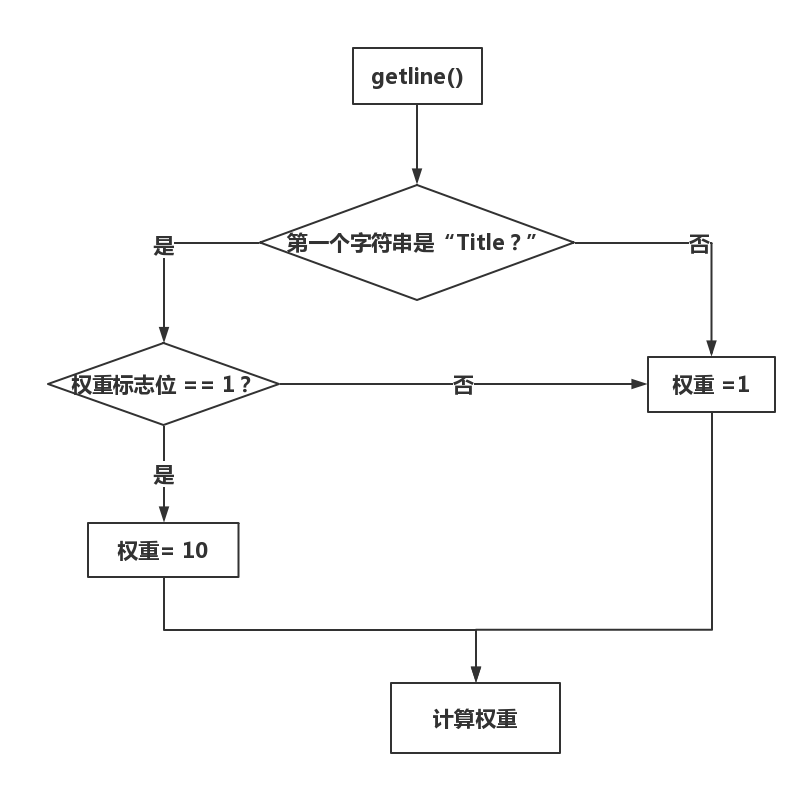
2.权重统计:
- 首先根据从-w参数后读出的数值是0和1分别选择两种权重模式。
- 每次利用getline函数读取一行,判断开头第一个单词是 “Title“” 还是“Absatra”,在根据权重模式来分别计算两种情况下单词的权重值。
- 流程图如下
-
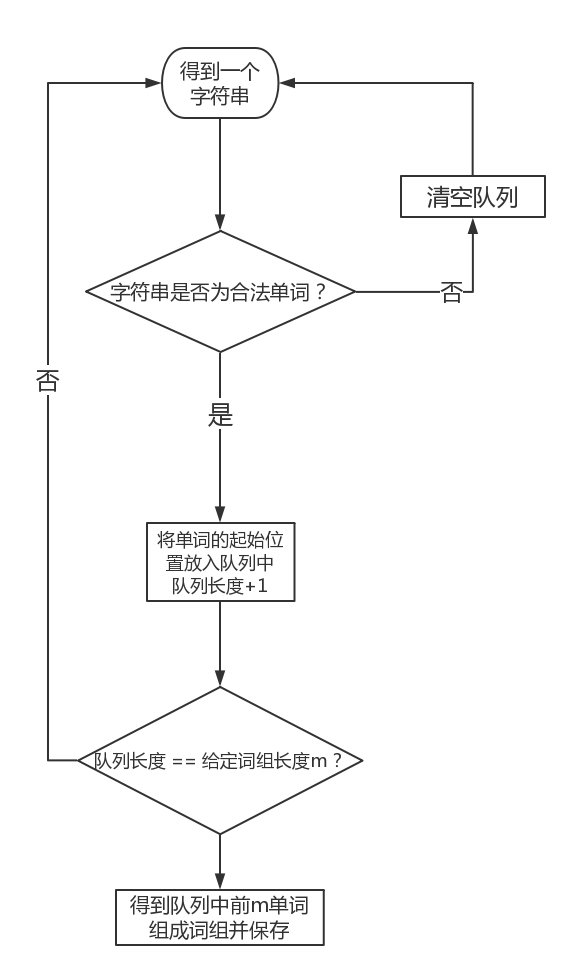
3.词组统计:
- 获取一个合法输入单词,将单词的起始加入队列,判断下一个单词是不是合法单词,如果不是,清空队列,重新获取单词;如果是,则循环上一次操作,队列长度+1,直到队列长度符合输入的指定词组长度,从队列中得到单词位置,记录词组。
- 流程图如下
-
04.附加题设计与展示:
设计的创意独到之处
- 1.本次作业基本要求是实现爬取包含Title, abstract的论文列表,我在这个基础上进行升级,从论文页面中爬取下了所以可以爬取的信息,包括作者,时间等信息
- 2.历年CVPR论文统计图
- 3.2018CVPR热词词云图
- 4.论文作者关系图
实现思路
- 1.基本思路是用find函数找出特定标签,之后在用正则或者get函数获得特定内容;
- 2.基本思路是对历年的CVPR论文进行爬取,通过WordCount统计出历年论文数量,同时结合python的pyecharts生成对应的环状图,如下

- 3.基本思路是对2018年798篇CVPR论文进行筛选统计,同时结合python的pyecharts生成热词图,如下
 ‘
‘ - 4.基本思路先爬取CVPR上论文的作者,然后让每篇论文的第一作者与其他作者形成联系,最后结合python的pyecharts生成Graph图,示意图如下

#部分实现代码
from pyecharts import WordCloud
if __name__ == "__main__":
#热词图
file = open('.\output.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
tx=file.read()
num=0
reword = r'd+'
result = re.findall(reword,tx)
reword2 = '<.*?>'
result2 = re.findall(reword2, tx)
results = []
nums = []
for r in result2:
results.append(r[1:-1])
for n in result:
num+=1
if(num<=3):continue
nums.append(n)
word = WordCloud(width = 1300,height = 600)
word.add("2018热门词频",results,nums,word_size_range=[20,100])
word.render()
实现成果展示
06.性能分析与改进:
改进思路
-
本次代码是在原有的WordCount的基础上对代码进行改进,在对命令行参数进行解析时,我主要是用一个循环匹配命令行标志位,之后用atoi函数获得对应参数;在单词/词组的存储上,我还是使用unordered_map进行存储,在词组判断方面我主要是用双向队列deque存储每个单词的起始位置,当队列当中存储的标志位达到上限时,输出标志位,截取字符串,这样做法的好处在于无论是单个的单词,还是一个词组,这样都可以使用,原本我打算用指针对单词标识位进行存储,后面发现链表查找效率太低,所以用了deque。暂时没有更好的思路了。
-
测试代码时其中一个测试样例如下(命令行参数为-i ./result.txt -o output.txt -w 1 -m 3 )
0
Title: Embodied Question Answering
Abstract: We present a new AI task -- Embodied Question Answering (EmbodiedQA) -- where an agent is spawned at a random location in a 3D environment and asked a question ("What color is the car?"). In order to answer, the agent must first intelligently navigate to explore the environment, gather necessary visual information through first-person (egocentric) vision, and then answer the question ("orange"). EmbodiedQA requires a range of AI skills -- language understanding, visual recognition, active perception, goal-driven navigation, commonsense reasoning, long-term memory, and grounding language into actions. In this work, we develop a dataset of questions and answers in House3D environments, evaluation metrics, and a hierarchical model trained with imitation and reinforcement learning.
- 样本输出结果:
characters: 817
words: 80
lines: 2
<embodied question answering>: 11
<active perception, goal>: 1
<agent must first>: 1
<answering (embodiedqa) -- where>: 1
<commonsense reasoning, long>: 1
<driven navigation, commonsense>: 1
<environment, gather necessary>: 1
<environments, evaluation metrics>: 1
<first intelligently navigate>: 1
<first-person (egocentric>: 1
-
本次性能分析测试主要使用从CVPR2018官网爬取的979篇文章的标题和摘要来进行测试,性能分析图如下:
-
测试得到代码覆盖率如下所示
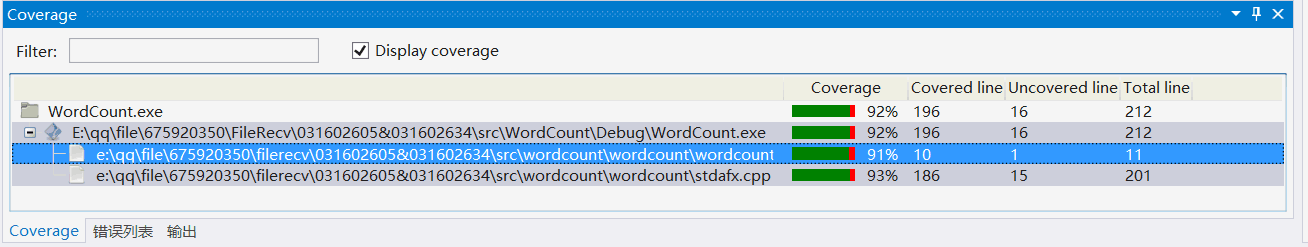
-
代码覆盖率达到了90%,没有更高的原因在于代码中有写入对文件的异常处理如下
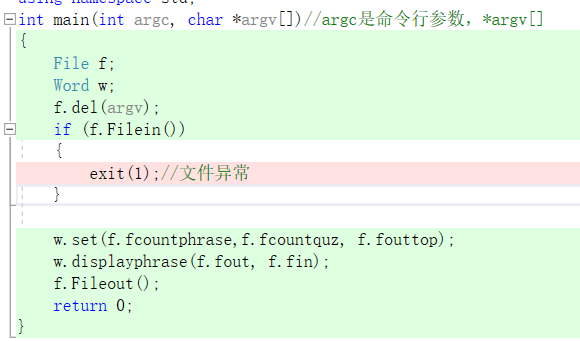
07.单元测试:
- 本次一共做了10组单元测试如下,重要测试附有代码,具体如下:
- 1.测试空白输入文本(行数、字符数和单词数都应该为0,测试函数Countcharacters、Countlines、Countwords)
TEST_CLASS(EmptyTest)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
//空白文本
File f;
Word w;
f.Filein();
int num = w.Countcharacters(f.fin);
int num1 = w.Countlines(f.fin);
int num2 = w.Countwords(f.fin);
Assert::IsTrue( (num==0) &&(num1==0) && (num2== 0) );
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
}
};
- 2.测试不存在输入文本文本输入(文本输入路径不存在,返回值为1,测试Filein函数)
TEST_CLASS(UnexistTest)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
//错误文本
File f;
Word w;
f.input = "./unexist.txt";
int num=f.Filein();
Assert::IsTrue(num == 1);
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
}
};
-
3.测试只含Title的输入文本(返回行数为1行,测试函数Countcharacters、Countlines、Countwords)
-
4.测试只含Abstract的文本输入(返回行数为1行,测试函数Countcharacters、Countlines、Countwords)
-
5.测试纯数字样本(返回字符数应该为0,测试函数Countwords)
TEST_CLASS(NumTest) { public: TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1) { //测试纯数字样本 File f; Word w; f.input = "./input2.txt"; f.Filein(); int num2 = w.Countwords(f.fin); Assert::IsTrue(num2 == 0); // TODO: 在此输入测试代码 } }; -
6.测试基本案例(从爬取论文列表中选出其中一项,测试函数Countcharacters、Countlines、Countwords)
-
7.测试大型样本含权重样本输出词组(从爬取论文列表中选出其中多项,测试函数Countcharacters、Countlines、Countwords、Counttop10)
TEST_CLASS(TopTest1) { public: TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1) { //测试大型样本含权重样本输出词组 File f; Word w; w.set(3, 1, 20); f.input = "./top.txt"; f.Filein(); vector<pair<string, int>> v = w.Counttop10(f.fin, 20); int characters = w.Countcharacters(f.fin); int word = w.Countwords(f.fin); int line = w.Countlines(f.fin); vector<pair<string, int>>::iterator iter = v.begin(); Assert::IsTrue(characters == 2915 && word ==287 && line == 6 && iter->second == 11); // TODO: 在此输入测试代码 } }; -
8.测试大型样本不含权重样本输出词组
-
9.测试含权重样本的输出词组(从爬取论文列表中选出其中多项,读取词组内容,测试函数Countcharacters、Countlines、Countwords、Counttop10)
TEST_CLASS(PhraseTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
//测试含权重样本的输出词组
File f;
Word w;
w.set(3, 1, 66);
f.input = "./P.txt";
f.Filein();
vector<pair<string, int>> v = w.Counttop10(f.fin,66);
int characters = w.Countcharacters(f.fin);
int word = w.Countwords(f.fin);
int line = w.Countlines(f.fin);
int num = v.size();
vector<pair<string, int>>::iterator iter = v.begin();
Assert::IsTrue(characters == 817 && word == 80 && line == 2 && num == 38 && iter->first == "embodied question answering" && iter->second==11);
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
}
};
- 10.测试不含权重样本的输出词组
08.Github的代码签入记录:

9.遇到的代码模块异常或结对困难及解决方法:
- 问题描述
在爬虫问题时遇到了困难、单元测试也遇到了问题 - 做过哪些尝试
- 爬虫问题
开始两个人一起讨论,是想要通过c++来实现的,查找资料后发现使用c++爬虫的资料很少,在仅有的几篇文章中,又由于自身水平有限,不能明白其中的许多函数和参数,后讨论决定使用Python来实现爬虫技术 - 单元测试问题
开始先从源代码分析,是不是代码写错了导致单元测试一直错误,后来发现代码没问题,就从单元测试代码方面入手,通过查阅资料,重新配置了单元测试需要的环境。
- 爬虫问题
- 是否解决
都解决了 - 有何收获
两个人一起解决问题时效率很高,并且可以一起讨论。
10.评价你的队友:
- 有点:编程能力强、学习效率高、善于交流、乐观。
- 不足:没有
11.学习进度条:
|第N周|新增代码(行)|累计代码(行)|学习耗时(小时)|重要成长|
---|---|---|---|---|---
|1|280|280|15|c++输入输出流、词频统计、单元测试|
|2|0|280|30|NABCD模型、学习使用Axure RP 、原型设计|
|3~4|461|731|35|爬虫技术、自定义控制台参数、性能分析和单元测试|